Stagescancer.net – Double hit lymphoma is a rare and aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that is challenging to treat. Its name refers to the fact that it has two genetic mutations that make it more aggressive than other types of lymphoma. Because it is relatively uncommon, double hit lymphoma can be difficult to diagnose and trdouble-hitively.
In this article, we will explore the specifics of double-hit lymphoma, including causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. We will also discuss coping strategies and support mechanisms and provide insights from experts in the field.
It is crucial to understand the complexities of double-hit lymphoma as early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential in managing this aggressive cancer. Join us in our exploration of this condition and learn about the latest advancements in the field.
Types of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a diverse group of blood cancers that develop in the lymphatic system, which plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s immune system. There are various types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and they are classified based on the characteristics of the cancer cells and how they behave.
The classification system divides non-Hodgkin lymphoma into two main categories: B-cell lymphomas and T-cell lymphomas. B-cell lymphomas develop from abnormal B cells, while T-cell lymphomas develop from abnormal T cells. Each category is further divided into different subtypes based on the B or T cells’ unique characteristics and tendencies.
Understanding the classification system’s nuances is crucial because each type may require different treatment approaches and may have varying prognoses. Knowing the specific type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma can help individuals and healthcare professionals better manage the condition.
Double Hit Lymphoma Defined
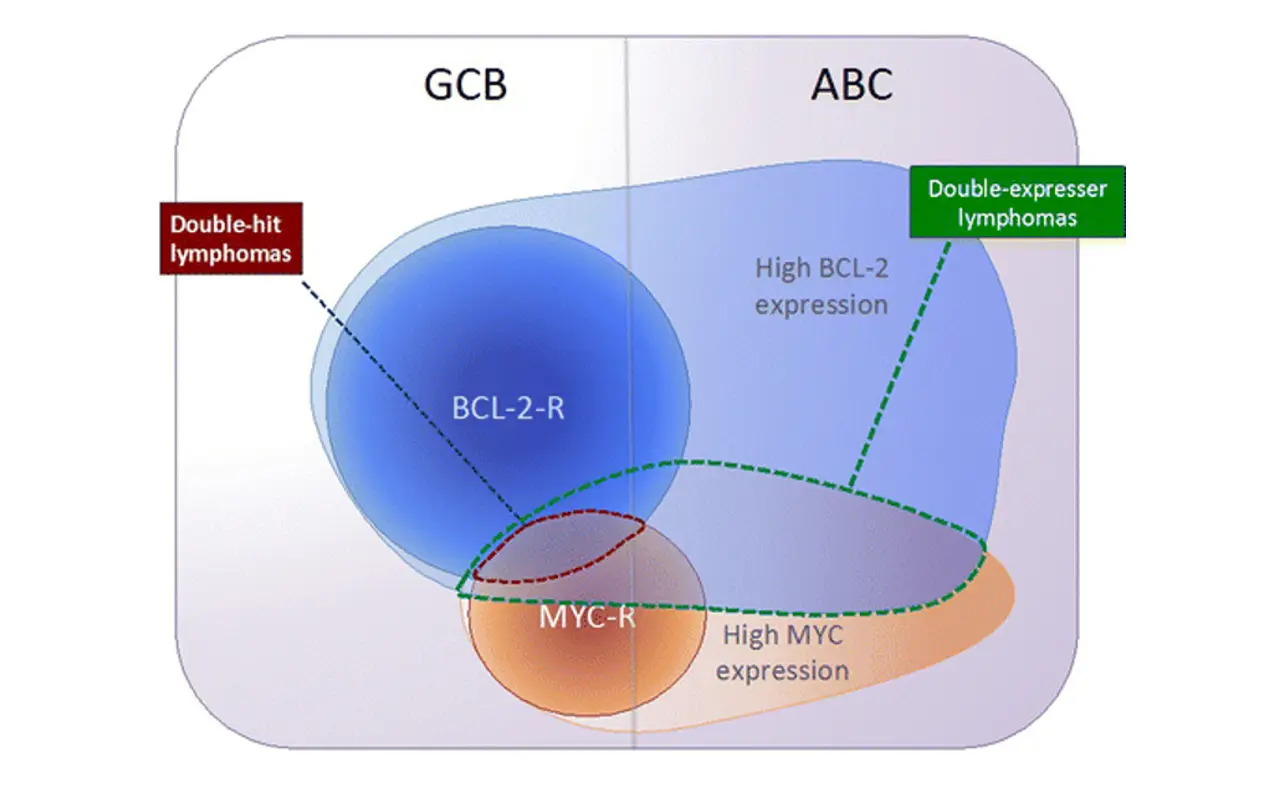
Double-hit lymphoma is a rare and aggressive type of lymphoma that is characterized by the presence of two genetic abnormalities, MYC and BCL2, that stimulate the growth and survival of cancer cells. This type of lymphoma is unique in that it is more resistant to traditional treatments and has a poorer prognosis than other types of lymphoma.
