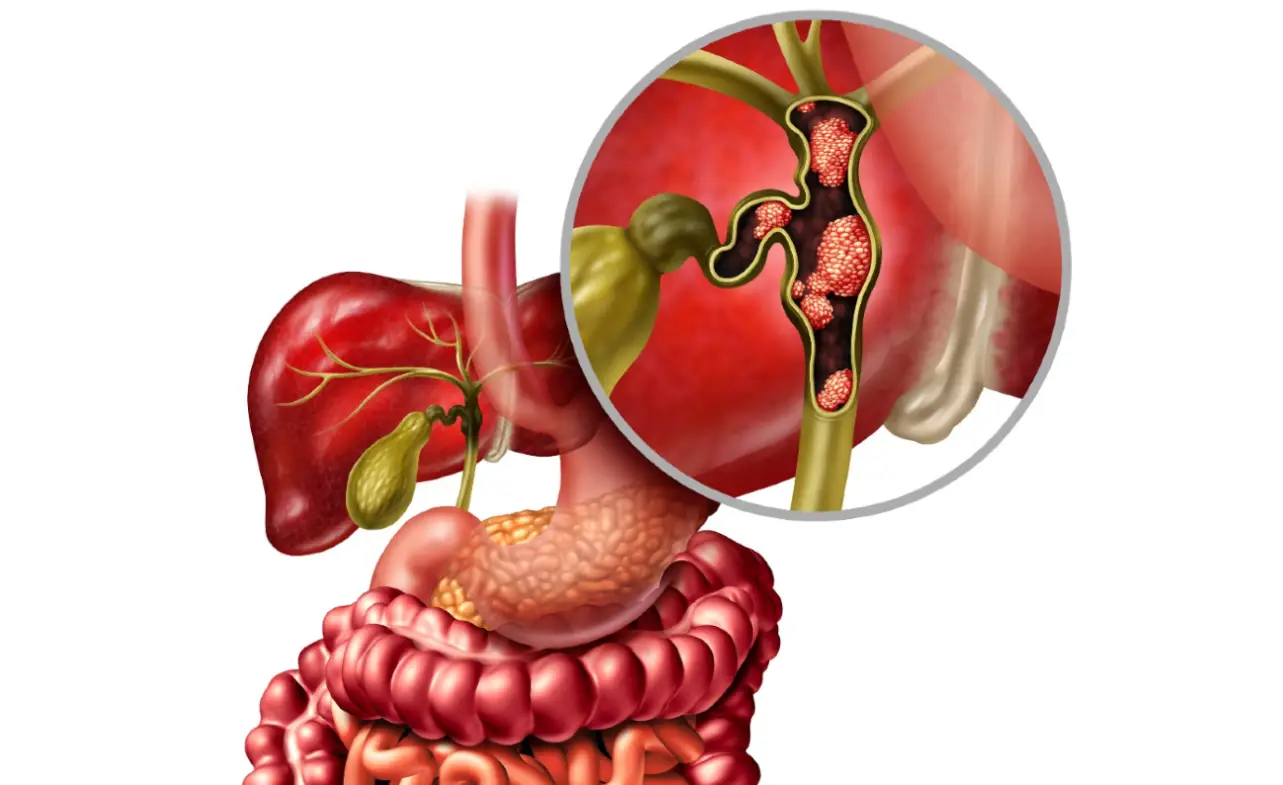
Stagescancer.net – Bile duct cancer is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that develops in the ducts that carry bile from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine. The disease is often challenging to diagnose and treat, and unfortunately, many individuals are diagnosed with stage 4 bile duct cancer, where cancer has metastasized, or spread, to distant organs or lymph nodes. In this section, we will delve into the life expectancy of individuals with stage 4 bile duct cancer, exploring the various factors that can impact their prognosis and discussing the treatment options available.
Understanding Bile Duct Cancer
Bile duct cancer is a rare type of cancer that affects the bile ducts, which are tubes that transport bile from the liver to the small intestine. There are different types of bile duct cancer, with the most common being cholangiocarcinoma, which starts in the cells that line the bile ducts.
