Prostate cancer remains one of the most common cancers affecting men worldwide. With advancements in medical research and technology, treatment approaches have evolved significantly over the years. Among the breakthroughs that shaped modern care, the new prostate cancer treatment 2018 era marked a turning point by introducing more precise and less invasive therapies.
This article explores everything you need to know about prostate cancer, from causes and symptoms to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. We will also highlight the importance of the new therapies introduced in 2018, how they changed the treatment landscape, and what patients can expect today.
Definition and Overview
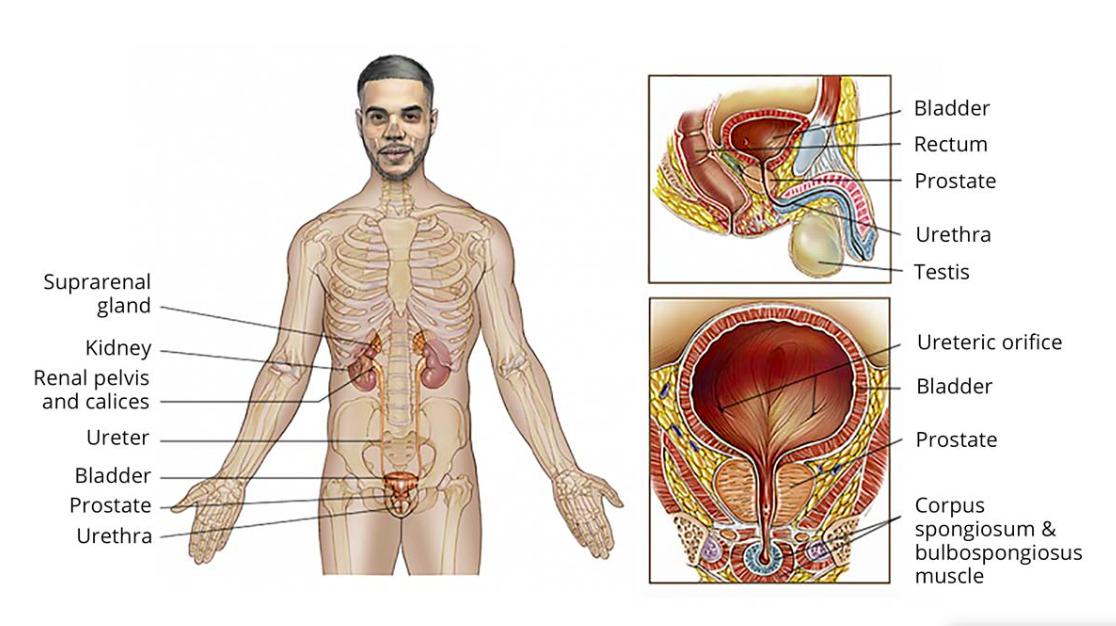
Prostate cancer is a malignant growth that develops in the prostate gland, a small organ responsible for producing seminal fluid. It is most common in older men, though it can affect younger individuals as well. The disease ranges from slow-growing tumors that may not cause symptoms to aggressive cancers requiring immediate treatment.
The introduction of new prostate cancer treatment in 2018 offered patients more targeted and personalized options, improving survival rates and reducing side effects.
Types
There are several types of prostate cancer, including:
- Adenocarcinoma: The most common type, starting in glandular cells.
- Small cell carcinoma: A rare and aggressive form.
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Extremely rare and aggressive.
- Transitional cell carcinoma: Begins in the bladder and spreads to the prostate.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of prostate cancer is unknown, but several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing it:
- Age: Most common in men over 50.
- Family history: Genetic factors play a role.
- Race: Higher incidence in African-American men.
- Lifestyle: Diets high in fat and low in vegetables increase risk.
