Stagescancer.net – Lung cancer is a devastating disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Unfortunately, when cancer spreads to the brain, it can be even more challenging to treat effectively. Brain metastasis from lung cancer can dramatically impact an individual’s life expectancy and overall prognosis. In this article, we will explore the factors that impact survival rates and discuss the available treatment options to combat this disease. We hope that this article provides helpful information for those affected by lung cancer spread to the brain, guiding them toward early detection, personalized treatment, and ongoing research that can improve their prognosis and life expectancy.
Through this article, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of lung cancer, brain metastasis, and their impact on life expectancy and prognosis. We will delve into the common symptoms, diagnostic tests, and available treatment options for individuals facing this challenging diagnosis. We believe that by providing helpful information, we can offer support and guidance to those fighting against lung cancer spread to the brain. In the following sections, we will provide detailed information about each aspect of the disease, emphasizing the importance of personalized treatment options and ongoing research in improving the prognosis for individuals affected by lung cancer.
Join us as we explore the latest advancements and treatment options for lung cancer spread to the brain, and most importantly, how to live a fulfilling life throughout the journey.
Understanding Lung Cancer and Brain Metastasis
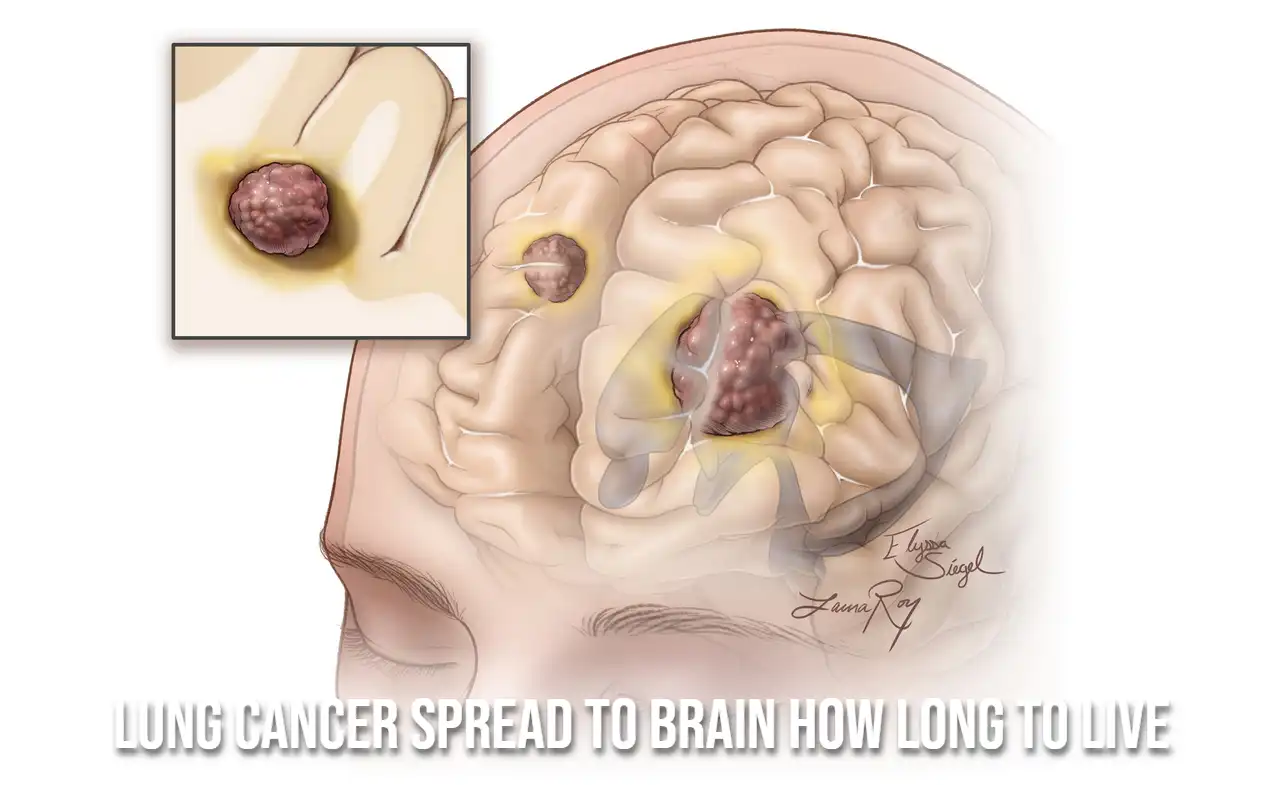
Lung cancer can spread to other parts of the body, including the brain, through either the bloodstream or lymphatic system. This process is known as metastasis, and secondary tumors can form as cancer cells travel to other organs, including the brain. Once metastasis occurs, the disease is considered advanced and can be more challenging to treat.
