Pancreatic cancer is often called a “silent killer” because it’s notoriously difficult to detect early and even harder to treat. With a five-year survival rate of just 10%, it’s one of the deadliest forms of cancer. But what if there was a way to harness the power of the body’s own immune system to fight this aggressive disease? Enter immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer treatment, a groundbreaking approach that’s changing the game for patients and doctors alike. In this article, we’ll explore how immunotherapy works, its potential benefits, and what it means for the future of pancreatic cancer care.
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that boosts the body’s natural defenses to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Unlike traditional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation, which directly attack cancer, immunotherapy empowers the immune system to do the heavy lifting. For pancreatic cancer, this approach is particularly promising because it offers a new way to tackle a disease that has long resisted conventional therapies. But how effective is immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer treatment, and who can benefit from it? Let’s dive into the science, the successes, and the challenges of this innovative treatment.
What Is Immunotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment?
To understand immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer treatment, it’s important to first grasp what immunotherapy is and how it works.
The Basics of Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy uses substances made by the body or in a lab to help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. Think of it as giving your immune system a “boost” or a “training session” to better fight the disease.
Why Pancreatic Cancer Is a Tough Opponent
Pancreatic cancer is particularly challenging because it often develops resistance to treatments and has a unique ability to hide from the immune system. This makes immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer treatment both a promising and complex option.
How Does Immunotherapy Work Against Pancreatic Cancer?
Immunotherapy works in several ways to combat pancreatic cancer. Here’s a breakdown of the key mechanisms:
| Type of Immunotherapy | How It Works |
|---|---|
| Checkpoint Inhibitors | Blocks proteins that prevent immune cells from attacking cancer. |
| CAR-T Cell Therapy | Modifies a patient’s T cells to better recognize and destroy cancer cells. |
| Cancer Vaccines | Stimulates the immune system to target specific cancer cells. |
| Cytokines | Uses proteins to enhance the immune response. |
Types of Immunotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
Several types of immunotherapy are being explored for pancreatic cancer. Let’s take a closer look at each.
1. Checkpoint Inhibitors
Checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, are drugs that “release the brakes” on the immune system, allowing it to attack cancer cells more effectively. While these drugs have shown success in other cancers, their effectiveness in pancreatic cancer is still being studied.
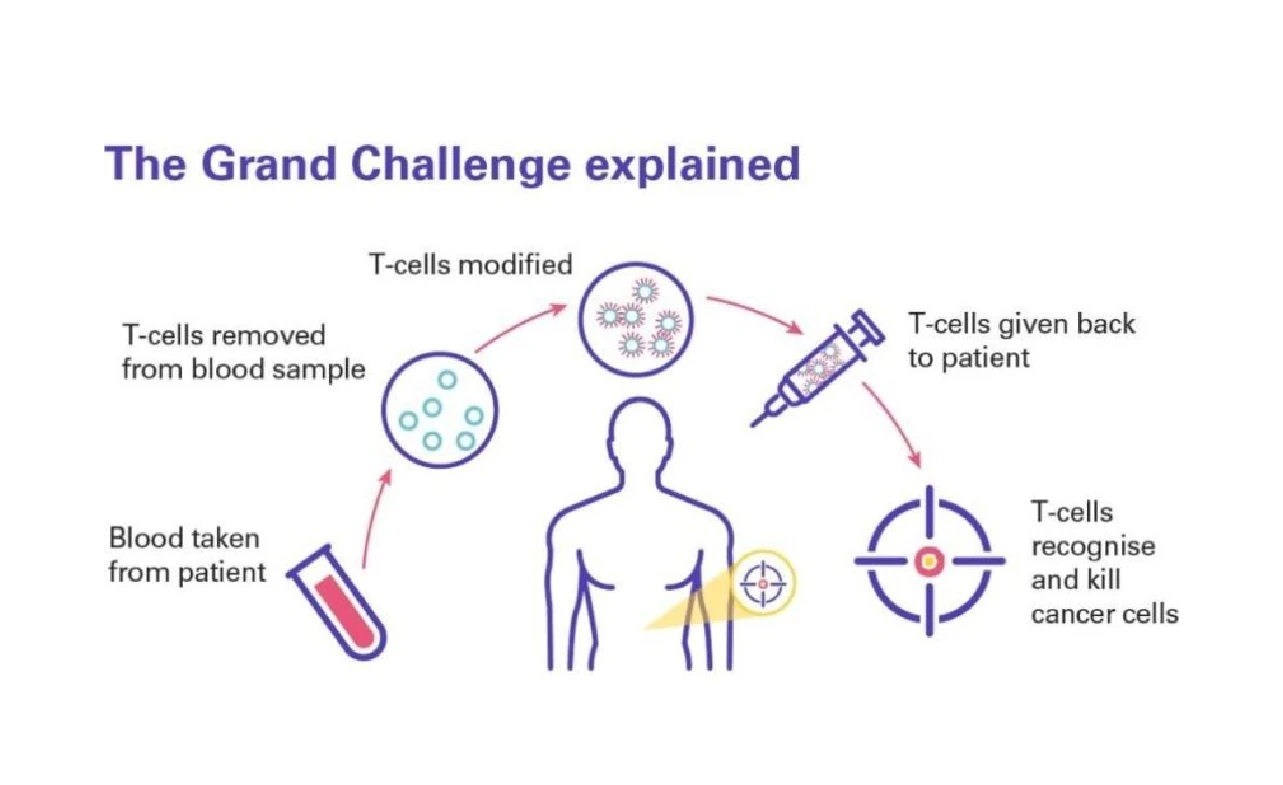
2. CAR-T Cell Therapy
CAR-T cell therapy involves extracting a patient’s T cells, genetically modifying them to target cancer cells, and then infusing them back into the body. This approach is still in early stages for pancreatic cancer but holds significant promise.
