Stagescancer.net – Recurrence of lung cancer after undergoing a lobectomy is a significant concern for patients and healthcare professionals alike. Despite the successful removal of cancerous cells through this surgical procedure, there is always a risk of the disease returning. In this article, we will provide an in-depth exploration of this topic, delving into the factors contributing to lung cancer recurrence, the importance of early detection, available treatment options, and emerging developments in the field.
A lobectomy is a common treatment approach for lung cancer, involving the removal of a lobe of the lung containing the tumor. While this procedure aims to eliminate cancerous cells and improve patient outcomes, it is crucial to understand the potential for cancer recurrence. Various factors play a role in the likelihood of recurrence, including smoking history, tumor stage, and genetic factors.
Early detection plays a crucial role in managing lung cancer recurrence after lobectomy. Regular follow-up appointments and surveillance through diagnostic imaging techniques such as CT scans, PET scans, and MRIs aid in identifying any signs of recurrence. Recognizing the symptoms of recurrence, such as persistent cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath, is also essential in prompt detection.
Once lung cancer recurrence is confirmed, several treatment options are available depending on individual circumstances. These may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Additionally, the emerging field of personalized medicine provides hope through tailored treatment approaches based on genetic testing and targeted therapies.
Prevention of lung cancer recurrence after lobectomy extends beyond medical interventions. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including smoking cessation, regular exercise, and a balanced diet, can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence. Supportive care and rehabilitation services are also vital in managing the physical and emotional challenges that may arise after recurrence.
This article aims to inform and empower individuals at risk of lung cancer recurrence after lobectomy, highlighting the importance of ongoing follow-up care and vigilance. By staying informed about the latest research efforts and future directions, patients and caregivers can make well-informed decisions and contribute to their well-being.
In conclusion, understanding the recurrence of lung cancer after lobectomy is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. By addressing the various aspects surrounding this topic, we strive to provide valuable insights and resources to ensure the best possible outcomes for individuals facing this challenge.
Understanding Lung Cancer Recurrence
To effectively manage and treat lung cancer, it is crucial to understand the concept of lung cancer recurrence. When discussing lung cancer, recurrence refers to the return of cancer cells or the regrowth of a tumor after an initial treatment. This can happen in the same part of the lung where the cancer first occurred or in a different area of the lung.
Lung cancer recurrence is a concern for individuals who have undergone a lobectomy, a surgical procedure to remove a lobe of the lung where the cancer was localized. While lobectomy is often successful in removing the tumor, there is still a risk that cancer cells may recur.
The exact causes of lung cancer recurrence are complex and not fully understood. However, several factors may contribute to the development of recurrent lung cancer, including:
- Persistence of microscopic cancer cells left behind after surgery
- Invasion of cancer cells into nearby lymph nodes or blood vessels
- Inadequate surgical margins, where cancer cells are not completely removed
- Presence of undetectable cancer cells that have spread to other parts of the body
It is important to note that not all lung cancer recurrences can be attributed to the same factors, and each case is unique. Therefore, it is essential for individuals who have undergone lobectomy to receive regular follow-up care and surveillance to detect and monitor any signs of lung cancer recurrence.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of lung cancer recurrence, it is essential to explore the risk factors, early detection methods, treatment options, and ongoing care for individuals who are at risk. The subsequent sections of this article will delve into these topics in detail, providing valuable insights to empower patients and healthcare professionals in their efforts to combat and manage recurrent lung cancer.
Lobectomy for Lung Cancer Treatment
Lobectomy is a commonly performed surgical procedure used for the treatment of lung cancer. In this procedure, the surgeon removes the affected lobe of the lung, where the tumor is located, to eliminate the cancerous cells.
The effectiveness of lobectomy in treating lung cancer has been well-established. It not only helps in removing the tumor but also reduces the risk of cancer recurrence in the treated area. This procedure is often recommended for patients with early-stage lung cancer, where the tumor is confined to a specific lobe of the lung.
During a lobectomy, the surgeon makes an incision in the chest wall to gain access to the lungs. The affected lobe is then carefully dissected and removed, along with nearby lymph nodes to check for the spread of cancer. The remaining lobes of the lung take over the function of the removed lobe, allowing the patient to breathe normally.