Cancer cells that originate in the lung can break away from the primary tumor and travel to the brain. They can enter the brain through small blood vessels or by moving through the cerebrospinal fluid. Once in the brain, these cells can grow and form tumors, which can then interfere with the brain’s normal functions and cause various neurological symptoms.
Symptoms of Brain Metastasis from Lung Cancer
When lung cancer spreads to the brain, it can cause a range of symptoms that can vary in severity depending on the location and extent of the metastasis. Some common symptoms of brain metastasis from lung cancer include:
- Headaches, often worsening in the morning or after physical activity
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seizures
- Difficulty with balance or coordination
- Changes in vision or hearing
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Cognitive changes, such as memory loss or confusion
It is important to note that these symptoms may also be caused by other conditions, which can make it difficult to diagnose brain metastasis from lung cancer. If you or a loved one experiences any of these symptoms, it is essential to speak with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnostic Tests for Brain Metastasis
Diagnosing brain metastasis in individuals with lung cancer typically involves a combination of physical exams, medical history reviews, and imaging tests. Imaging techniques like MRI, CT scans, and PET scans are the most common diagnostic tests used for detecting brain metastasis.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This imaging test uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain. It is a non-invasive procedure that can provide detailed information about the size and location of tumors and damage to the brain tissue.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: These scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the brain. They can help detect abnormalities such as brain tumors by highlighting differences in tissue density.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans: These scans use radioactive tracers to detect changes in cellular activity in the brain. This test can help identify areas of the brain with increased glucose uptake, which may indicate the presence of a tumor.
| Imaging Technique | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| MRI | Provides detailed images of the brain | May not detect small tumors |
| CT Scans | Quick and widely available | Exposes the patient to ionizing radiation |
| PET Scans | Can detect areas of increased cellular activity | Requires the injection of a radioactive tracer |
Occasionally, a biopsy may be required to confirm the presence of brain metastasis. This involves the surgical removal of a small tissue sample for laboratory analysis.
When Diagnostic Tests Are Necessary
Diagnostic testing is essential for detecting brain metastasis and determining the most appropriate treatment options. If an individual with lung cancer experiences neurological symptoms or is at high risk of developing brain metastasis, a diagnostic test may be recommended by their healthcare provider.
Factors Affecting Life Expectancy
When lung cancer spreads to the brain, the prognosis can be difficult to determine. The life expectancy for an individual with brain metastasis from lung cancer depends on various factors.
Cancer Stage
The stage of lung cancer at the time of diagnosis is a key factor in determining life expectancy. Individuals with early-stage lung cancer have a better prognosis than those with advanced-stage cancer. Brain metastasis often occurs in advanced-stage cancer, which can impact survival rates.
Overall Health
Another factor that can impact life expectancy is the overall health of an individual. Age, pre-existing medical conditions, and lifestyle choices can all affect a person’s ability to tolerate cancer treatment and fight the disease.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment for brain metastasis from lung cancer can significantly influence an individual’s life expectancy. Available treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. In some cases, a combination of these treatments is necessary. The effectiveness of each treatment modality varies based on the individual’s specific situation.
Overall, the prognosis for individuals with lung cancer that has spread to the brain can be challenging. However, advances in treatment options and ongoing research offer hope for improving survival rates and quality of life. Choosing the optimal treatment plan and working closely with a healthcare team can help maximize life expectancy and maintain the highest possible quality of life.
Treatment Options for Brain Metastasis
When lung cancer spreads to the brain, there are several treatment options available to help manage the disease. The treatment plan will depend on various factors, such as the extent and location of the tumors, the overall health of the patient, and the available resources.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgery may be recommended to remove or reduce the size of the tumors. The goal of surgery is to alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and potentially extend survival. However, not all tumors are surgically resectable. A neurosurgeon will evaluate the patient to determine if they are a candidate for surgical intervention.
| Type of Surgery | Description |
|---|---|
| Craniotomy | A surgical opening is created in the skull to access the brain and remove the tumor. |
| Minimally Invasive Surgery | A small incision is made in the scalp insert a tiny camera and surgical tools to remove the tumor. |
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to shrink tumors and kill cancer cells. It can be delivered using different techniques, such as stereotactic radiosurgery or whole-brain radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is often recommended in combination with surgery or as a palliative treatment to manage symptoms.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs to specifically target cancer cells with certain genetic mutations. It can be an effective treatment option for individuals with advanced lung cancer and brain metastasis.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It can be administered orally or through intravenous infusion. Chemotherapy is often recommended when the tumors are too widespread for surgery or radiation therapy.
