Neuroendocrine cancer, often referred to as neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), is a rare and complex form of cancer that originates in the neuroendocrine cells. These cells are found throughout the body, acting as a bridge between the nervous and endocrine systems. While neuroendocrine cancer can be slow-growing, it can also be aggressive, leading to severe complications and, in some cases, death. But how does neuroendocrine cancer kill you? This article delves into the mechanisms, progression, and impact of this disease, offering a comprehensive understanding of its life-threatening nature.
Neuroendocrine tumors are often called “silent killers” because they can develop without noticeable symptoms for years. By the time they are diagnosed, the cancer may have already spread to other parts of the body, making treatment more challenging. The severity of neuroendocrine cancer depends on factors such as the tumor’s location, size, and whether it produces excess hormones. Understanding how this cancer progresses and its potential to become fatal is crucial for patients, caregivers, and anyone seeking to learn more about this condition.
What Is Neuroendocrine Cancer?
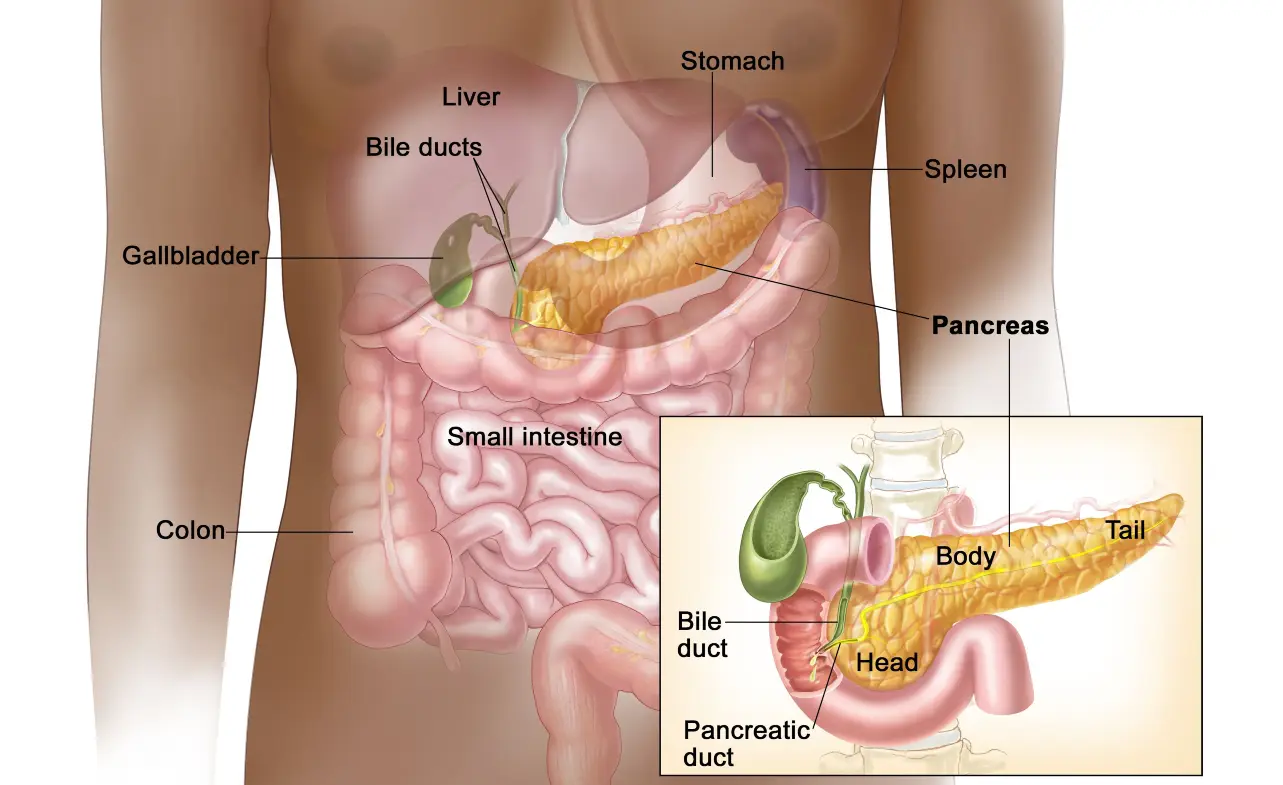
Neuroendocrine cancer arises from neuroendocrine cells, which are responsible for producing hormones and regulating various bodily functions. These tumors can develop in multiple organs, including the pancreas, lungs, intestines, and stomach. While some NETs are benign, others are malignant and can metastasize, spreading to other organs like the liver, bones, or lymph nodes.
