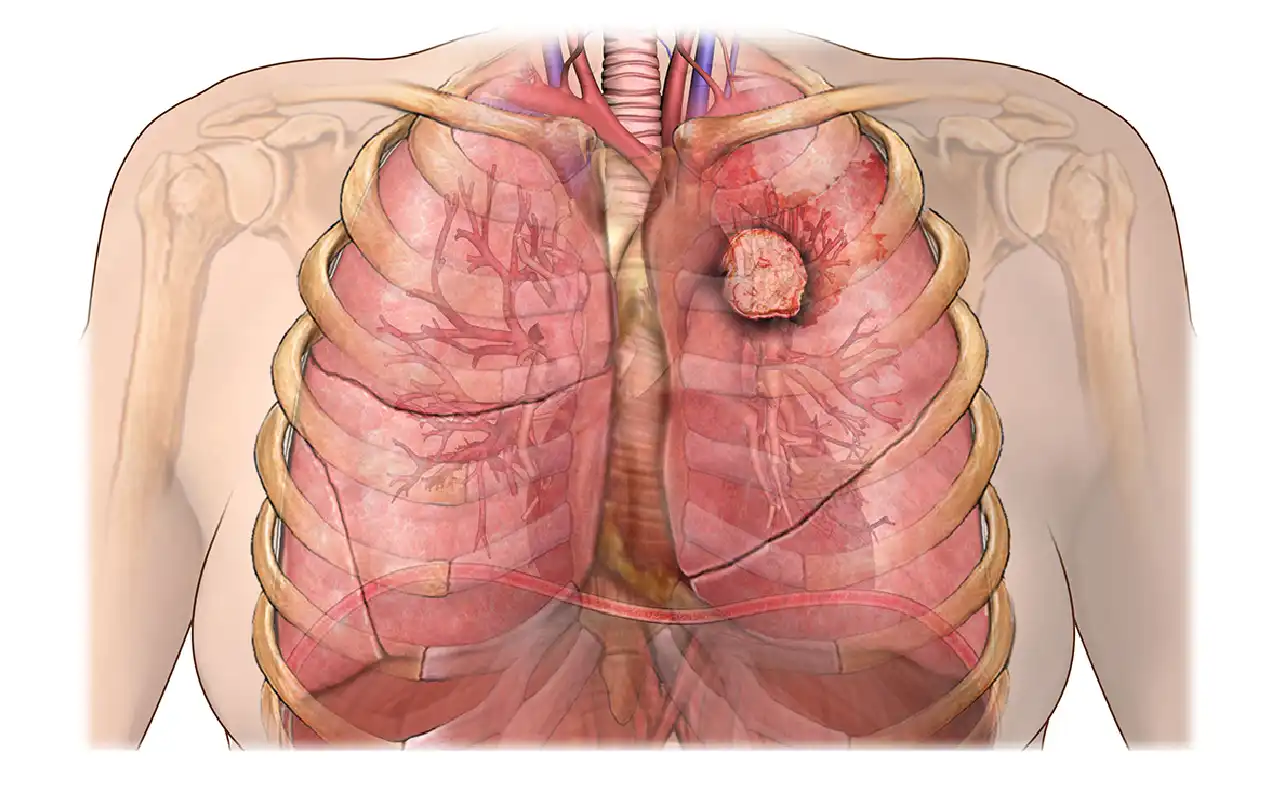
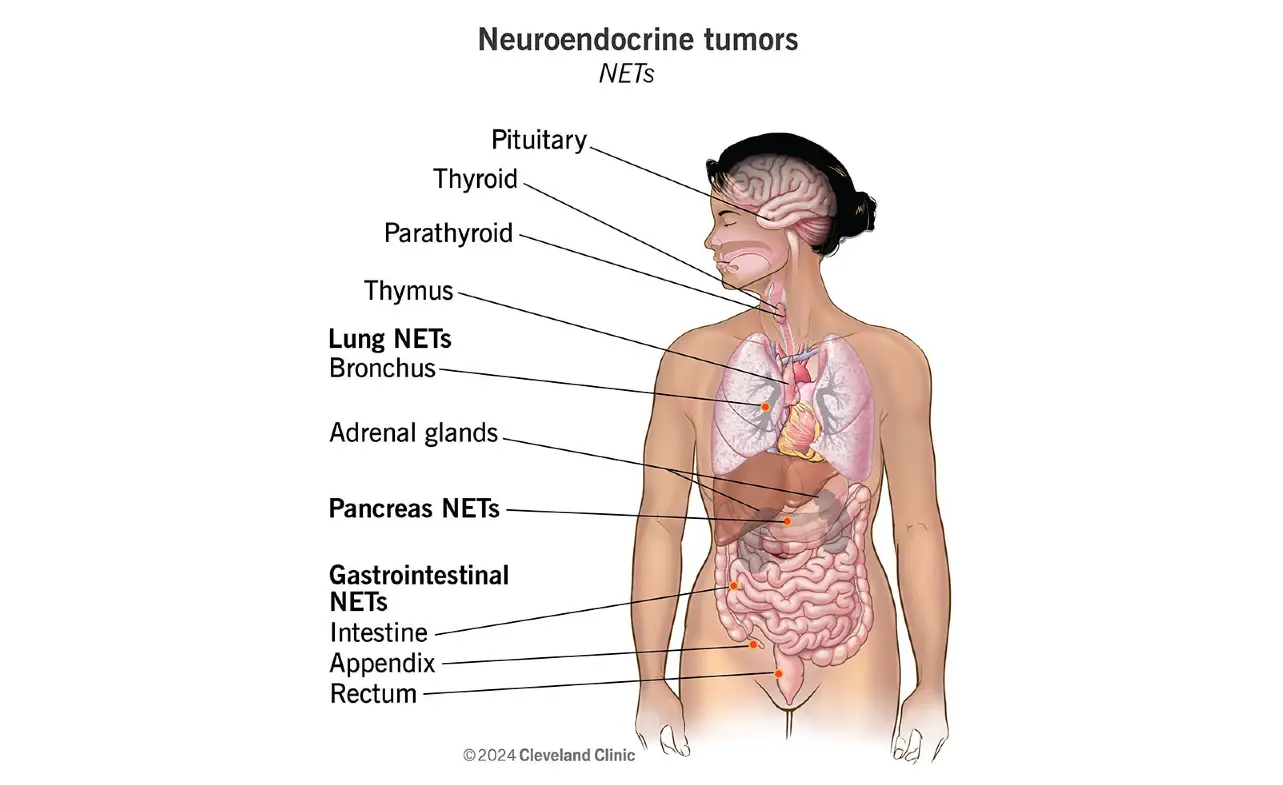
Neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer is a rare and complex form of lung cancer that often goes unnoticed until it reaches advanced stages. Unlike more common types of lung cancer, this condition originates from neuroendocrine cells, which are specialized cells that release hormones into the bloodstream. These cells are found throughout the body, including the lungs, and when they become cancerous, they can lead to a unique set of challenges for patients and healthcare providers alike.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into what neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer is, how it differs from other lung cancers, and what you need to know about its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Whether you’re a patient, a caregiver, or simply someone looking to learn more, this guide will provide you with clear, actionable information. So, let’s get started—what exactly is neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer, and why is it so different?