For a better understanding, let’s take a look at the following table, which summarizes the benefits and potential risks associated with lobectomy:
| Benefits of Lobectomy | Potential Risks |
|---|---|
| – Removal of cancerous cells | – Bleeding |
| – Reduced risk of cancer recurrence | – Infection |
| – Restores lung function | – Air leakage from the lung |
| – Improved prognosis | – Chest pain |
It’s important to note that lobectomy may not be suitable for all patients, especially those with advanced-stage lung cancer or underlying health conditions that pose a high surgical risk. In such cases, alternative treatment options, such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy, may be considered.
In the next section, we will explore the factors that contribute to the recurrence of lung cancer after a lobectomy, providing a deeper understanding of this critical aspect of treatment.
Factors Contributing to Lung Cancer Recurrence
After undergoing a lobectomy for lung cancer, it is crucial to be aware of the various factors that can increase the chances of cancer recurrence. Understanding these risk factors can help patients and healthcare providers develop personalized strategies for long-term management and surveillance.
1. Smoking History
Smoking remains the leading cause of lung cancer, and it significantly impacts the risk of cancer recurrence after lobectomy. Research has shown that current or former smokers have a higher likelihood of cancer recurrence compared to non-smokers. Quitting smoking before surgery has been found to reduce the risk of recurrence, highlighting the importance of smoking cessation as part of post-lobectomy care.
2. Tumor Stage
The stage of the initial lung cancer diagnosis plays a crucial role in determining the risk of recurrence. Higher stages, such as stage III or IV, are associated with a greater likelihood of cancer coming back after lobectomy. The size of the tumor, lymph node involvement, and metastasis to other organs also contribute to the risk of recurrence.
3. Genetic Factors
Genetic factors can influence the risk of lung cancer recurrence. Certain genetic mutations, such as EGFR and ALK alterations, have been linked to a higher likelihood of cancer recurrence after surgery. Identifying these genetic abnormalities through molecular testing can help tailor treatment plans and surveillance strategies for patients.
4. Adjuvant Therapy
The use of adjuvant therapy, such as chemotherapy or radiation, after lobectomy can significantly reduce the risk of cancer recurrence. Patients who do not receive appropriate adjuvant therapy based on their tumor characteristics may be at a higher risk of recurrence. Tailoring treatment plans based on individual patient factors is essential to minimize the chances of cancer coming back.
5. Surgical Margins
The completeness of surgical removal, known as negative surgical margins, is an important factor in preventing cancer recurrence. A study by Johnson et al. found that patients with positive surgical margins had a higher recurrence rate compared to those with negative margins. Ensuring adequate resection and clear margins during lobectomy is crucial in minimizing the risk of cancer recurrence.
6. Post-Operative Care
The post-operative care and follow-up provided to patients after lobectomy can also impact the risk of lung cancer recurrence. Close monitoring, regular check-ups, and timely imaging studies can help detect any signs of recurrence at an early stage, improving treatment outcomes. Health promotion activities such as smoking cessation, regular exercise, and healthy eating habits are also important in reducing the risk of recurrence.
| Risk Factors | Impact on Lung Cancer Recurrence |
|---|---|
| Smoking History | Increases the risk of recurrence |
| Tumor Stage | Higher stages have a greater risk of recurrence |
| Genetic Factors | Specific mutations can contribute to recurrence risk |
| Adjuvant Therapy | Appropriate use reduces the risk of recurrence |
| Surgical Margins | Clear margins lower the risk of recurrence |
| Post-Operative Care | Regular monitoring and health promotion activities can reduce the risk of recurrence |
By understanding the factors contributing to lung cancer recurrence after lobectomy, both patients and healthcare providers can work together to minimize the risk and develop effective long-term management plans.
Early Detection of Lung Cancer Recurrence
Early detection plays a crucial role in identifying the recurrence of lung cancer after a lobectomy. Regular monitoring and diagnostic tests are essential to detect any signs of cancer recurrence at the earliest stage possible. By detecting recurrence early, healthcare professionals can develop an appropriate treatment plan and improve patient outcomes.
Diagnostic Tools and Tests
Several diagnostic tools and tests are used to monitor patients who have undergone a lobectomy for lung cancer. These tests help identify any potential signs of recurrence and allow for timely intervention. Some common diagnostic tools and tests used for early detection of lung cancer recurrence include:
- Chest X-rays: A chest X-ray is a simple and non-invasive test that can provide an initial indication of any abnormalities in the lung area.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans: CT scans provide detailed images of the chest and can detect tiny nodules or other abnormalities that may indicate cancer recurrence.