It is important to discuss all treatment options with your healthcare team and make an informed decision based on your individual needs and goals.
Surgical Interventions for Brain Metastasis
In some cases, surgical interventions may be a viable option for individuals with lung cancer that has spread to the brain. Surgery is typically recommended for individuals with resectable tumors, meaning the tumors can be removed surgically.
Types of Surgeries
| Type of Surgery | Description | Potential Impact on Life Expectancy |
|---|---|---|
| Craniotomy | A surgical procedure that involves opening the skull to remove brain tumors. | May improve survival rates for individuals with resectable tumors. |
| Metastasectomy | A surgical procedure that involves removing the metastatic tumors from the brain. | May improve survival rates for individuals with resectable tumors. |
While surgical interventions for brain metastasis from lung cancer may have a positive impact on life expectancy, it is important to weigh the potential risks and benefits with an experienced medical team. Surgery carries the risk of complications such as infections, bleeding, and neurological deficits.
In some cases, surgery may be followed by other treatments like radiation therapy or chemotherapy to improve the chances of long-term survival.
Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastasis
Radiation therapy is a common treatment for brain metastasis from lung cancer. It works by using high-energy radiation to shrink or destroy cancer cells in the brain. There are several different radiation therapy techniques available, including:
- Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS): This non-invasive treatment uses multiple beams of radiation to target a specific area of the brain. It is often used for small, well-defined brain metastases and offers a high degree of precision and accuracy.
- Whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT): This treatment targets the entire brain, rather than specific areas. It is often used for multiple or larger brain metastases and can help to improve symptoms and quality of life.
The choice of radiation therapy technique will depend on various factors, including the number and size of brain metastases, overall health and well-being, and previous treatments. Your healthcare team will work with you to determine the most appropriate radiation therapy approach for your specific needs.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy for Brain Metastasis
Lung cancer patients with brain metastasis may benefit from targeted therapy and immunotherapy. Unlike chemotherapy, which attacks healthy cells and cancerous cells, targeted therapy works by blocking specific genes or proteins that help the cancer cells grow. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, on the other hand, help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells by removing the brakes on the immune system.
Patients with genetic alterations, such as EGFR mutations or ALK rearrangements, may benefit from targeted therapy drugs such as osimertinib or alectinib. These drugs have been shown to improve the response rates and progression-free survival of patients with brain metastasis from lung cancer.
Another promising approach is personalized treatment, where doctors analyze the patient’s genetic profile to identify the most effective treatment options. Personalized treatment may include targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of both depending on the patient’s genetic mutations.
Benefits of Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Targeted Therapy
| Benefits | Example Drugs |
|---|---|
| Improved response rates and survival | Osimertinib, alectinib, crizotinib |
| Reduced side effects compared to chemotherapy | Erlotinib, afatinib, ceritinib |
Immunotherapy
| Benefits | Example Drugs |
|---|---|
| Improved overall survival rates | Pembrolizumab, nivolumab |
| Reduced risk of recurrence | Atezolizumab |
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy also provide an alternative to patients who are ineligible or intolerant to chemotherapy. However, these treatments may not be suitable for every patient, and it is important to discuss with your doctor if you are a candidate for targeted therapy or immunotherapy.
Chemotherapy for Brain Metastasis
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment that involves the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells throughout the body, including in the brain. This treatment may be recommended for individuals with lung cancer that has spread to the brain, either alone or in combination with other therapies.
There are several chemotherapy drugs available for brain metastasis treatment, including:
| Drug Name | Usage | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Etoposide | Used in combination with other drugs to destroy cancer cells | Nausea, vomiting, hair loss, fatigue |
| Carboplatin | Used in combination with other drugs to destroy cancer cells | Nausea, vomiting, anemia, increased risk of infection |
| Cisplatin | Used alone or in combination with other drugs to destroy cancer cells | Nausea, vomiting, kidney damage, hearing loss |
Chemotherapy drugs can have several side effects, some of which can be severe. These may include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hair loss
- Anemia
- Increased risk of infection
- Kidney damage
- Hearing loss
It is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of chemotherapy with your healthcare provider and to closely monitor side effects throughout treatment.