What Is Neuroendocrine Carcinoid Lung Cancer?
Neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer is a subtype of lung cancer that arises from neuroendocrine cells. These cells play a crucial role in regulating hormone production and are found in various organs, including the lungs. When these cells become cancerous, they form tumors that can be either slow-growing (typical carcinoids) or more aggressive (atypical carcinoids).
Unlike non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or small cell lung cancer (SCLC), neuroendocrine carcinoid tumors are relatively rare, accounting for only 1-2% of all lung cancers. However, their rarity doesn’t make them any less serious. In fact, because they often present with vague or subtle symptoms, they can be challenging to diagnose early.
Symptoms of Neuroendocrine Carcinoid Lung Cancer
One of the most challenging aspects of neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer is its symptoms, which can be easily mistaken for other conditions. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
- Persistent cough: A cough that doesn’t go away or worsens over time.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Chest pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest area.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound while breathing.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness or weakness.
- Flushing: Redness or warmth in the face and neck.
- Diarrhea: Frequent, loose stools that may be accompanied by abdominal pain.
While these symptoms can be caused by a variety of conditions, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional if they persist or worsen. Early detection is key to improving outcomes for patients with neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer.
How Is Neuroendocrine Carcinoid Lung Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosing neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer requires a combination of imaging tests, biopsies, and laboratory analyses. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the diagnostic process:
- Imaging Tests:
- Chest X-ray: Often the first test to identify abnormalities in the lungs.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the lungs and surrounding tissues.
- PET Scan: Helps determine if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Biopsy:
- A small sample of tissue is taken from the tumor and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of neuroendocrine cells.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Blood and urine tests may be conducted to check for elevated levels of certain hormones or markers associated with neuroendocrine tumors.
- Bronchoscopy:
- A thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the airways to visualize the tumor and collect tissue samples.
Staging Neuroendocrine Carcinoid Lung Cancer
Once diagnosed, the cancer is staged to determine its extent and guide treatment decisions. The stages range from I (localized) to IV (advanced and spread to other organs). Here’s a quick overview:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Stage I | Tumor is small and confined to the lung. |
| Stage II | Tumor has spread to nearby lymph nodes. |
| Stage III | Tumor has spread to surrounding tissues or distant lymph nodes. |
| Stage IV | Cancer has metastasized to other organs, such as the liver or bones. |
Treatment Options for Neuroendocrine Carcinoid Lung Cancer
The treatment approach for neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer depends on the stage of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and the tumor’s characteristics. Here are the most common treatment options:
1. Surgery
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for early-stage neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer. The goal is to remove the tumor and any affected lymph nodes. Types of surgery include:
- Lobectomy: Removal of an entire lobe of the lung.
- Wedge Resection: Removal of a small, wedge-shaped portion of the lung.
- Pneumonectomy: Removal of an entire lung (rarely performed).
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It may be used before surgery to shrink the tumor or after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. It’s typically reserved for advanced-stage neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer or when surgery isn’t an option.
4. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. For example, drugs like everolimus may be used to slow tumor progression.
5. Somatostatin Analogs
These drugs, such as octreotide, help control symptoms caused by hormone-secreting tumors. They can also slow tumor growth in some cases.
Living with Neuroendocrine Carcinoid Lung Cancer
A diagnosis of neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer can be overwhelming, but there are steps you can take to manage the disease and maintain your quality of life:
- Follow Your Treatment Plan: Adhere to your doctor’s recommendations and attend all follow-up appointments.
- Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking.
- Seek Support: Join a support group or connect with others who are facing similar challenges.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest research and treatment options.
Conclusion
Neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer is a rare but serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and tailored treatment. While its symptoms can be subtle, understanding the signs and seeking medical attention early can make a significant difference in outcomes. From surgery and radiation to targeted therapy and lifestyle changes, there are numerous ways to manage this disease and improve quality of life.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with neuroendocrine carcinoid lung cancer, remember that you’re not alone. With the right care and support, it’s possible to navigate this challenging journey and find hope for the future. Stay informed, stay proactive, and never hesitate to reach out for help.
Read more: