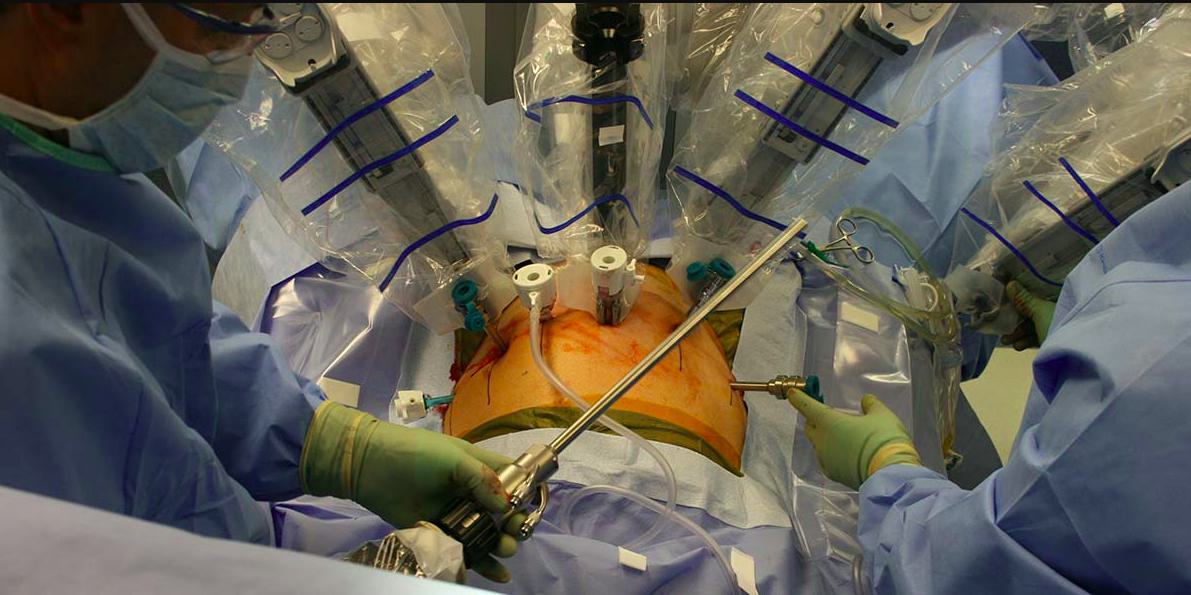
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men worldwide, and early detection has significantly improved survival rates. With advancements in medical technology, treatment methods have evolved to become less invasive and more precise. One of the most revolutionary approaches in recent years is robotic surgery for prostate cancer, which has transformed how surgeons operate and how patients recover.
This surgical innovation combines the expertise of skilled urologists with cutting-edge robotic-assisted systems. It allows for enhanced accuracy, reduced complications, and faster recovery compared to traditional surgical techniques. Understanding robotic surgery for prostate cancer can empower patients and their families to make informed treatment decisions.
Definition and Overview
Robotic surgery for prostate cancer, often referred to as robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy, is a minimally invasive procedure performed with the help of robotic systems. The most widely used platform is the da Vinci Surgical System, which provides surgeons with a 3D view, greater precision, and enhanced dexterity. Unlike traditional open surgery, robotic-assisted surgery requires only small incisions, leading to less blood loss and reduced post-operative pain.
Types
There are two primary types of prostate cancer surgeries:
- Open Radical Prostatectomy – Traditional surgery involving a large incision to remove the prostate gland.
- Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy (RARP) – A minimally invasive technique where surgeons control robotic instruments to remove the prostate with precision.
Robotic surgery for prostate cancer is now considered the preferred method in many hospitals due to its effectiveness and faster recovery times.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of prostate cancer remains unclear, several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing the disease, including:
- Age: Men over 50 are at higher risk.
- Family history: Having close relatives with prostate cancer raises the risk.
- Genetics: Certain inherited mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, may play a role.
- Lifestyle factors: High-fat diets, obesity, and smoking may contribute to increased risk.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
In its early stages, prostate cancer often shows no symptoms. As it progresses, common warning signs may include:
- Difficulty urinating or weak urine flow
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Blood in urine or semen
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area
- Erectile dysfunction
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of:
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test – Measures PSA levels in the blood.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) – Physical examination of the prostate gland.
- Biopsy – Removal of small prostate tissue samples for lab testing.
- Imaging Tests – MRI, CT scans, or bone scans to determine cancer spread.
Treatment Options
Treatment for prostate cancer depends on the stage, patient health, and personal preferences. Options include:
- Active surveillance for slow-growing cancers.
- Radiation therapy to target and kill cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy to lower testosterone levels.
- Chemotherapy for advanced cases.
- Robotic surgery for prostate cancer, offering minimally invasive removal of the prostate with excellent precision.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
Although prostate cancer cannot always be prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce risks:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Limit red meat and high-fat foods.
- Exercise regularly to maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Get regular check-ups and prostate screenings after age 50, or earlier with family history.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for prostate cancer is generally favorable, especially when detected early. According to recent statistics, the 5-year survival rate for localized and regional prostate cancer is nearly 100%. Robotic surgery for prostate cancer has further improved outcomes by reducing complications, preserving urinary function, and improving sexual health recovery.
Latest Research and Innovations
Research continues to enhance prostate cancer treatment. Innovations include:
- AI-assisted robotic surgery for even greater precision.
- Focal therapies targeting only cancerous areas of the prostate.
- Personalized medicine using genetic profiling to guide treatment.
- Immunotherapy to boost the body’s natural defenses.
Coping and Support for Patients
A prostate cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. Emotional support and counseling are crucial for patients and families. Support groups, mental health therapy, and patient education resources can help individuals cope with stress and anxiety. Maintaining open communication with doctors about concerns related to robotic surgery for prostate cancer also helps patients feel empowered throughout their treatment journey.
Conclusion
Robotic surgery for prostate cancer has become a breakthrough in urologic oncology, offering patients a less invasive, more precise, and faster-recovery alternative to traditional surgery. While prevention and early detection remain key, robotic-assisted procedures have greatly improved the prognosis and quality of life for patients. Staying informed about available treatments, lifestyle changes, and support systems ensures that patients can face prostate cancer with strength and confidence.
FAQ
1. What is robotic surgery for prostate cancer?
It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses robotic-assisted technology to remove the prostate gland with precision.
2. Is robotic surgery better than traditional surgery?
Yes, robotic surgery often results in smaller incisions, less blood loss, faster recovery, and better preservation of urinary and sexual function.
3. How long is recovery after robotic prostate surgery?
Most patients recover within 2–4 weeks, compared to 6–8 weeks for traditional open surgery.
4. Does robotic surgery guarantee cancer cure?
No treatment guarantees a cure, but robotic surgery for prostate cancer offers excellent cancer control and survival rates when performed by experienced surgeons.
5. Is robotic surgery safe?
Yes, robotic-assisted procedures are considered safe, with fewer complications compared to open surgery, especially in specialized medical centers.