Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide, yet it is also one of the most preventable and treatable when detected early. Early detection through routine check-ups or specialized screenings can significantly increase the chances of successful treatment and survival. For many people, searching for free skin cancer screening near me has become an essential step toward protecting their health without financial burden.
Access to screenings is crucial because not everyone has the resources to pay for regular dermatology visits. Community programs, hospitals, nonprofit organizations, and local health fairs often provide free skin cancer screenings to make preventive care more accessible. Understanding the importance of these screenings can empower you to take charge of your skin health and reduce your risk of late-stage diagnosis.
Definition and Overview
Skin cancer occurs when abnormal skin cells grow uncontrollably due to DNA damage, often caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. A skin cancer screening is a quick, non-invasive examination performed by healthcare professionals to identify suspicious moles, lesions, or skin changes that may require further evaluation.
Finding free skin cancer screening near me means locating local resources that provide this important service at no cost, helping individuals detect cancer early without financial stress. These screenings are vital tools in community health initiatives.
Types
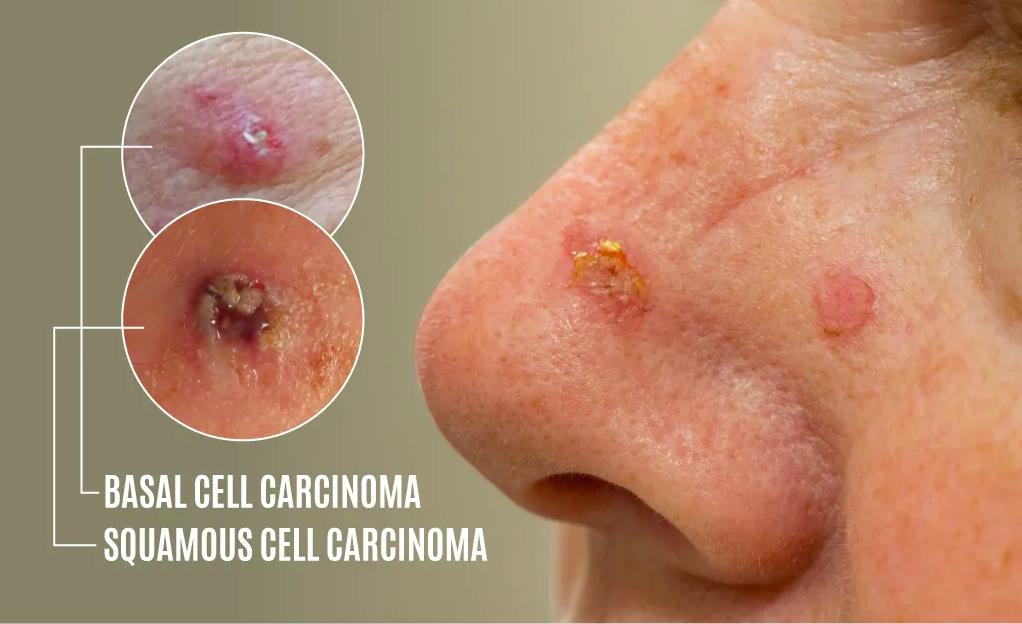
There are three primary types of skin cancer:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): The most common, usually slow-growing and less likely to spread.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Can grow more quickly and spread if left untreated.
- Melanoma: The most dangerous form, known for spreading rapidly to other parts of the body.
Causes and Risk Factors
The main cause of skin cancer is overexposure to UV radiation, but several risk factors increase vulnerability:
- Frequent sunburns or tanning bed use
- Fair skin, light eyes, or blonde/red hair
- Family history of skin cancer
- Weakened immune system
- High number of moles or unusual skin growths
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Recognizing early warning signs can save lives. The ABCDE rule helps detect melanoma:
- A: Asymmetry
- B: Border irregularity
- C: Color variation
- D: Diameter larger than 6mm
- E: Evolving size, shape, or color
Other warning signs include sores that do not heal, new growths, or red, scaly patches on the skin. If you notice these, searching for free skin cancer screening near me can help you get evaluated quickly.
Diagnosis
If a suspicious spot is found during a screening, doctors may perform a skin biopsy to determine whether the cells are cancerous. Advanced imaging tests are used in more severe cases. Early diagnosis greatly improves treatment outcomes.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type and stage of cancer and may include:
- Surgical removal of cancerous tissue
- Cryotherapy (freezing abnormal cells)
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy (topical or systemic)
- Immunotherapy or targeted therapy for advanced melanoma
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
Prevention remains the best defense. Key tips include:
- Regularly use broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher)
- Wear protective clothing and hats outdoors
- Avoid tanning beds
- Schedule annual skin checks
- Take advantage of free skin cancer screenings near me when available
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for skin cancer varies by type:
- BCC and SCC: High survival rates when detected early, often above 95%
- Melanoma: 5-year survival rate is over 99% if caught early, but drops significantly once it spreads
This makes regular screenings critical to improving survival rates.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent advances in skin cancer research include:
- AI-powered diagnostic tools that analyze skin images
- New immunotherapy drugs showing promising results in melanoma treatment
- Genetic testing for identifying high-risk individuals
- Community-driven initiatives expanding access to free skin cancer screening near me
Coping and Support for Patients
A skin cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but emotional and social support is key. Patients can benefit from:
- Counseling or support groups
- Patient education programs
- Online communities and forums
- Local cancer support organizations that also share information about free skin cancer screenings and preventive resources
Conclusion
Finding a free skin cancer screening near me is a proactive step that could save your life. Screenings are quick, painless, and often available at local hospitals, community health centers, and nonprofit events. With skin cancer being both common and highly treatable when caught early, regular check-ups and preventive care are crucial for maintaining healthy skin and long-term wellness.
FAQ
1. What is a free skin cancer screening?
It is a no-cost examination performed by a healthcare professional to detect suspicious skin changes that may indicate cancer.
2. Where can I find free skin cancer screening near me?
You can often find them at hospitals, local dermatology clinics, health fairs, or events organized by nonprofit organizations.
3. How long does a screening take?
Most screenings take about 10–15 minutes, depending on the number of areas being checked.
4. Do I need an appointment for free skin cancer screenings?
Some programs require appointments, while others offer walk-in services. It’s best to check with the local provider.
5. How often should I get screened?
Dermatologists recommend annual screenings, or more frequently if you have higher risk factors such as a family history of skin cancer.