- PET-CT scans: A PET-CT scan combines positron emission tomography (PET) and computed tomography (CT) to produce images that can identify areas of abnormal metabolic activity in the body.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to detect specific tumor markers or evaluate the overall health of the patient, providing valuable information about the possibility of cancer recurrence.
These diagnostic tools and tests, along with regular follow-up appointments and thorough physical examinations, enable healthcare professionals to closely monitor patients and detect any signs of lung cancer recurrence as early as possible.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer Recurrence
After undergoing a lobectomy for lung cancer, it is essential to stay vigilant for any signs of recurrence. Recognizing the symptoms of lung cancer recurrence can help individuals seek timely medical attention and potentially improve treatment outcomes. The following are some common symptoms that may indicate the recurrence of lung cancer:
- Cough: A persistent or worsening cough that lasts for a prolonged period can be a cause for concern.
- Chest pain: Any unexplained chest pain, especially if it is accompanied by difficulty breathing or coughing up blood, should be evaluated promptly.
- Shortness of breath: If you experience sudden or progressive shortness of breath, it could be indicative of lung cancer recurrence.
- Unexplained weight loss: A significant and unexplained weight loss may be a symptom of cancer recurrence.
- Fatigue: Persistent fatigue or weakness that affects your daily activities could be a sign of recurrent lung cancer.
- Hoarseness: Changes in your voice, such as hoarseness or persistent throat irritation, should not be overlooked.
- Recurrent infections: Frequent respiratory infections or pneumonia may suggest a compromised immune system due to cancer recurrence.
It is important to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to lung cancer recurrence and can be caused by other factors as well. However, if you have undergone a lobectomy for lung cancer, any new or persistent symptoms should be discussed with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and appropriate course of action.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Cough | A persistent or worsening cough that lasts for a prolonged period. |
| Chest pain | Unexplained chest pain, especially if accompanied by difficulty breathing or coughing up blood. |
| Shortness of breath | Sudden or progressive shortness of breath. |
| Unexplained weight loss | Significant and unexplained weight loss. |
| Fatigue | Persistent fatigue or weakness that affects daily activities. |
| Hoarseness | Changes in voice, such as hoarseness or persistent throat irritation. |
| Recurrent infections | Frequent respiratory infections or pneumonia. |
Diagnostic Imaging for Lung Cancer Recurrence
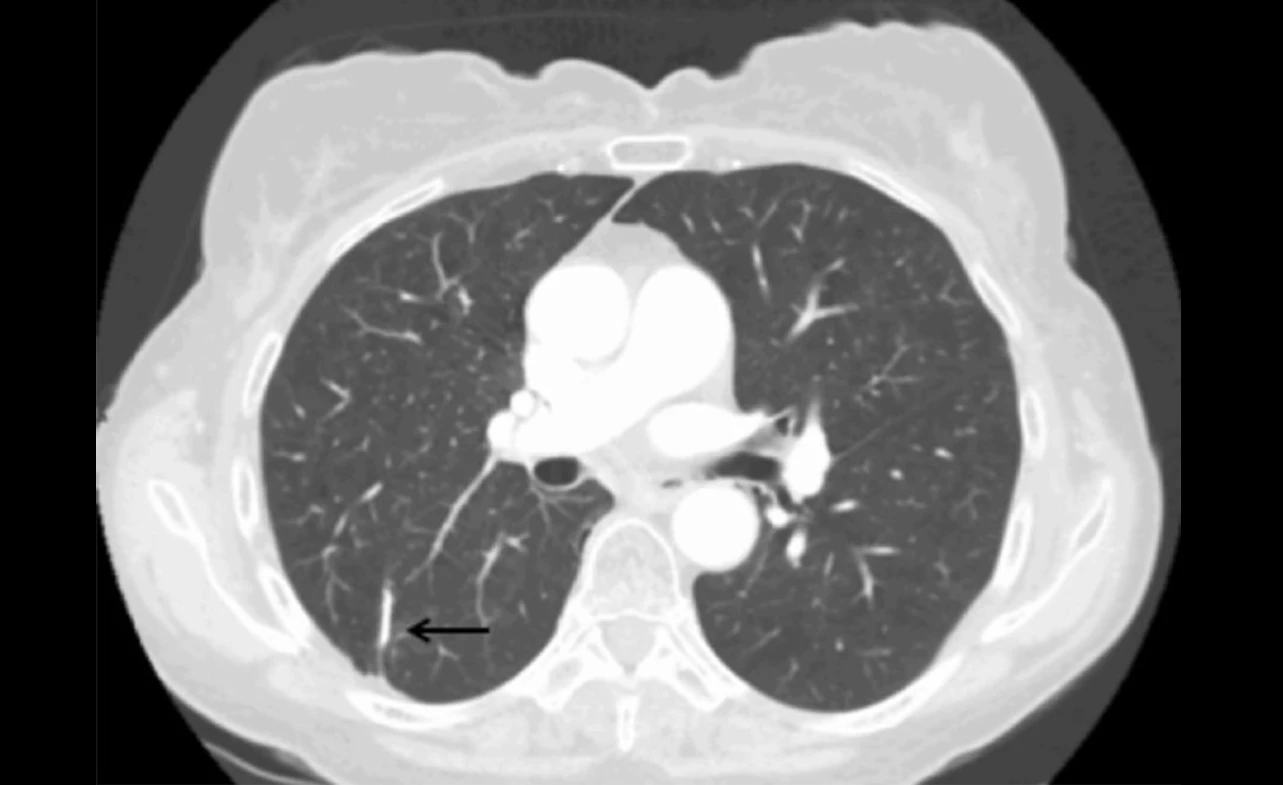
Accurate and timely diagnosis of lung cancer recurrence plays a crucial role in planning effective treatment strategies. Diagnostic imaging techniques offer valuable insights into detecting recurrent tumors and evaluating their extent. Various imaging modalities, including computed tomography (CT) scans, positron emission tomography (PET) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are employed to visualize lung cancer recurrence and guide appropriate interventions.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans utilize X-rays and computer technology to create detailed cross-sectional images of the lungs. These scans can identify abnormal growths, tumors, or lesions, providing vital information about the presence and location of lung cancer recurrence. CT scans are particularly useful for assessing the size, shape, and structure of tumors, aiding in treatment planning.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans: PET scans involve the injection of a small amount of radiopharmaceutical, which emits positrons that are detected by a special camera. By highlighting areas of increased metabolic activity, PET scans can help identify cancerous cells and distinguish them from noncancerous tissues. This imaging technique is valuable for detecting lung cancer recurrence and assessing its spread to other parts of the body.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to generate detailed images of the body’s internal structures. By providing high-resolution images, MRI can aid in the detection of lung cancer recurrence and provide valuable information about tumor size, location, and invasion of surrounding tissues. Additionally, MRI is particularly useful for assessing the involvement of mediastinal lymph nodes.
While these imaging techniques provide valuable diagnostic information, they also have certain limitations. CT scans, PET scans, and MRIs may not always accurately distinguish between recurrent tumors and benign scar tissue or inflammation. False-positive and false-negative results are possible, requiring careful interpretation by experienced radiologists. Further, different imaging modalities have varying sensitivity and specificity in detecting lung cancer recurrence. Therefore, a combination of these imaging techniques and clinical assessments is often necessary for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Treatment Options for Recurrent Lung Cancer
After a lobectomy, it is important to consider the different treatment options available for recurrent lung cancer. These options aim to control the cancer, manage symptoms, and potentially improve overall survival. Treatment plans for recurrent lung cancer often involve a combination of therapies tailored to individual patients.
Common treatment options for recurrent lung cancer after a lobectomy include:
- Chemotherapy: This systemic treatment uses drugs to target and destroy cancer cells throughout the body. Chemotherapy may be administered orally, intravenously, or through a combination of both.
- Radiation Therapy: This localized treatment uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. It can be delivered externally or internally, depending on the specific case.
- Targeted Therapy: These drugs are designed to target and block specific molecules or genetic changes within cancer cells, preventing their growth and spread. Targeted therapy is often used in cases where specific gene mutations are present.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment harnesses the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Immunotherapy drugs can help enhance the immune response and slow down the growth of cancer.
