Cancer has long been one of the most feared diseases in the world, affecting millions of lives each year. In the United States, the growing concern over cancer during the 20th century led to a historic moment that shaped modern cancer research, prevention, and treatment. This pivotal decision marked the beginning of a national commitment to combating cancer at every level.
You may wonder, when did the United States declare a “war on cancer” by passing the National Cancer Act? The answer lies in 1971, when President Richard Nixon signed the National Cancer Act into law. This legislation significantly expanded federal funding, empowered research institutions, and strengthened the fight against cancer, making it a turning point in U.S. healthcare history.
Definition and Overview
The National Cancer Act of 1971 was a groundbreaking law that provided the National Cancer Institute (NCI) with enhanced authority and resources to lead the nation’s cancer research efforts. By passing this act, the United States officially declared a “war on cancer,” recognizing the urgent need to address the disease through coordinated research, early detection, and advanced treatments.
Types
Cancer is not a single disease but a group of related diseases that occur when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably. Major types include:
- Carcinomas (breast, lung, colon, prostate)
- Sarcomas (bones, muscles, connective tissues)
- Leukemias (blood and bone marrow)
- Lymphomas (immune system)
- Central nervous system cancers (brain and spinal cord)
Causes and Risk Factors
Cancer develops due to genetic mutations, environmental exposures, and lifestyle factors. Key risk factors include:
- Tobacco and alcohol use
- Poor diet and obesity
- Family history of cancer
- Exposure to radiation or carcinogenic chemicals
- Chronic infections (e.g., HPV, hepatitis B and C)
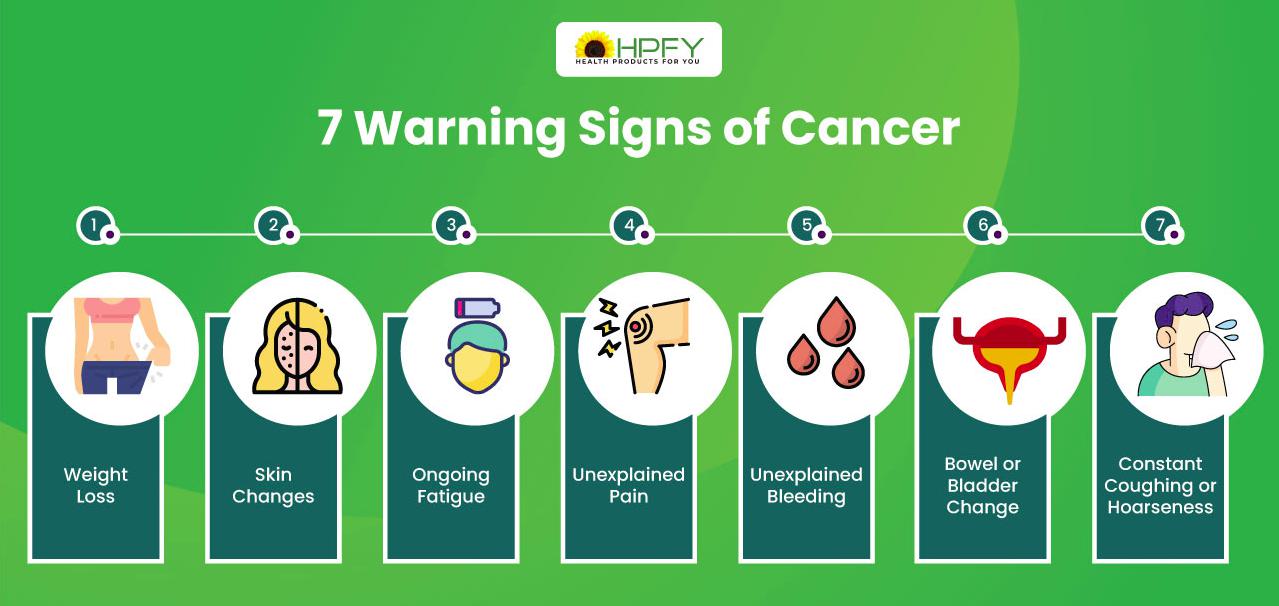
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Recognizing symptoms early can save lives. Common warning signs include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent fatigue
- Changes in skin or moles
- Unusual bleeding or discharge
- Chronic cough or difficulty swallowing
- Lumps or swelling in the body
Diagnosis
Advancements in cancer diagnosis have improved survival rates. Standard diagnostic tools include:
- Imaging scans (MRI, CT, PET)
- Biopsies
- Blood tests and tumor markers
- Genetic testing for inherited cancer risk
Treatment Options
Since the passage of the National Cancer Act, cancer treatment has advanced tremendously. Current options include:
- Surgery to remove tumors
- Radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells
- Chemotherapy to attack rapidly dividing cells
- Immunotherapy to strengthen the body’s immune response
- Targeted therapy that focuses on cancer-specific molecules
- Hormone therapy for hormone-driven cancers
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all cancers are preventable, lifestyle changes can reduce risk:
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol use
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight
- Protect skin from excessive sun exposure
- Get recommended screenings and vaccinations
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Survival rates depend on cancer type, stage at diagnosis, and access to treatment. Thanks to research and innovation since 1971, many cancers now have significantly higher survival rates than before the National Cancer Act was passed.
Latest Research and Innovations
Cancer research has evolved dramatically since the U.S. declared the war on cancer in 1971. Today’s innovations include precision medicine, gene editing (CRISPR), liquid biopsies, artificial intelligence in diagnostics, and personalized immunotherapy—all promising to improve patient outcomes.
Coping and Support for Patients
A cancer diagnosis can be emotionally overwhelming. Support systems such as counseling, patient advocacy groups, support networks, and palliative care services play a critical role in improving quality of life for patients and families.
Conclusion
So, when did the United States declare a “war on cancer” by passing the National Cancer Act? It was in 1971, under President Nixon’s leadership. This landmark legislation reshaped the nation’s approach to cancer, fueling decades of progress in prevention, detection, treatment, and research. While the battle continues, the legacy of the National Cancer Act remains a cornerstone in the global fight against cancer.
FAQ
1. What year did the U.S. pass the National Cancer Act?
The United States passed the National Cancer Act in 1971.
2. Why was the National Cancer Act important?
It significantly expanded federal funding for cancer research, empowering the National Cancer Institute to lead a nationwide effort against cancer.
3. What does “war on cancer” mean?
It refers to the U.S. government’s coordinated efforts to reduce cancer cases and deaths through research, education, prevention, and advanced treatments.
4. How has cancer survival improved since 1971?
Survival rates for many cancers have increased due to early detection, better treatments, and advances in personalized medicine.
5. Can cancer be prevented?
Not entirely, but healthy lifestyle choices, early screenings, and vaccinations can significantly reduce the risk.