Types of Neuroendocrine Tumors
Neuroendocrine tumors are classified based on their origin and behavior. Here are the primary types:
| Type of NET | Common Locations | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Carcinoid Tumors | Lungs, intestines | Often slow-growing; may cause carcinoid syndrome if they secrete hormones. |
| Pancreatic NETs | Pancreas | Can be functional (hormone-producing) or non-functional; may lead to insulinomas. |
| Pheochromocytomas | Adrenal glands | Rare tumors that produce excess adrenaline, causing high blood pressure and anxiety. |
| Merkel Cell Carcinoma | Skin | Aggressive and fast-growing; often linked to sun exposure and a weakened immune system. |
How Does Neuroendocrine Cancer Progress?
Neuroendocrine cancer progresses differently depending on the type and location of the tumor. Some tumors grow slowly and remain localized, while others spread rapidly. The progression of neuroendocrine cancer can be broken down into stages:
- Localized Stage: The tumor is confined to its original location and has not spread to nearby tissues or organs.
- Regional Stage: The cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or tissues.
- Metastatic Stage: The cancer has spread to distant organs, such as the liver, bones, or lungs.
When neuroendocrine cancer reaches the metastatic stage, it becomes significantly more dangerous. The spread of cancer cells to vital organs can disrupt their function, leading to life-threatening complications.
How Does Neuroendocrine Cancer Kill You?
Neuroendocrine cancer can be fatal due to several factors, including tumor growth, hormone overproduction, and organ failure. Here’s a closer look at how this disease can lead to death:
1. Tumor Growth and Organ Damage
As neuroendocrine tumors grow, they can invade and damage surrounding tissues and organs. For example, a tumor in the pancreas may impair its ability to produce digestive enzymes and insulin, leading to diabetes or malnutrition. Similarly, a tumor in the liver can disrupt its detoxification functions, causing toxins to accumulate in the body.
2. Hormonal Imbalances
Some neuroendocrine tumors produce excessive amounts of hormones, leading to severe hormonal imbalances. For instance, carcinoid tumors can cause carcinoid syndrome, characterized by symptoms like flushing, diarrhea, and heart damage. Over time, these symptoms can weaken the body and contribute to death.
3. Metastasis
When neuroendocrine cancer metastasizes, it often spreads to the liver, which plays a critical role in filtering blood and metabolizing nutrients. Liver metastasis can lead to liver failure, a condition that is often fatal if not treated promptly.
4. Complications from Treatment
While treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation can help manage neuroendocrine cancer, they can also cause complications. For example, surgery to remove a tumor may result in infections or bleeding, while chemotherapy can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections.
Symptoms That Signal Advanced Neuroendocrine Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of advanced neuroendocrine cancer is crucial for early intervention. Here are some common signs that the disease may have progressed:
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden and significant weight loss can indicate that the cancer is affecting your metabolism.
- Persistent Pain: Pain in the abdomen, chest, or bones may suggest that the tumor has spread.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes can signal liver involvement.
- Severe Fatigue: Extreme tiredness may result from hormonal imbalances or organ dysfunction.
- Difficulty Breathing: Lung involvement can cause shortness of breath or chronic coughing.
Can Neuroendocrine Cancer Be Treated?
Yes, neuroendocrine cancer can be treated, especially when diagnosed early. Treatment options depend on the tumor’s location, size, and stage. Common approaches include:
- Surgery: Removing the tumor is often the first line of treatment for localized NETs.
- Medications: Somatostatin analogs can help control hormone production and slow tumor growth.
- Radiation Therapy: This is used to target and shrink tumors, particularly in cases where surgery is not an option.
- Chemotherapy: For aggressive or metastatic NETs, chemotherapy may be recommended to kill cancer cells.
While these treatments can improve quality of life and extend survival, they may not always cure the disease, especially in advanced stages.
Preventing Neuroendocrine Cancer: Is It Possible?
Since the exact cause of neuroendocrine cancer is often unknown, prevention can be challenging. However, adopting a healthy lifestyle may reduce your risk. Here are some tips:
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking is linked to several types of cancer, including neuroendocrine tumors.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall health.
- Regular Check-Ups: Early detection through routine medical exams can improve outcomes.
Conclusion: Facing Neuroendocrine Cancer with Knowledge and Hope
Neuroendocrine cancer is a complex and potentially life-threatening disease that requires careful management. Understanding how it progresses and the factors that contribute to its lethality is essential for patients and their loved ones. While the journey can be daunting, advancements in medical research and treatment options offer hope for those affected by this condition.
Read more: