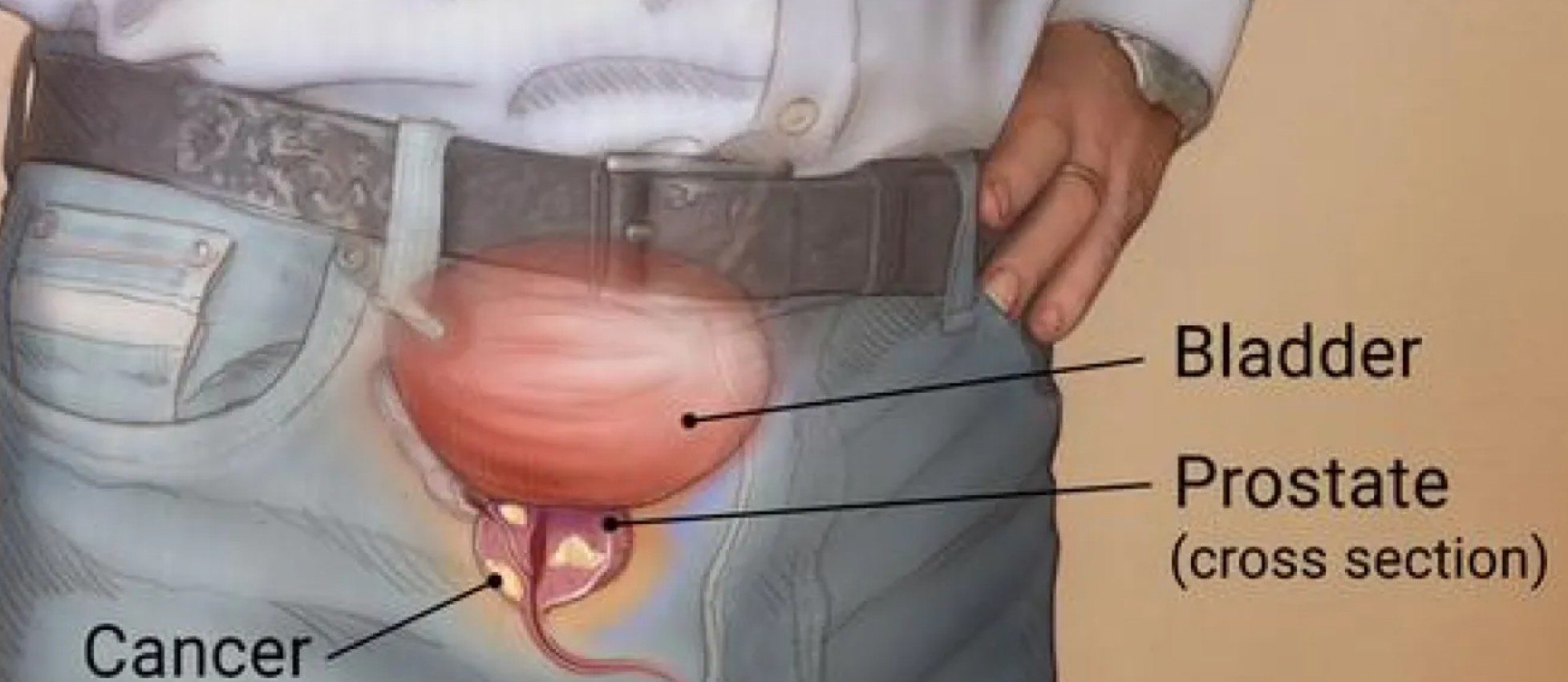
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men worldwide. Advances in medical technology have transformed the way this disease is treated, giving patients more effective options with fewer side effects. Among these innovations, minimally invasive prostate cancer surgery has gained significant attention for its precision and faster recovery outcomes.
Many patients and families often wonder what makes this surgical approach different from traditional methods. Understanding how it works, its benefits, and its limitations is essential for anyone facing a prostate cancer diagnosis. This article explores everything you need to know, from symptoms and diagnosis to treatment options and the latest research advancements.
Definition and Overview
Minimally invasive prostate cancer surgery refers to surgical techniques that treat prostate cancer with smaller incisions and advanced technology compared to open surgery. These methods, such as laparoscopic and robotic-assisted procedures, aim to remove cancerous tissue while preserving important structures like nerves and the bladder.
This approach not only reduces blood loss and pain but also shortens hospital stays and speeds up recovery. For many patients, minimally invasive surgery offers an improved quality of life during and after cancer treatment.