- Hormonal factors: Elevated testosterone levels can influence tumor growth.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Prostate cancer often develops silently. Early detection is crucial, and symptoms may include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak urine flow
- Blood in urine or semen
- Pelvic or lower back pain
- Erectile dysfunction
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of:
- PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) Test
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
- MRI scans
- Prostate biopsy for confirmation
These methods allow doctors to stage the cancer and determine the most suitable treatment, including options introduced as part of the new prostate cancer treatment 2018.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer. Options include:
- Active surveillance for slow-growing cancers
- Surgery (prostatectomy)
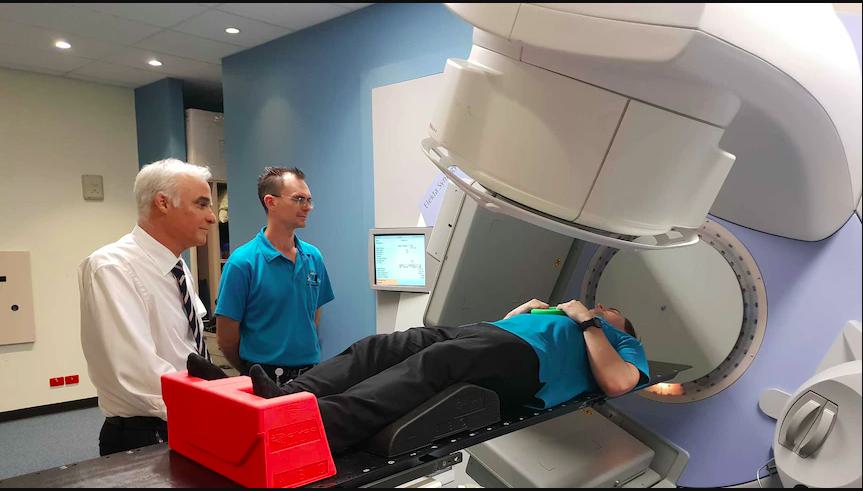
- Radiation therapy
- Hormone therapy
- Chemotherapy for advanced stages
- New prostate cancer treatment 2018 innovations, such as immunotherapy, targeted drug therapies, and advanced imaging-guided treatments, which improved precision and minimized side effects
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While prostate cancer cannot always be prevented, healthy lifestyle choices reduce risk:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vegetables and low in processed fats
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol
- Get regular screenings, especially if you are at high risk
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for prostate cancer is generally positive when detected early. According to medical data, the 5-year survival rate for localized and regional prostate cancer is nearly 100%. However, aggressive or late-stage cancers may significantly lower survival chances. The new prostate cancer treatment 2018 therapies have contributed to better outcomes, especially for patients with advanced stages.
Latest Research and Innovations
Since 2018, research has continued to expand the possibilities for treatment. The new prostate cancer treatment 2018 breakthroughs included advances in immunotherapy, precision medicine, and robotic surgery. These innovations reduced side effects and improved recovery times. Ongoing studies are exploring genetic testing and personalized therapy to further refine treatment options.
Coping and Support for Patients
A prostate cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. Patients benefit from emotional support, counseling, and joining support groups. Family involvement, open communication with healthcare providers, and exploring holistic approaches such as stress management and proper nutrition can make the journey more manageable.
Conclusion
The introduction of new prostate cancer treatment 2018 marked a significant advancement in the fight against prostate cancer. With better precision, fewer side effects, and higher success rates, these treatments changed the way doctors manage the disease. Early detection, lifestyle choices, and ongoing research continue to offer hope for patients and their families.
FAQ
1. What is the most common type of prostate cancer?
The most common type is adenocarcinoma, which develops in the glandular cells.
2. What were the key innovations in new prostate cancer treatment 2018?
They included targeted therapies, immunotherapy, robotic-assisted surgery, and advanced radiation techniques.
3. Can prostate cancer be cured?
When detected early and treated effectively, many men are cured or live long, healthy lives after treatment.
4. Who is at higher risk of developing prostate cancer?
Men over 50, those with a family history, and African-American men are at higher risk.
5. How can I lower my risk of prostate cancer?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and routine screenings can help lower your risk.