Personalized treatment plans for recurrent lung cancer may involve a combination of these therapies, determined by factors such as the stage of cancer, the individual’s overall health, and the genetic profile of the tumor.
Personalized Medicine in Lung Cancer Recurrence
As the field of oncology continues to advance, personalized medicine has emerged as a game-changer in managing lung cancer recurrence. Rather than taking a one-size-fits-all approach, personalized medicine tailors treatment strategies based on individual patient characteristics and genetic profiles. By understanding the specific genetic mutations associated with lung cancer recurrence, healthcare providers can offer targeted therapies that have the potential to improve outcomes and increase survival rates.
One of the key components of personalized medicine in lung cancer recurrence is genetic testing. This process involves analyzing a patient’s tumor tissue or blood sample to identify specific genetic mutations or alterations that may be driving the cancer’s growth. Armed with this information, healthcare professionals can determine the most effective treatment options, such as targeted therapies that specifically target and inhibit the action of these genetic abnormalities.
The integration of personalized medicine into the management of lung cancer recurrence has shown promising results. Through the identification of actionable genetic alterations, patients can receive treatments that directly target the underlying driver of their cancer, leading to improved response rates and prolonged survival. Not only does this approach offer more effective treatment options, but it also helps to minimize unnecessary treatments and potential side effects.
To better understand the impact of personalized medicine on lung cancer recurrence, let’s explore a case study:
| Patient | Genetic Mutation | Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mr. Smith | EGFR mutation | EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor | Complete remission, no evidence of recurrence after 2 years |
| Ms. Johnson | ALK fusion | ALK inhibitor | Partial response, stable disease for 1 year |
| Mr. Rodriguez | ROS1 rearrangement | ROS1 inhibitor | Partial response, stable disease for 9 months |
This table highlights how personalized medicine has revolutionized the treatment of lung cancer recurrence. By matching specific genetic alterations with targeted therapies, patients are experiencing improved outcomes and prolonged survival.
The future of managing lung cancer recurrence lies in the continued development and application of personalized medicine. Through ongoing research and advancements in genetic profiling and targeted therapies, healthcare providers strive to offer tailored treatment options that precisely address the underlying causes of lung cancer recurrence. This individualized approach has the potential to transform the landscape of lung cancer treatment, providing new hope and improved outcomes for patients.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Lung Cancer Recurrence Risk
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of lung cancer recurrence after a lobectomy. Making specific lifestyle changes can help improve overall well-being and reduce the chances of cancer cells returning. Incorporating the following habits into your daily routine can significantly contribute to lowering the risk:
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking is one of the most impactful lifestyle changes you can make to reduce the risk of lung cancer recurrence. Seek support from healthcare professionals, join smoking cessation programs, or use nicotine replacement therapies to increase your chances of success.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can play a significant role in improving lung function and overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Consult with your healthcare team to determine the most suitable exercise routine for your specific needs.
- Healthy diet: Consuming a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can boost your immune system and provide essential nutrients for optimal health. Limit processed foods, unhealthy fats, and sugary snacks, and drink alcohol in moderation or avoid it altogether.
- Avoidance of environmental toxins: Minimize exposure to harmful substances, such as secondhand smoke, asbestos, and air pollution. Take necessary precautions and follow safety guidelines if you work in or live close to environments with potential carcinogens.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can hurt your overall health and immune system function. Explore stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or seeking support from a mental health professional.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of lung cancer recurrence after a lobectomy and improve your overall health and well-being. It is important to remember that these lifestyle changes should be discussed with your healthcare team to ensure they align with your specific medical condition and treatment plan.
Supportive Care and Rehabilitation After Lung Cancer Recurrence
Supportive care and rehabilitation play a crucial role in the management of patients dealing with lung cancer recurrence after a lobectomy. These services are designed to improve quality of life, alleviate symptoms, and assist in the physical and emotional recovery process. By providing comprehensive support, both patients and their caregivers can navigate the challenges associated with lung cancer recurrence more effectively.
