Breast cancer remains one of the most prevalent and challenging diseases affecting women worldwide. Every year, millions are diagnosed, and countless families face the physical, emotional, and financial impact that comes with it. Organizations like the Breast Cancer Charities of America (BCCA) play a crucial role in providing education, early detection programs, patient assistance, and holistic care support.
Understanding the mission and initiatives of the Breast Cancer Charities of America helps raise awareness and empowers individuals to take part in the fight against breast cancer. This article explores the key aspects of breast cancer—from causes and symptoms to treatments and prevention—while highlighting the essential work done by BCCA in improving lives and advancing breast health education.
Definition and Overview
The Breast Cancer Charities of America is a nonprofit organization dedicated to eliminating breast cancer as a life-threatening disease through education, prevention, research, and direct patient support. Founded with the vision of addressing both medical and emotional needs, BCCA emphasizes integrated care that includes nutrition, wellness, and mind-body balance.
Breast cancer itself occurs when abnormal cells in the breast grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor that can invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body. It affects both women and men, although it is significantly more common in women.
Types of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can manifest in several forms, and understanding the type is crucial for effective treatment. The main types include:
- Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS): A non-invasive form where abnormal cells remain in the milk ducts.
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC): The most common type, where cancer cells spread beyond the ducts.
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC): Originates in the lobules (milk-producing glands) and can spread to nearby tissues.
- Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): Lacks estrogen, progesterone, and HER2 receptors, making it harder to treat.
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC): A rare and aggressive type that causes redness and swelling.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of breast cancer remains unknown, several factors increase risk:
- Genetic mutations (e.g., BRCA1 and BRCA2)
- Family history of breast or ovarian cancer
- Hormonal factors, including early menstruation or late menopause
- Lifestyle habits, such as smoking, poor diet, or lack of exercise
- Exposure to radiation
- Age, as risk increases with aging
The Breast Cancer Charities of America emphasizes the importance of understanding these risks and adopting proactive screening habits for early detection.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Recognizing symptoms early can dramatically improve survival rates. Common signs include:
- A lump or thickening in the breast or underarm area
- Changes in breast size, shape, or appearance
- Nipple discharge or inversion
- Skin dimpling or redness
- Persistent pain in the breast area
BCCA encourages regular self-examinations and mammogram screenings as key steps toward early intervention.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing breast cancer typically involves a combination of tests, including:
- Mammography: The most common imaging method for early detection.
- Ultrasound and MRI scans: Used for further evaluation.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample taken to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
- Hormone receptor tests: Determine the cancer type and guide treatment options.
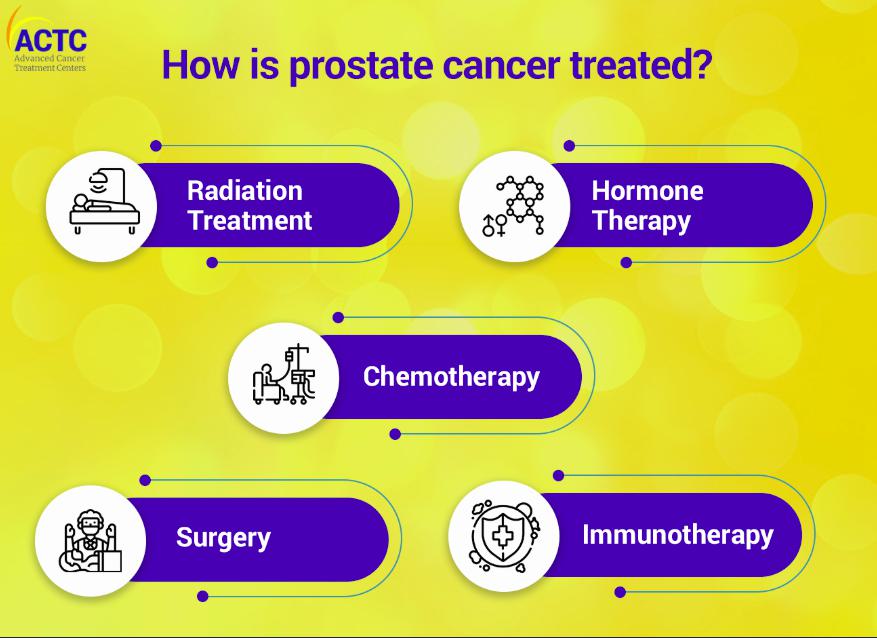
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage and type of breast cancer. Common approaches include:
- Surgery: Lumpectomy or mastectomy to remove cancerous tissue.
- Radiation therapy: Targets and destroys remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Uses powerful drugs to eliminate cancer cells throughout the body.
- Hormone therapy: Blocks hormone receptors to slow cancer growth.
- Targeted therapy: Focuses on specific cancer cell mechanisms, such as HER2 proteins.
The Breast Cancer Charities of America also promotes integrative care, focusing on nutrition, stress management, and physical wellness alongside traditional treatments.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all breast cancer cases can be prevented, healthy lifestyle choices can significantly reduce risk:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Limit alcohol consumption and avoid smoking.
- Schedule regular screenings and self-exams.
- Manage stress through mindfulness and relaxation techniques.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
With early detection and advanced treatments, breast cancer survival rates have improved significantly. According to global health data, the five-year survival rate for localized breast cancer is over 90%. Factors such as cancer stage, type, and response to treatment affect prognosis. The ongoing efforts of organizations like the Breast Cancer Charities of America help ensure that more patients have access to care and support for better outcomes.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent advancements in breast cancer research focus on personalized medicine, immunotherapy, and genetic testing. Clinical trials continue to explore new drugs and technologies aimed at improving patient survival and quality of life. The Breast Cancer Charities of America actively supports research initiatives and educational programs that bridge scientific progress with community outreach.
Coping and Support for Patients
A breast cancer diagnosis can be emotionally overwhelming. BCCA provides numerous programs to help patients and families cope, including:
- Financial assistance for treatment costs and medical supplies.
- Emotional support groups and counseling services.
- Educational resources on nutrition, wellness, and survivorship.
- Community outreach programs to connect patients with advocates and mentors.
Emotional resilience, family support, and access to comprehensive care play vital roles in recovery and long-term well-being.
Conclusion
The Breast Cancer Charities of America continues to be a beacon of hope for countless patients and families affected by breast cancer. Through education, prevention, and compassionate care, BCCA inspires individuals to take charge of their health and supports the global mission to eradicate breast cancer. Staying informed, living healthily, and supporting organizations like BCCA are meaningful ways to make a lasting difference.
FAQ
1. What is the main goal of the Breast Cancer Charities of America?
The organization focuses on education, prevention, research, and patient support to eliminate breast cancer as a life-threatening disease.
2. How can I support the Breast Cancer Charities of America?
You can donate, volunteer, or participate in fundraising events to help expand their programs and reach.
3. Does breast cancer only affect women?
No, while it is more common in women, men can also develop breast cancer, though it is rare.
4. How often should I get a mammogram?
It’s generally recommended for women aged 40 and above to have a mammogram every one to two years, depending on risk factors and doctor recommendations.
5. Can a healthy lifestyle really reduce breast cancer risk?
Yes. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding alcohol and tobacco can significantly lower the risk.