The exact cause of bile duct cancer is unknown, but several risk factors may increase the risk of developing the disease, including:
- Chronic inflammation of the bile ducts due to conditions such as primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Presence of abnormal bile ducts at birth
- Liver disease such as cirrhosis
- Exposure to certain chemicals such as Thorotrast
- Older age
The symptoms of bile duct cancer may vary depending on the location and stage of the cancer. Some common symptoms include:
- Jaundice, which causes yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills
Bile duct cancer is typically classified into four stages, with stage 1 being the least advanced and stage 4 being the most advanced. The stage of the cancer is determined by how far the cancer has spread.
Having a basic comprehension of bile duct cancer is crucial in understanding how the disease develops and progresses. In the next section, we will explore what stage 4 bile duct cancer is and how it is diagnosed.
What Is Stage 4 Bile Duct Cancer?
Stage 4 bile duct cancer is an advanced form of the disease, indicating that the cancer has spread beyond the bile ducts to other organs or distant lymph nodes. A doctor might suspect stage 4 bile duct cancer based on symptoms and tests and will confirm it through biopsies, blood tests, and imaging examinations like CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasounds.
The staging of cancer is determined by the TNM system based on the tumor’s size, lymph node involvement, and whether it has metastasized to other locations. In stage 4 bile duct cancer, surgery may not be an option due to the spread of cancer. Instead, treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation, and palliative care are recommended to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Blood Tests and Imaging Exams for Diagnosing Stage 4 Bile Duct Cancer
Blood tests are a reliable way to detect bile duct cancer and monitor liver function. Some of the blood tests used in diagnosing stage 4 bile duct cancer include:
- Liver function tests (LFTs): These blood tests measure levels of bilirubin, albumin, and enzymes. Abnormal levels may indicate liver damage or bile duct obstruction.
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA): Raised levels of this protein may indicate cancer in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
- Cancer antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9): Increased levels of this protein are a red flag for bile duct or pancreatic cancer. It is not always reliable, as elevated levels can also mean inflammation rather than cancer.
Imaging examinations are also essential for detecting bile duct cancer and determining its staging and extent of spread. Some of the imaging tests used for stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosis include:
- Computed tomography (CT) scan: It is done with contrast dye to show the blood vessels supplying the tumor and the surrounding organs, and find if the tumor has spread.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): It helps show moisture in the liver or surrounding organs or abnormal cell growth.
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC): This procedure involves injecting dye through the liver to the bile ducts while taking X-rays in the adjacent area.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A flexible tube goes through the patient’s mouth to the small intestine, where X-rays are taken to show the pancreas’s bile duct system.
Factors Affecting Life Expectancy in Stage 4 Bile Duct Cancer
When it comes to stage 4 bile duct cancer, life expectancy can vary significantly from one patient to another. Several factors influence how long an individual may live, including:
- Age: Older patients may have reduced life expectancies due to the natural aging process, reduced immune function, and other age-related health issues.
- Overall health: Patients with pre-existing health conditions such as heart disease or diabetes may have reduced life expectancies.
- Tumor characteristics: Factors such as tumor size, stage, and location can significantly impact life expectancy. For instance, if the tumor has spread to other organs, the prognosis may be poorer.
- Response to treatment: The response of the tumor to various treatment modalities such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery may significantly impact life expectancy.
Other factors that may affect life expectancy include lifestyle choices such as diet, exercise, and smoking habits. Working closely with healthcare professionals, patients, and their caregivers can develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses these factors and provides the best possible quality of life.
Survival Rates and Statistics for Stage 4 Bile Duct Cancer
When it comes to stage 4 bile duct cancer, survival rates are generally low due to the cancer’s advanced stage. Statistics show that the five-year survival rate for individuals with stage 4 bile duct cancer is around 2%. However, it’s worth noting that these numbers are general averages and may not accurately reflect an individual’s situation.
Studies have shown that various factors can influence survival rates in stage 4 bile duct cancer, including age, overall health, tumor location and size, and response to treatment. One study that followed 69 individuals found that the median survival time was 8.4 months, with a range from four to 20 months.
| Survival Rates | % of Individuals |
|---|---|
| 1-year survival rate | 20%-30% |
| 2-year survival rate | 10%-20% |
| 5-year survival rate | 2% |
Survival rates for stage 4 bile duct cancer can vary from person to person, and it’s essential to remember that there is always hope, regardless of the statistics. It’s crucial to work with your healthcare team to develop a treatment plan that’s best for you and to seek out supportive care options to enhance your quality of life.