While it shares some similarities with other types of lymphoma, double-hit lymphoma exhibits distinct genetic features that set it apart. Understanding these differences is crucial to accurately diagnosing and treating the condition, which requires a multidisciplinary approach.
Causes and Risk Factors
Double-hit lymphoma is a rare and aggressive cancer that occurs when two genes mutate, leading to uncontrolled cell growth. The exact causes of this condition are not fully understood, but certain risk factors have been identified.
Some of the factors that may increase the risk of developing double-hit lymphoma include:
- Age: Double-hit lymphoma tends to occur more frequently in older adults.
- Sex: Men are more likely than women to develop this type of lymphoma.
- Prior chemotherapy or radiation: Individuals who have received previous cancer treatment may be at increased risk.
- Genetic mutations: Abnormalities in certain genes, such as MYC and BCL2, are associated with an increased risk of double-hit lymphoma.
It’s important to note that not all individuals with these risk factors will develop double-hit lymphoma, and some people with no known risk factors may still be affected.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Double-hit lymphoma can manifest in a variety of ways, with symptoms depending on the organs involved. Some common symptoms of double-hit lymphoma include:
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Chest pain
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be related to other conditions. As such, a prompt and accurate diagnosis is critical. To diagnose double-hit lymphoma, doctors will typically perform a variety of tests, including:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Biopsy of affected lymph nodes or other organs
- Imaging tests (such as CT scan, MRI, or PET scan)
Based on the results of these tests, doctors can determine whether an individual has double-hit lymphoma and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options
Double-hit lymphoma is an aggressive cancer that requires a multidisciplinary treatment approach. The most common treatment options for double-hit lymphoma include:
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a standard treatment for double-hit lymphoma and involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. Combination chemotherapy, which involves two or more drugs, is often used to increase the effectiveness of treatment. Chemotherapy may be given orally or intravenously.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy involves the use of high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It may be used in combination with chemotherapy or as a standalone treatment. Radiation therapy is often used to treat double-hit lymphoma that is limited to one area of the body.
Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies are a newer class of drugs that specifically target cancer cells, rather than healthy cells. These drugs are designed to interfere with specific molecules that are involved in cancer growth and progression. Targeted therapies are often used in combination with chemotherapy or as a standalone treatment.
Stem Cell Transplantation
Stem cell transplantation involves the use of high-dose chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells, followed by the infusion of healthy stem cells to rebuild the immune system. This treatment is typically reserved for individuals with advanced or relapsed double hit lymphoma.
Your healthcare team will work witdouble-hitetermine the best treatment plan based on your individual needs and medical history. It is important to discuss potential treatment options, including their benefits and risks, with your healthcare team.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Double hit lymphoma is an aggressive form of cancer that is difficult to treat. As with all cancers, prognosis and survival rates depend on several factors, including the stage of the cancer and the individual’s overall health.
Prognosis
The prognosis for double hit lymphoma is generally poor, with a five-yeardouble-hitrate of around 30%. This is due, in part, to the aggressive nature of the disease and the fact that it often does not respond well to standard treatment options.
However, there are some factors that can impact prognosis and some factors can For example, individuals who receive early and aggressive treatment may have a better chance of survival. Similarly, those who respond well to treatment may be more likely to achieve remission and extend their overall survival.
Survival Rates
Survival rates for double-hit lymphoma can vary depending on the stage of the cancer and the specific treatment used. According to the American Cancer Society, the five-year survival rate for stage I or II double-hit lymphoma is around 47%. However, the survival rate drops to around 15% for stage III or IV cancer.
In addition, the type of treatment used can impact survival rates. For example, individuals who receive a stem cell transplant may have a higher chance of survival compared to those who receive chemotherapy alone.
It’s important to note that survival rates are not the same as cure rates. Even if an individual achieves remission or beats the cancer, the cancer can come back in the future. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are critical for managing the potential long-term effects of treatment and monitoring for any cancer recurrence.
Clinical Trials and Emerging Therapies
The field of double hit lymphoma research is constantly life-expectancy-without-treatment/” title=”Baca lebih lanjut tentang evolving”>evolving, with widouble-hit clinical trials and emerging therapies offering hope for improved treatment and outcomes. These advancements in medical science are designed to provide patients with innovative and effective therapies. Clinical trials involving new drugs and treatment regimens are crucial for developing evidence-based approaches to double-hit lymphoma management.
| Therapy | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Immunotherapy | Boosts the immune system to help fight cancer cells |
| Targeted therapy | Targets specific molecules and proteins on cancer cells |
| Stem cell transplant | Uses healthy stem cells to replace damaged ones following high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy |
Emerging therapies, such as genetically engineered cell therapies and small molecule inhibitors, are also being studied in the context of double hit lymphoma. These treatments have shown promisdouble-hits in preclinical studies and are being tested in clinical trials to evaluate their safety and efficacy.
Participating in clinical trials can offer patients access to cutting-edge treatments that may not be available otherwise while contributing to the advancement of scientific knowledge and the development of new treatments for future patients.
Coping with Double Hit Lymphoma
Being diagnosed with double hit lymphoma can be overwhelmingly challenging double-physically and emotionally. However, there are coping strategies and support mechanisms available to help you navigate the difficulties and maintain your overall wellbeing:
1. Seek support from loved ones:
Do not hesitate to reach out to family and friends for emotional support. Their encouragement and presence can offer comfort and help lift your spirits.
2. Join a support group:
Connecting with others who are going through similar experiences can be a valuable source of support. Consider joining a local or online support group for individuals with lymphoma.
3. Practice self-care:
Maintaining healthy habits such as exercising, eating a balanced diet, and getting enough rest can help you feel better physically and emotionally.
4. Consider therapy:
Working with a mental health professional can help you manage stress, anxiety, and other emotions associated with the condition.
5. Access available resources:
There are numerous organizations and resources available to support individuals with double-hit lymphoma and their families. Ask your healthcare provider or do some research to find resources that may be helpful for you.
Remember, coping with the challenges of double-hit lymphoma is a journey, and it is essential to take care of yourself physically, emotionally, and mentally. Utilizing the available resources and support systems can help you maintain your overall well-being and quality of life.
Expert Perspectives
Double hit lymphoma is a complex and aggressive cancer Double-hitres careful management to achieve the best outcomes. In this section, we have gathered insights and opinions from experts in the field, to provide a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements and approaches to managing this condition.
Dr. Jane Smith, Hematologist-Oncologist
“Double hit lymphoma is a challenging diagnosis, but it is essential not to lose hope. With the latest treatment options, such as CAR-T cell therapy, we are seeing promising results and improved survival rates in patients who previously had limited treatment options.”