Importance of Supportive Care
Supportive care encompasses a range of services that address the unique needs of patients facing lung cancer recurrence. It focuses on managing symptoms and side effects, ensuring optimal pain control, promoting emotional well-being, and enhancing overall quality of life. Some essential components of supportive care include:
- Physical therapy to restore strength, flexibility, and mobility
- Psychotherapy and counseling to address emotional and psychological needs
- Nutritional support and dietary guidance to maintain a balanced and healthy diet
- Pain management strategies to alleviate discomfort
- Palliative care to improve symptom control and enhance comfort
Rehabilitation Services
Rehabilitation services focus on restoring physical function and improving overall well-being after lung cancer recurrence. These services are tailored to the specific needs of each patient, considering their overall health, treatment history, and individual goals. Some common rehabilitation interventions include:
- Exercise programs to enhance cardiovascular fitness and muscle strength
- Respiratory therapy to optimize lung function and reduce respiratory complications
- Occupational therapy to regain independence in daily activities
- Speech therapy to address speech and swallowing difficulties
By participating in supportive care and rehabilitation programs, patients can experience a multitude of benefits, including:
- Improved physical functioning and reduced disability
- Enhanced emotional well-being and psychological resilience
- Better symptom management and quality of life
- Increased social support and connection with others
Healthcare providers need to assess each patient’s specific needs and tailor the supportive care and rehabilitation interventions accordingly. By addressing the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of lung cancer recurrence, these services can significantly contribute to improving the overall well-being of patients and their successful recovery.
Coping Strategies for Patients and Caregivers
Dealing with the recurrence of lung cancer after a lobectomy can be emotionally and mentally challenging for both patients and their caregivers. Coping strategies and support resources can play a vital role in helping individuals navigate these difficulties and maintain their overall well-being.
1. Seek Emotional Support
Patients and caregivers need to seek emotional support during this difficult time. Joining support groups, either in-person or online, can provide a safe space to share experiences, gain insights from others in similar situations, and receive emotional support.
2. Practice Self-Care
Taking care of one’s physical and mental health is crucial when coping with the recurrence of lung cancer. Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as exercise, meditation, or pursuing hobbies, can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
3. Communicate Openly
Open and honest communication with healthcare providers, family members, and friends is key in coping with lung cancer recurrence. Expressing fears, concerns, and needs can strengthen support networks and facilitate better understanding and empathy from loved ones.
4. Educate Yourself
Understanding the nature of lung cancer recurrence and its treatment options can empower patients and caregivers. Stay informed about the latest research and developments in the field, and ask healthcare professionals for reliable resources and educational materials.
5. Create a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive environment at home can make a significant difference in coping with lung cancer recurrence. Ensure that the physical space is comfortable, well-organized, and conducive to relaxation. Encourage open communication and provide a caring and understanding atmosphere for all family members.
6. Access Professional Help
Seeking professional help, such as therapy or counseling, can provide valuable guidance and support in coping with the emotional and mental challenges of lung cancer recurrence. Mental health professionals can offer specialized coping strategies and help individuals develop effective coping mechanisms.
7. Take Breaks
Caring for a loved one with recurrent lung cancer can be physically and emotionally draining. Caregivers need to take breaks and prioritize their well-being. Respite care, where trained professionals provide temporary care for the patient, can offer much-needed relief and time for self-care.
By implementing these coping strategies and utilizing available support resources, patients and caregivers can better navigate the emotional and mental challenges associated with lung cancer recurrence. Remember, reaching out for help is a sign of strength and can greatly enhance the overall well-being and resilience of individuals facing this difficult situation.
| Coping Strategies for Patients and Caregivers | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Seek Emotional Support | – Provides a safe space for sharing experiences – Offers emotional support and understanding |
| Practice Self-Care | – Reduces stress and improves overall well-being – Enhances resilience and coping abilities |
| Communicate Openly | – Strengthens support networks – Fosters empathy and understanding from loved ones |
| Educate Yourself | – Empowers patients and caregivers with knowledge – Facilitates informed decision-making |
| Create a Supportive Environment | – Enhances overall well-being for all family members – Encourages open communication and understanding |
| Access Professional Help | – Provides specialized coping strategies and guidance – Supports the development of effective coping mechanisms |
| Take Breaks | – Enables caregivers to prioritize their well-being – Offers respite and relief from caregiving responsibilities |
Follow-up Care and Surveillance After Lung Cancer Recurrence
To effectively monitor for lung cancer recurrence after a lobectomy, regular follow-up care and surveillance are essential. These measures play a crucial role in ensuring early detection and prompt intervention, improving outcomes for patients. Ongoing medical evaluations and tests are key components of this follow-up process.