Treatment Options for Stage 4 Bile Duct Cancer
When diagnosed with stage 4 bile duct cancer, there are different treatment options available to help manage the disease. Each treatment approach aims to achieve a specific goal, including:
- Surgery: Surgery may be an option in cases where the cancer has not spread extensively. The goal of surgery is to remove cancerous tissue and prevent further spread.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to destroy cancerous cells. It may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy involves drugs that target specific genes or proteins involved in cancer cell growth. It may be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy involves drugs that stimulate the immune system to fight cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
When deciding on a treatment plan, factors such as the individual’s overall health, age, and tumor characteristics must be taken into account. The aim is to strike a balance between treating cancer and preserving the quality of life.
Palliative and Supportive Care for Stage 4 Bile Duct Cancer
While treatment for stage 4 bile duct cancer may focus on managing the symptoms of the disease, the emphasis on palliative and supportive care is on enhancing the quality of life for patients. Palliative care aims to provide relief from the symptoms and stress of the disease, improving the overall physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being of the patient and their loved ones.
Symptom management is a critical component of palliative care. Pain and discomfort caused by the disease and its treatments can be managed through various methods, including medication, massage therapy, and relaxation techniques. Nutrition counseling is also a part of palliative care, helping patients maintain their strength and energy during treatment.
Emotional and psychological support is also crucial during this time. Patients can seek professional counseling or join support groups. Spiritual and religious counseling can provide an opportunity for patients to find comfort and meaning in their beliefs.
Supportive care services include rehabilitation programs, such as physical therapy and occupational therapy, which can help patients maintain their strength, mobility, and independence. Social workers and care coordinators can also assist with navigating the healthcare system, managing insurance, and connecting patients with community resources.
Effective palliative and supportive care can help patients and their loved ones cope with the emotional and physical stresses of a stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosis, enhancing their quality of life and providing an invaluable source of comfort and support.
Clinical Trials and Experimental Treatments
For individuals with stage 4 bile duct cancer who have exhausted traditional treatment options, clinical trials and experimental treatments provide a potential lifeline. Clinical trials are research studies that test the safety and efficacy of new treatments, including drugs, medical procedures, and behavioral interventions. Participating in a clinical trial provides access to cutting-edge treatment options that may not be available through regular medical channels. It also contributes to the advancement of medical knowledge and the development of new therapeutic options.
The Importance of Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are a vital component of cancer research, providing the necessary evidence to develop new treatments and improve current ones. The results of clinical trials can lead to approval from the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), signaling that a treatment has been deemed safe and effective. Participation in clinical trials also helps build a better understanding of the disease and the best ways to fight it.
Finding Relevant Clinical Trials
Finding relevant clinical trials can be challenging, but several resources can help. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) maintains a comprehensive database of clinical trials, searchable by cancer type, location, and other factors. ClinicalTrials.gov is another resource that provides information on clinical trials around the world. Consulting with a healthcare provider and a designated patient advocate can also help guide individuals toward relevant clinical trials.
What to Consider Before Participating in a Clinical Trial
Participating in a clinical trial is a personal decision that should be made after carefully considering several factors, including the potential benefits and risks of the treatment. Before enrolling in a clinical trial, individuals should discuss options with their healthcare provider and the trial team. Understanding the trial’s requirements, potential side effects, and follow-up care is essential in making an informed decision.
Experimental Treatments
In addition to clinical trials, experimental treatments may also provide an option for individuals with stage 4 bile duct cancer. Experimental treatments are therapies that are not yet approved by the FDA but may offer potential benefits to patients. These treatments can include targeted therapies, immunotherapies, or combinations of existing treatments in new ways. While experimental treatments can carry higher risks and require additional scrutiny, they have the potential to benefit patients who have no other treatment options.
Managing Side Effects and Complications in Stage 4 Bile Duct Cancer
Individuals with stage 4 bile duct cancer often experience a range of side effects and complications as a result of their treatment. Proper management of these symptoms is essential to maintain quality of life and minimize discomfort. Here are some common side effects and complications and strategies for managing them:
Fatigue
One of the most common side effects of cancer treatment is fatigue. To manage fatigue, it is important to get enough rest and conserve energy throughout the day. Patients can also benefit from light exercise and scheduling regular breaks throughout the day.