Types of Minimally Invasive Prostate Cancer Surgery
There are two main types of minimally invasive prostate cancer surgery:
- Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy (LRP): A surgeon operates using long, thin instruments inserted through small incisions in the abdomen.
- Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy (RARP): A more advanced method where surgeons control robotic arms that provide enhanced precision, flexibility, and 3D visualization.
Both methods are effective, but robotic-assisted surgery is increasingly becoming the preferred choice due to its accuracy and improved outcomes in preserving urinary and sexual function.
Causes and Risk Factors
Prostate cancer does not have a single known cause, but several risk factors contribute to its development:
- Age: Most common in men over 50.
- Family history: Having a father or brother with prostate cancer increases risk.
- Genetic mutations: BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations can raise susceptibility.
- Race: African American men face a higher risk and more aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
- Lifestyle: Poor diet, obesity, and lack of physical activity may also increase the likelihood.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Prostate cancer often develops slowly and may not show symptoms in its early stages. However, some warning signs include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Blood in urine or semen
- Erectile dysfunction
- Pelvic or back pain
Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
Diagnosis
Doctors use several methods to diagnose prostate cancer:
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Measures PSA levels in the blood.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): Checks the prostate for abnormalities.
- MRI and Imaging Scans: Provides detailed visualization of the prostate.
- Biopsy: Confirms the presence of cancer cells.
These diagnostic tools help determine whether minimally invasive prostate cancer surgery is a suitable option.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer. Options include:
- Active Surveillance: Monitoring slow-growing cancers without immediate treatment.
- Radiation Therapy: Targeted radiation to kill cancer cells.
- Hormone Therapy: Reduces testosterone to slow cancer growth.
- Minimally Invasive Prostate Cancer Surgery: Removes the cancer while minimizing side effects.
Choosing the right treatment requires a personalized approach guided by medical professionals.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While prostate cancer cannot always be prevented, healthy habits can lower the risk:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly to support overall health.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce hormone-related risks.
- Limit red meat and processed foods.
- Get regular checkups, especially if you have a family history of prostate cancer.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Thanks to medical advancements, the prognosis for prostate cancer has improved dramatically. When detected early and treated with minimally invasive prostate cancer surgery, survival rates are very high. The five-year relative survival rate for localized and regional prostate cancer is nearly 100%.
Long-term outcomes also depend on age, overall health, and adherence to follow-up care. Many patients live long, healthy lives after treatment.
Latest Research and Innovations
Ongoing research continues to enhance prostate cancer treatment:
- Improved robotic surgery systems for greater accuracy.
- Focal therapy approaches that target only cancerous areas, preserving more healthy tissue.
- Genomic testing to personalize treatment strategies.
- New drug therapies combined with surgery for advanced cases.
These innovations are making minimally invasive prostate cancer surgery even safer and more effective.
Coping and Support for Patients
A prostate cancer diagnosis can be emotionally overwhelming. Patients benefit from:
- Support groups to share experiences and reduce anxiety.
- Counseling services for mental health and stress management.
- Family involvement in treatment decisions.
- Rehabilitation programs to aid recovery after surgery.
Emotional and social support plays a critical role in improving quality of life during and after treatment.
Conclusion
Minimally invasive prostate cancer surgery has revolutionized the treatment of prostate cancer, offering less pain, quicker recovery, and improved outcomes for patients. With early detection and the right treatment plan, survival rates are highly favorable, and many men return to normal, active lives.
By staying informed, making healthy lifestyle choices, and seeking support, patients and families can navigate the challenges of prostate cancer with confidence. The future holds even greater promise as research continues to refine surgical methods and treatment strategies.
FAQ
1. What is minimally invasive prostate cancer surgery?
It is a surgical method that uses small incisions and advanced technology to remove the prostate while minimizing side effects and recovery time.
2. How long does recovery take after surgery?
Most patients recover within 2–4 weeks, though full healing and regaining normal functions may take longer.
3. Is robotic-assisted surgery better than traditional surgery?
Yes, robotic-assisted procedures generally offer greater precision, less pain, and faster recovery compared to open surgery.
4. Can prostate cancer return after minimally invasive surgery?
Yes, recurrence is possible, which is why regular follow-up appointments and PSA monitoring are essential.
5. Who is a good candidate for minimally invasive prostate cancer surgery?
Men with localized prostate cancer, good overall health, and no severe medical complications are usually the best candidates.