During follow-up care appointments, healthcare professionals closely monitor patients for any signs or symptoms of recurrent lung cancer. These appointments provide an opportunity to assess the patient’s overall health, discuss any concerns or questions, and create a personalized plan for ongoing surveillance.
Surveillance typically involves various diagnostic tests and imaging procedures, such as CT scans, PET scans, and blood tests. These tools allow doctors to closely monitor the patient’s lung health, detect any potential cancerous activity, and determine the appropriate course of action.
In addition to medical evaluations and imaging, follow-up care also includes discussions about lifestyle modifications and support services. Patients are encouraged to adopt healthy habits, such as smoking cessation, regular exercise, and a balanced diet, which can help reduce the risk of recurrence. Supportive care services, including counseling and rehabilitation, can also play a vital role in managing the physical and emotional challenges associated with recurrent lung cancer.
By emphasizing the importance of regular follow-up care and surveillance, healthcare professionals can ensure that patients receive the necessary support and interventions to effectively manage lung cancer recurrence after a lobectomy. Through ongoing medical evaluations, diagnostic tests, and a holistic approach to care, the chances of early detection and successful treatment can be significantly improved.
Latest Research and Future Directions in Lung Cancer Recurrence
Research in the field of lung cancer recurrence after lobectomy continues to shed light on new insights and potential future directions for treatment and prevention. Ongoing studies aim to improve patient outcomes and enhance our understanding of the underlying mechanisms of recurrence.
Advancements in Biomarkers Research
One area of focus in current research is the identification and validation of biomarkers that can help predict the risk of lung cancer recurrence. By analyzing specific genetic, epigenetic, or protein markers, researchers aim to develop personalized approaches to managing lung cancer recurrence.
Immunotherapies and Targeted Therapies
Advances in immunotherapies and targeted therapies are also providing hope for patients with recurrent lung cancer. Clinical trials are underway to explore the efficacy of new immunotherapy agents and targeted therapies in treating lung cancer recurrence after lobectomy.
Artificial Intelligence in Recurrence Prediction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in predicting lung cancer recurrence. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of patient data to identify patterns and develop models that can accurately predict the likelihood of recurrence, aiding in personalized treatment plans.
Preventive Strategies
Researchers are actively investigating preventive strategies to reduce the risk of lung cancer recurrence. This includes evaluating lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes, exercise programs, and smoking cessation interventions to minimize the chances of recurrence.
Collaborative Efforts and Multidisciplinary Approaches
The future of lung cancer recurrence research lies in collaborative efforts among experts from various disciplines. By fostering multidisciplinary partnerships, researchers can explore innovative approaches, share knowledge, and advance our understanding of lung cancer recurrence.
Potential Future Directions
While research is ongoing, future directions in the field of lung cancer recurrence may include:
- Leveraging genomic profiling to identify mutations associated with resistance to treatment
- Developing novel therapeutic strategies to target residual cancer cells
- Exploring the role of epigenetic modifications in driving recurrence
- Investigating the impact of the tumor microenvironment on recurrence
| Advancements | Implications |
|---|---|
| Improved biomarker identification | Predictive tools for personalized treatment plans |
| Advances in immunotherapies and targeted therapies | Potential for more effective and tailored treatments |
| Integration of AI in recurrence prediction | Enhanced accuracy in prognosis and treatment decisions |
| Preventive strategies | Reduced risk of lung cancer recurrence |
| Multidisciplinary collaborations | A holistic approach to understanding and managing recurrence |
Conclusion
After exploring the various aspects of lung cancer recurrence after lobectomy, it is evident that vigilance and ongoing care are crucial for individuals at risk. The potential for lung cancer to recur following a lobectomy highlights the importance of early detection and regular follow-up care.
Factors such as smoking history, tumor stage, and genetic factors play a significant role in determining the risk of recurrence. Diagnostic imaging techniques, such as CT scans and PET scans, aid in detecting any signs of recurrence, allowing for prompt intervention and treatment.
Treatment options for recurrent lung cancer include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. The evolving field of personalized medicine, with its focus on targeted therapies and genetic testing, provides hope for improved outcomes in managing lung cancer recurrence.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including smoking cessation, regular exercise, and a balanced diet, can help reduce the risk of recurrence. Additionally, supportive care and rehabilitation services play a vital role in enhancing quality of life and managing side effects.