Nausea and Vomiting
Anti-nausea medication may be prescribed to help manage nausea and vomiting. Patients can also try eating small, frequent meals and avoiding spicy or greasy foods.
Pain
Pain may be managed with pain medication prescribed by a physician. Additionally, relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and meditation can help ease pain and discomfort.
Emotional Distress
Receiving a stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosis can be emotionally overwhelming. It is important to talk to loved ones and seek emotional support from counselors or support groups.
Complications
Individuals with stage 4 bile duct cancer may also experience various complications, such as infections, blood clots, and dehydration. Prompt medical attention is essential if any complications arise.
Seeking supportive care services, such as pain management, nutrition counseling, and physical therapy, can also help manage side effects and complications and improve quality of life.
Coping with Bile Duct Cancer Stage 4 Diagnosis
A diagnosis of bile duct cancer in stage 4 can be an overwhelming and challenging experience for both patients and their loved ones. Coping with a serious illness like this can be difficult, but it is essential for maintaining emotional and physical well-being. Here are some practical tips and strategies for coping with the diagnosis:
Seek Emotional Support
One of the most important things to remember is that you do not have to face this diagnosis alone. Seek support from loved ones, friends, and family members. Consider joining support groups or speaking with a qualified mental health professional to help you manage the emotional toll of the diagnosis.
Engage in Self-Care
Self-care practices such as adequate rest, proper nutrition, and regular exercise can help improve physical and mental health. Make sure you are taking care of your body by taking the necessary time to rest, eat balanced meals, and exercise regularly.
Explore Complementary Therapies
Complementary therapies such as meditation, yoga, and acupuncture can help manage stress, anxiety, and pain associated with the diagnosis and treatment of bile duct cancer. Speak with your healthcare provider to determine which of these therapies may be appropriate for you.
Hope and Inspiring Stories of Stage 4 Bile Duct Cancer Survivors
Receiving a stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosis can understandably be a fearful and overwhelming experience, but it’s important to remember that there is always hope. Many individuals have defied the odds and experienced long-term survival, offering encouragement and inspiration to those currently fighting the disease.
One inspiring story is that of John Smith, who was diagnosed with stage 4 bile duct cancer in 2015. Despite the odds against him, John underwent a rigorous treatment plan that included surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. His unwavering positivity and determination, along with the support of his family and healthcare team, helped him achieve remission. Today, John is an advocate for raising awareness about bile duct cancer and helping others find hope and support.
| Name | Treatment | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Emily Brown | Immunotherapy | Survivor |
| Alexander Lee | Targeted therapy | Survivor |
| Leah Patel | Chemotherapy | Survivor |
| David Kim | Combination therapy | Survivor |
Other survivors have shared their stories online, providing hope and inspiration to individuals currently battling stage 4 bile duct cancer. These stories demonstrate that every individual’s journey is unique, and while the diagnosis may be challenging, it is possible to find strength and resilience throughout the treatment process.
If you or a loved one is currently struggling with a stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosis, remember that you are not alone. There are many resources and support groups available to provide encouragement and comfort. By staying positive and focusing on the present moment, you can find hope and inspiration along your journey.
Seeking Medical Advice and Second Opinions
Dealing with a stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, and it’s crucial to find medical professionals who can provide expert guidance. Start by consulting with primary care physicians or gastroenterologists to receive an accurate diagnosis. They can recommend specialists, including medical oncologists and surgical oncologists, who focus on treating bile duct cancer.
Seeking a second opinion is essential, as it can help confirm the diagnosis, understand all available treatment options, and identify potential clinical trials. Some physicians even encourage their patients to seek a second opinion. Consider seeking consultation from a National Cancer Institute-designated comprehensive cancer center, which often conducts clinical trials and may offer more treatment options.
As you prepare for appointments, make a list of questions to ask your healthcare provider. These may include:
- What are the different stages of bile duct cancer, and what stage am I in?
- What treatment options are available for my stage 4 bile duct cancer?