3. Cancer Vaccines
Cancer vaccines, like GVAX, are designed to train the immune system to recognize and attack pancreatic cancer cells. These vaccines are often used in combination with other treatments to enhance their effectiveness.
4. Cytokines
Cytokines, such as interleukins and interferons, are proteins that help regulate the immune response. They can be used to boost the immune system’s ability to fight cancer.
Benefits of Immunotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
Immunotherapy offers several potential benefits for pancreatic cancer patients, including:
1. Targeted Action
Unlike chemotherapy, which can harm healthy cells, immunotherapy specifically targets cancer cells, reducing side effects.
2. Long-Lasting Effects
Immunotherapy can create a “memory” in the immune system, providing long-term protection against cancer recurrence.
3. Combination Potential
Immunotherapy can be combined with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation, to enhance overall effectiveness.
Challenges and Limitations
While immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer treatment is promising, it’s not without its challenges.
1. Limited Effectiveness in Some Patients
Not all patients respond to immunotherapy, and researchers are still working to understand why.
2. Side Effects
Immunotherapy can cause side effects, such as fatigue, skin reactions, and autoimmune responses, where the immune system attacks healthy tissues.
3. High Costs
Immunotherapy treatments can be expensive, making access a challenge for some patients.
Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy?
Immunotherapy is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Here’s who might benefit the most:
1. Patients with Specific Biomarkers
Certain genetic markers, such as microsatellite instability (MSI), can indicate a better response to immunotherapy.
2. Those with Advanced or Recurrent Cancer
Immunotherapy may be an option for patients with advanced or recurrent pancreatic cancer who have not responded to other treatments.
3. Participants in Clinical Trials
Clinical trials offer access to cutting-edge immunotherapy treatments and contribute to advancing research.
The Future of Immunotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
The future of immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer treatment is bright, with ongoing research and new developments on the horizon.
1. Personalized Medicine
Advances in genetic testing are enabling doctors to tailor immunotherapy treatments to individual patients.
2. Combination Therapies
Researchers are exploring combinations of immunotherapy with other treatments to improve outcomes.
3. Early Detection
Improved screening methods and biomarkers are helping detect pancreatic cancer earlier, when immunotherapy may be more effective.
Conclusion
Immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer treatment represents a beacon of hope in the fight against one of the deadliest cancers. By harnessing the power of the immune system, this innovative approach offers new possibilities for patients who have few other options. While challenges remain, ongoing research and advancements are paving the way for more effective and accessible treatments. For patients and their families, immunotherapy is not just a treatment—it’s a promise of a brighter future. As science continues to unlock the potential of the immune system, the fight against pancreatic cancer is becoming more hopeful than ever.