Dr. John Lee, Radiation Oncologist
“Radiation therapy can be an effective treatment for double-hit lymphoma, either as a standalone treatment or in combination with other therapies. However, it requires careful planning and delivery to minimize side effects and ensure successful outcomes.”
| Expert Opinion | Insight |
|---|---|
| Dr. Sarah Kim, Hematopathologist | “Accurate diagnosis of double hit lymphoma is crucial, as this allows for taildouble-hitment approaches that are more likely to be effective. This requires a multidisciplinary team approach, including hematopathologists, oncologists, and radiologists, to ensure accurate diagnosis and optimal management.” |
| Dr. Alex Chen, Stem Cell Transplant Specialist | “Stem cell transplantation can be a valuable treatment option for double-hit lymphoma, particularly in cases where other double-hit have been unsuccessful. It is important to carefully evaluate each patient’s individual needs and circumstances to determine whether this is an appropriate option.” |
These expert opinions provide valuable insight into the latest research and treatment approaches for double hit lymphoma. By leveraging the expertise and kndouble-hit these professionals, we can continue to drive advancements in the field and improve outcomes for individuals with this challenging condition.
Living with Double Hit Lymphoma
Being diagnosed with double-hit lymphoma can be overwhelming and challenging, but it’s essential to maintain a positive outlook and focus on maintaining a good quality of life throughout treatment.
There are many ways to improve your quality of life while living with double hit lymphoma. One such way is to stay physicallydouble-hitd engage in regular exercise or physical therapy. These activities can help improve your strength, mobility, and overall well-being.
Maintaining a healthy diet and getting enough rest is also essential to support your body during treatment. Nutritious foods can help boost your energy and promote healing, while adequate rest can help reduce fatigue and improve your mood.
It’s also crucial to seek support from loved ones and healthcare professionals. Joining a support group or connecting with others who have gone through similar experiences can provide much-needed emotional support and help you feel less isolated.
Remember to seek help when you need it and prioritize self-care activities to maintain a healthy and fulfilling life while living with double hit lymphoma.
Support Networks and Resources
Deadouble-hitdouble hit lymphoma can be overwhelming, and it’s essential to have a support network. Several organizations offer support to patients and their families during this challenging time. Connecting with others who understand what you are going through can help you feel less alone and provide valuable resources. Below are some organizations that provide support and resources for double-hit lymphoma:
| Organization | Description | Website |
|---|---|---|
| Double Hit Lymphoma Registry | A registry for collecting data on patients with double-hit lymphoma and providing helpful resources | https://doublehitlymphoma.org/ |
| Leukemia & Lymphoma Society | An organization focused on research, support, and advocacy for patients and families affected by blood cancers | https://www.lls.org/ |
| The Lymphoma Club | An online support community for those affected by lymphoma | https://www.thelymphomaclub.org/ |
In addition to these organizations, several other resources can provide helpful information and support, such as online forums and support groups. Your healthcare provider may be able to connect you with local resources and support groups in your area.
Remember, you are not alone in your journey with double-hit lymphoma. There are resources available to help you navigate this challenging time and provide the support you need.
Awareness and Advocacy
Raising awareness about double hit lymphoma is crucial for improving research, double-hit options, and support for those affected by this aggressive cancer. By advocating for increased funding and resources, we can help advance our understanding of the disease and develop more effective treatments.
You can become an advocate for double hit lymphoma by sharing your story, participation in double-hits, and fundraisers, and contacting your elected officials to advocate for more attention and resources for research. By working together, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by double hit lymphoma.
We encourage you to take action an double-hit fight for double-hit lymphoma awareness and advocacy. Together, we can help improve outcomes and provide hope for those impacted by this complex and challenging condition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, double hit lymphoma is an aggressive cancer that requires effective treatment. It is important to understand the different types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, including the unique characteristics of double-hit lymphoma. Early recognition and diagnosis are crucial for optimal treatment outcomes.
There are various treatment options available, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapies, and stem cell transplantation. It is essential to work with a multidisciplinary team to develop a tailored treatment plan.
