When it comes to early detection of cancer, recognizing symptoms and understanding how the disease develops are crucial. One of the lesser-known cancers is tonsil cancer, a type of throat cancer that originates in the tissues of the tonsils. Many people ask, “What does tonsil cancer look like?” because its symptoms can sometimes be mistaken for common infections or oral health issues.
This article will provide an in-depth explanation of tonsil cancer, from what it looks like to the risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and coping strategies. By understanding these details, you can take proactive steps toward early detection, timely treatment, and better health outcomes.
Definition and Overview
Tonsil cancer is a form of oropharyngeal cancer that develops in the tonsils, which are located at the back of the throat. The tonsils are part of the lymphatic system and play a role in fighting infections. However, abnormal cell growth in these tissues can lead to cancer. Most cases are linked to squamous cell carcinoma, a type of cancer that starts in the thin, flat cells lining the throat.
Types
There are several types of tonsil cancer, including:
- Squamous cell carcinoma: The most common type, arising from the surface lining of the tonsils.
- Lymphoma: Less common, developing in the lymphatic cells of the tonsils.
- Other rare cancers: Such as sarcomas or minor salivary gland cancers.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors may contribute to the development of tonsil cancer:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV): Especially HPV-16, strongly linked to many cases.
- Tobacco use: Smoking or chewing tobacco increases risk.
- Alcohol consumption: Heavy drinking is a known factor.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with compromised immunity are more vulnerable.
- Age and gender: More common in middle-aged and older adults, and more frequently seen in men.
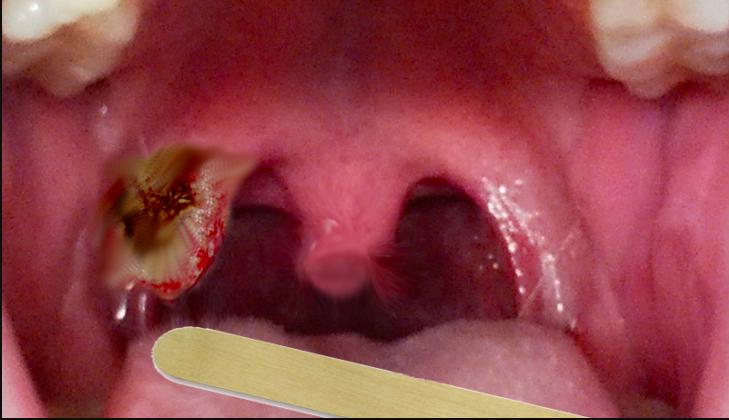
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Many people wonder, what does tonsil cancer look like in the mouth? It often appears as a persistent sore, growth, or lump on the tonsil that does not heal. Other symptoms include:
- A visible red or white patch on the tonsil
- One-sided tonsil enlargement
- A lump in the neck due to swollen lymph nodes
- Difficulty swallowing or persistent sore throat
- Ear pain without infection
- Bad breath or unexplained weight loss
If you notice any of these signs lasting longer than two weeks, it is important to seek medical attention.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical examination: Checking the throat and tonsils for visible abnormalities.
- Biopsy: Removing a sample of tissue for laboratory analysis.
- Imaging tests: CT scans, MRI, or PET scans help determine the extent of the cancer.
- HPV testing: To see if the cancer is related to HPV infection.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage, type, and overall health of the patient. Common options include:
- Surgery: Removal of the tumor or affected tonsil.
- Radiation therapy: To target and kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Often used in combination with radiation.
- Targeted therapy and immunotherapy: For advanced or HPV-related cancers.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While tonsil cancer cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle changes reduce risk:
- Avoid tobacco and limit alcohol consumption
- Maintain good oral hygiene
- Consider HPV vaccination, especially for younger individuals
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Get regular medical checkups and report persistent throat issues promptly
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for tonsil cancer varies depending on the stage at diagnosis and whether HPV is involved. HPV-related tonsil cancers generally have a better prognosis compared to those caused by tobacco and alcohol. With early detection and proper treatment, survival rates have significantly improved.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of immunotherapy and advanced targeted therapies in treating tonsil cancer. Clinical trials are exploring vaccines against HPV-related cancers and minimally invasive surgical techniques that reduce recovery time and improve outcomes.
Coping and Support for Patients
A cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but support systems are available. Patients can benefit from:
- Counseling and mental health support
- Joining cancer support groups
- Working with nutritionists for dietary guidance
- Physical therapy to regain strength after treatment
- Open communication with doctors and family members
Conclusion
So, what does tonsil cancer look like? It often appears as a persistent sore, growth, or discoloration on the tonsil that doesn’t heal, accompanied by symptoms such as difficulty swallowing and swollen lymph nodes. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options can make a life-saving difference. Early detection remains key, and regular checkups should never be overlooked.
FAQ
1. What does tonsil cancer look like in the early stages?
It may appear as a small sore, patch, or lump on the tonsil that does not heal, often mistaken for an infection.
2. Is tonsil cancer always caused by HPV?
Not always. While HPV is a leading cause, smoking and alcohol use are also major risk factors.
3. Can tonsil cancer be cured?
Yes, especially when detected early. Treatment options like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy are effective.
4. How fast does tonsil cancer spread?
The speed varies, but some cases can spread quickly to lymph nodes. Early detection is critical.
5. Who is most at risk of tonsil cancer?
Middle-aged men, smokers, heavy drinkers, and individuals with HPV infection face higher risks.