In conclusion, understanding the risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic tools, treatment options, and the importance of ongoing care is essential in the management of lung cancer recurrence after lobectomy. By staying vigilant and following a comprehensive care plan, individuals can optimize their chances of early detection and successful treatment.
FAQ
What is the recurrence of lung cancer after lobectomy?
Recurrence of lung cancer after lobectomy refers to the reappearance of cancer cells in the lung or nearby tissues following the surgical removal of a lobe of the lung. It is a challenging situation that requires ongoing monitoring and treatment.
Why does lung cancer recurrence happen?
Lung cancer recurrence can occur due to various factors, including the presence of residual cancer cells in the body, incomplete removal of the tumor during surgery, the spread of cancerous cells to other parts of the body, or the development of new cancerous growths in the lungs.
What is lobectomy, and how is it used in lung cancer treatment?
Lobectomy is a surgical procedure in which a lobe of the lung, or a portion of it, is removed to treat lung cancer. It is commonly used for localized tumors or early-stage lung cancer, aiming to eliminate the cancerous cells and prevent further spread.
What are the risk factors for lung cancer recurrence after lobectomy?
Several risk factors can contribute to the recurrence of lung cancer after lobectomy. These include a history of smoking, advanced stage of the tumor at the time of diagnosis, the presence of certain genetic mutations, and inadequate follow-up care and surveillance.
How is the recurrence of lung cancer detected early?
Early detection of lung cancer recurrence after lobectomy is crucial for timely intervention. Diagnostic tools such as CT scans, PET scans, and regular medical evaluations are used to monitor patients and identify any signs of recurring cancer cells or new tumor growth.
What are the common symptoms of lung cancer recurrence?
The symptoms of lung cancer recurrence may vary from person to person, but common signs include persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and recurrent respiratory infections. It is important to report any concerning symptoms to healthcare professionals.
What imaging techniques are used for detecting lung cancer recurrence?
Diagnostic imaging plays a crucial role in detecting lung cancer recurrence. CT scans, PET scans, and MRIs are commonly used to obtain detailed images of the lungs and identify areas of concern. These imaging techniques help determine the extent and location of any recurrent cancerous growths.
What are the treatment options for recurrent lung cancer?
Treatment options for recurrent lung cancer after lobectomy may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy (such as medications that specifically target cancer cells), immunotherapy (which enhances the body’s immune system to fight cancer), or a combination of these treatments. The chosen approach depends on various factors, including the extent of recurrence and the individual’s overall health.
How does personalized medicine affect lung cancer recurrence treatment?
Personalized medicine is a rapidly advancing field that tailors medical treatment to an individual’s specific genetic makeup and other molecular characteristics. In the context of lung cancer recurrence, personalized medicine plays a role in identifying targeted therapies that can effectively treat specific genetic mutations or molecular alterations associated with the recurrence.
Can lifestyle changes reduce the risk of lung cancer recurrence?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help minimize the risk of lung cancer recurrence after lobectomy. Quitting smoking, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress are essential for overall well-being and can contribute to reducing the risk of recurrence.
What supportive care and rehabilitation services are available for patients after lung cancer recurrence?
Supportive care and rehabilitation services aim to improve the quality of life for patients dealing with lung cancer recurrence. These services may include pain management, counseling, pulmonary rehabilitation, nutritional support, and assistance with managing treatment side effects.
How can patients and caregivers cope with the challenges of lung cancer recurrence?
Coping with lung cancer recurrence can be emotionally and mentally challenging for patients and their caregivers. Various coping strategies, such as seeking support from loved ones, joining support groups, practicing relaxation techniques, and accessing counseling services, can help individuals navigate this difficult journey.
What is the importance of follow-up care and surveillance after lung cancer recurrence?
Regular follow-up care and surveillance are critical for monitoring lung cancer recurrence and detecting any new cancerous growth at an early stage. Ongoing medical evaluations, imaging tests, and other diagnostic procedures are essential to ensure timely intervention and appropriate management.
What are the latest research and future directions in lung cancer recurrence?
The field of lung cancer recurrence is an active area of research, with ongoing studies exploring novel treatment approaches, advancements in diagnostic imaging, and potential preventive strategies. The future holds promise for improved outcomes and better management of lung cancer recurrence.