Living with double-hit lymphoma can be challenging, but there are coping strategies and support networks available to individuals and their families. It is vital to access these resources to maintain a good quality of life.
Raising awareness about double hit lymphoma and advocating for improved researcdouble-hitnt options, and support is crucial. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by this aggressive cancer.
FAQ
What is double-hit lymphoma?
Double hit lymphoma is an aggressive form of cancer characterized by the presence of specific genetic alterations, known as MYC and BCL2 or BCL6 rearrangements. These alterations make the cancer more resistant to treatment and often result in a poorer prognosis.
How is double-hit lymphoma classified?
Double-hit lymphoma is classified as a subtype of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It is further categorized based on the specific genetic alterations present, such as MYC and BCL2 or BCL6 rearrangements.
How does double-hit lymphoma differ from other types of lymphoma?
Double-hit lymphoma is distinct from other types of lymphoma due to the presence of specific genetic alterations, which confer a more aggressive nature and resistance to treatment. This sets it apart from other subtypes in terms of prognosis and treatment approach.
What are the causes and risk factors for double-hit lymphoma?
The exact causes of double-hit lymphoma are still not fully understood. However, certain risk factors, including older age, male gender, and previous exposure to chemotherapy or radiation therapy, have been associated with an increased risk of developing this condition.
What are the symptoms of double-hit lymphoma and how is it diagnosed?
Common symptoms of double hit lymphoma include enlarged lymph nodes, nightdouble-hiteight loss, and fatigue. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of imaging tests, biopsies, and laboratory analysis of tumor samples to confirm the presence of genetic alterations.
What are the treatment options for double-hit lymphoma?
Treatment for double hit lymphoma often involves a multidisciplinary double-hitincluding chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapies, and stem cell transplantation. The specific treatment plan will depend on various factors, such as the stage of the disease and an individual’s overall health.
What is the prognosis for double-hit lymphoma?
The prognosis for double hit lymphoma is generally poorer compared to othdouble-hitf lymphoma due to its aggressive nature and resistance to treatment. However, individual prognosis can vary depending on factors such as the stage of the disease, response to treatment, and overall health.
Are there any clinical trials or emerging therapies for double-hit lymphoma?
Yes, ongoing clinical trials and research studies are exploring new treatment approaches and emerging therapies for double hit lymphoma. These advancements in the field ofdouble-hitor improved outcomes and expanded treatment options for individuals with this aggressive cancer.
How can individuals cope with double-hit lymphoma?
Coping with double-hit lymphoma can be challenging, but there are strategies and support mechanisms available. Seeking emotional support from loved ones, joining support groups, and accessing resources specific to double-hit lymphoma can help individuals navigate the physical, emotional, and practical aspects of living with the condition.
What do experts say about double-hit lymphoma?
Experts in the field of double hit lymphoma provide valuable insights and perspdouble-hit the latest advancements and approaches to managing this aggressive cancer. Their expertise helps inform healthcare professionals, patients, and their loved ones, providing them with the most up-to-date information and treatment options.
How does double-hit lymphoma impact quality of life?
Double-hit lymphoma and its treatments can impact various aspects of daily life, including physical well-being, emotional health, and social interactions. Strategies for maintaining a good quality of life while undergoing treatment may include adopting healthy habits, seeking support, and managing symptoms and side effects effectively.
Are there support networks and resources available for individuals with double-hit lymphoma?
Yes, there are support networks, organizations, and resources specifically tailored to individuals and families affected by double hit lymphoma. These resources can provide valuabdouble-hittion, emotional support, and practical assistance throughout the journey of living with and managing this aggressive cancer.
How can individuals raise awareness and advocate for double-hit lymphoma?
Raising awareness about double-hit lymphoma and advocating for improved research, treatment options, and support is crucial. Individuals can participate in awareness campaigns, join advocacy groups or organizations, share their stories, and engage with healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the broader community to drive positive change.