Ovarian cysts are a common gynecological condition that most women experience at some point in their lives. While many cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, complex ovarian cysts require more attention due to their irregular structure and potential connection with cancer risk. Understanding the difference between simple and complex ovarian cysts is essential for early detection and proper medical care.
The concern about the complex ovarian cyst cancer risk is a significant issue for women’s health. Not all complex cysts are cancerous, but their presence can increase the chances of malignancy compared to simple cysts. This makes awareness, timely diagnosis, and treatment crucial in lowering the risks and ensuring better outcomes.
Definition and Overview
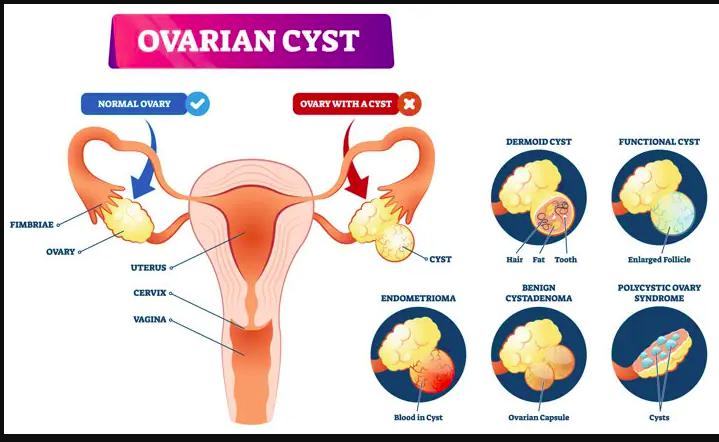
A complex ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that develops on or inside the ovary but contains both solid and liquid components. Unlike simple cysts, which are usually harmless and disappear over time, complex cysts often need closer monitoring. These cysts may be benign, precancerous, or malignant, which is why evaluating the cancer risk is a critical part of gynecological health care.
Types
Complex ovarian cysts are generally categorized into different types, including:
- Endometriomas: Often caused by endometriosis, containing blood and tissue.
- Dermoid cysts: Made up of various tissue types such as hair, fat, or bone.
- Cystadenomas: Can be filled with mucus or fluid and grow quite large.
- Hemorrhagic cysts: Formed when bleeding occurs within a cyst.
Each type has a different potential impact on a woman’s health and contributes differently to the overall cancer risk.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of complex ovarian cysts vary, but common factors include hormonal imbalances, endometriosis, pregnancy, and pelvic infections. Certain genetic predispositions, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, may also increase the likelihood of developing ovarian cancer. Age is another important risk factor, as women over 50 are more prone to malignant transformations.
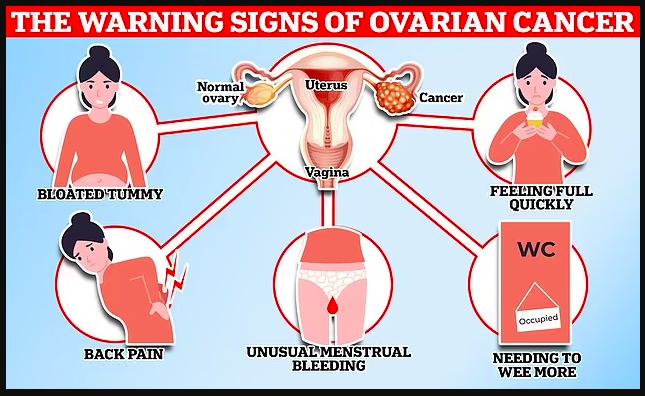
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Symptoms of complex ovarian cysts may not always be noticeable. However, some women may experience:
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Pain during intercourse
- Frequent urination or bowel changes
If these symptoms persist or worsen, medical evaluation is strongly recommended to rule out potential cancer risk.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing complex ovarian cysts usually involves imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans. Blood tests like CA-125 are also used to assess the likelihood of cancer. In some cases, laparoscopy or biopsy may be required to determine the exact nature of the cyst. Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in reducing the complex ovarian cyst cancer risk.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type, size, and symptoms of the cyst. Options may include:
- Watchful waiting for smaller, asymptomatic cysts
- Hormonal therapy to prevent recurrence
- Surgical removal (cystectomy or oophorectomy) for larger or suspicious cysts
- Chemotherapy or targeted therapy if cancer is detected
Individualized treatment plans are essential to balance effective care and fertility preservation.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all complex ovarian cysts can be prevented, adopting healthy lifestyle choices can lower risks. Regular gynecological check-ups, maintaining a healthy weight, managing hormonal imbalances, and avoiding smoking may help. Women with a family history of ovarian cancer should also consider genetic counseling for risk assessment.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for complex ovarian cysts largely depends on whether cancer is present. Benign cysts usually have excellent outcomes with minimal treatment. However, if malignant, early-stage detection significantly improves survival rates. With modern treatment options, many women diagnosed with ovarian cancer can achieve long-term remission.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent research is focusing on improving imaging techniques, genetic testing, and biomarkers to better predict complex ovarian cyst cancer risk. Advances in targeted therapy and immunotherapy are offering new hope for women diagnosed with ovarian cancer, potentially improving both survival rates and quality of life.
Coping and Support for Patients
Receiving a diagnosis of a complex ovarian cyst can be emotionally overwhelming. Support groups, counseling, and patient education play a vital role in helping women cope. Building a strong support system with family, friends, and healthcare professionals ensures emotional well-being alongside medical care.
Conclusion
Understanding complex ovarian cyst cancer risk is essential for early detection and effective treatment. While many complex cysts are benign, their potential connection to ovarian cancer should never be ignored. Regular check-ups, awareness of symptoms, and timely medical care are key factors in managing risks and improving women’s health outcomes.
FAQ
1. Are all complex ovarian cysts cancerous?
No, most complex ovarian cysts are benign, but they do carry a higher risk of malignancy compared to simple cysts.
2. How is cancer risk determined in complex ovarian cysts?
Doctors use imaging tests, blood markers like CA-125, and sometimes biopsies to evaluate the cancer risk.
3. Can complex ovarian cysts go away on their own?
Some may resolve naturally, but many require monitoring or treatment depending on size, type, and symptoms.
4. What age group is most at risk for ovarian cancer from cysts?
Women over 50 have a higher risk, especially those with genetic predispositions.
5. What lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of ovarian cyst complications?
Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, exercise, and avoiding smoking may help reduce risks.