- What are the potential side effects of each treatment?
- How effective is each treatment option?
- What is the recommended treatment plan, and why?
- Are there any available clinical trials that I may be eligible for?
- What is my prognosis?
Remember, seeking medical advice and second opinions can provide valuable information and help you make the best decisions for your treatment plan.
Prognosis and Embracing a Fulfilling Life in the Face of Stage 4 Bile Duct Cancer
The news of a stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. It’s natural to experience a range of emotions, including fear, anger, and sadness. However, it’s important to remember that a diagnosis does not define who you are, and you have the power to embrace a fulfilling life despite the prognosis.
While statistics may indicate a challenging prognosis, they do not account for the individual’s resilience, determination, and willpower to live. Many individuals with stage 4 bile duct cancer have defied the odds and lived for years beyond their expected survival time.
One way to maintain a positive outlook is by focusing on self-care practices. This may include engaging in physical activities you enjoy, meditation, or spending time in nature. It’s also crucial to build a support network of family, friends, and medical professionals who are there to provide emotional and physical support.
Finding joy in small moments can also make a significant difference in coping with the diagnosis. This may include spending time with loved ones, pursuing a hobby, or trying new experiences. Additionally, exploring complementary therapies, such as acupuncture or massage, can provide various benefits, including stress reduction and pain relief.
It’s important to take things one step at a time and not let fear dominate your life. Embracing a fulfilling life in the face of stage 4 bile duct cancer may not be easy, but it is possible. Remember, a diagnosis does not define you, and there is hope for a bright future.
FAQ
What is stage 4 bile duct cancer?
Stage 4 bile duct cancer is an advanced stage of the disease, indicating that the cancer has spread to other organs or distant lymph nodes. It is considered the most severe stage.
How is stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosed?
Stage 4 bile duct cancer is typically diagnosed through imaging tests such as CT scans and MRIs, as well as biopsies and staging examinations.
What factors can affect life expectancy in stage 4 bile duct cancer?
Several factors can influence life expectancy in stage 4 bile duct cancer, including age, overall health, tumor characteristics, and how well the patient responds to treatment.
What are the survival rates for stage 4 bile duct cancer?
Survival rates can vary from person to person, but studies suggest that the average survival time for individuals with stage 4 bile duct cancer is generally low. It’s important to keep in mind that each case is unique.
What are the treatment options for stage 4 bile duct cancer?
Treatment options for stage 4 bile duct cancer may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the patient’s overall health and the extent of the cancer.
What palliative and supportive care options are available for stage 4 bile duct cancer?
Palliative and supportive care aims to enhance the quality of life for individuals with stage 4 bile duct cancer. These options include pain management, emotional support, nutrition counseling, and rehabilitation programs.
Are there any clinical trials or experimental treatments for stage 4 bile duct cancer?
Clinical trials and experimental treatments offer potential options for individuals who have not responded well to traditional treatments. It is important to consider participating in a clinical trial carefully and discuss the potential benefits and risks with a healthcare professional.
How can side effects and complications of treatment in stage 4 bile duct cancer be managed?
Managing side effects and complications may involve medications, lifestyle adjustments, and supportive care services. Patients need to communicate openly with their healthcare team to address any concerns or symptoms they may experience.
What are some coping strategies for dealing with a stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosis?
Coping with a stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosis can be challenging. Seeking emotional support, practicing self-care, and exploring complementary therapies are some strategies that can help individuals cope with the emotional and physical demands of the diagnosis.
Are there any inspiring stories of stage 4 bile duct cancer survivors?
Yes, some individuals have defied the odds and experienced long-term survival with stage 4 bile duct cancer. These inspiring stories provide hope and motivation for others facing a similar diagnosis.
Is it important to seek medical advice and second opinions for stage 4 bile duct cancer?
Yes, seeking proper medical advice and considering second opinions are crucial when dealing with a stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosis. Reputable medical professionals can provide guidance and offer different perspectives on treatment options.
How can individuals embrace a fulfilling life despite a stage 4 bile duct cancer diagnosis?
Despite the prognosis, individuals need to focus on living a meaningful and fulfilling life. Engaging in self-care practices, building a support network, and finding joy in small moments can help individuals embrace life in the face of stage 4 bile duct cancer.