Palliative Care and Supportive Measures
Palliative care and supportive measures are crucial aspects of managing brain metastasis from lung cancer. While medical interventions and treatments aim to prolong life and reduce the spread of cancer, palliative care focuses on managing symptoms, minimizing pain, and supporting patients’ overall well-being.
Pain management is an essential element of palliative care. There are various approaches to managing pain associated with brain metastasis, including medication, surgery, and radiation therapy. Psychological support is also crucial for patients with brain metastasis, who may experience anxiety, depression, and other emotional challenges. Counseling, support groups, and other therapy options can provide the necessary support and assistance in coping with these challenges.
In addition to physical and emotional symptom management, supportive measures can help improve patients’ quality of life and overall well-being. Nutrition counseling, exercise programs, and social activities can be integrated into a patient’s care plan to improve their overall mood, physical health, and emotional well-being.
Pain Management
Pain management is a vital aspect of palliative care for patients with brain metastasis from lung cancer. Pain may arise from cancer itself or treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy. There are various approaches to managing pain, including medication, nerve blocks, and other pain management techniques.
Medications like opioids, NSAIDs, and nerve-blocking agents can be used to manage different types of pain in cancer patients. Patients may also undergo treatments like radiation therapy or surgery to alleviate pain caused by tumors. In addition to medical interventions, complementary therapies like acupuncture, massage, and relaxation techniques can also help manage pain and improve physical and emotional well-being.
Psychological Support
Patients with brain metastasis from lung cancer may experience psychological symptoms like depression, anxiety, and fear. These symptoms can be managed with various psychological support options like counseling, support groups, and other therapy options.
Counseling may involve individual or family therapy to help patients and their loved ones deal with the emotional challenges of cancer. Support groups allow patients to connect with others who are in a similar situation, providing a sense of community and emotional support. Lastly, other therapy options like cognitive-behavioral therapy and meditation can help patients reduce stress and anxiety and improve their overall mood and emotional well-being.
Supportive Measures
Supportive measures are non-medical interventions that can play an essential role in improving a patient’s quality of life and overall well-being. An emphasis on good nutrition, exercise, and social activities can help manage psychological and emotional symptoms and support physical health.
Nutrition counseling is crucial, as cancer and cancer treatments can impact a patient’s appetite and nutrition. Exercise programs can improve physical well-being and reduce stress and anxiety. Social activities like arts and crafts, music therapy, and pet therapy can provide social support and emotional comfort.
| Benefits of Palliative Care and Supportive Measures | Examples |
|---|---|
| Improves pain management | Medication, radiation therapy, nerve blocks, complementary therapies |
| Provides emotional support | Counseling, support groups, cognitive-behavioral therapy |
| Improves overall well-being | Nutrition counseling, exercise programs, social activities |
Regardless of the treatment plan or prognosis, palliative care and supportive measures can provide substantial benefits to patients with brain metastasis from lung cancer. They can help manage physical and emotional symptoms, minimize pain, and improve overall quality of life.
Research and Advancements in Brain Metastasis Treatment
The field of brain metastasis treatment for individuals with lung cancer is constantly evolving with ongoing research and advancements. Clinical trials are at the forefront of this progress, paving the way for new treatments and increased understanding of the disease.
New Treatment Approaches
Recent research has uncovered promising new treatment approaches, such as immunotherapy and targeted therapy, that have shown improved outcomes and better tolerability in clinical trials for brain metastasis from lung cancer. These treatments are designed to attack specific cancer cells and minimize damage to healthy tissues.
In addition to targeted therapy and immunotherapy, researchers are also looking into the potential of combination therapy for brain metastasis from lung cancer. This approach combines different treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, to improve outcomes and potentially reduce side effects.
Personalized Treatment
Advancements in technology have allowed for the development of personalized treatment plans based on genetic mutations associated with individual cancers. This precision medicine approach allows for more targeted and effective treatment tailored to the unique needs of the patient.
Collaborative Efforts
Collaboration between researchers, oncologists, and patients is also driving advancements in brain metastasis treatment for individuals with lung cancer. This collaboration is helping to identify new treatment targets, trial new therapies, and develop better ways to monitor and manage the disease.
| Research | Advancements |
|---|---|
| Better understanding of the biology of cancer cells and their behavior in the brain | Precision medicine and personalized treatment plans |
| Identification of new treatment targets | Combination therapy |
| Clinical trials testing new therapies | Improved imaging techniques for more accurate diagnosis and tracking of the disease |
Participants in clinical trials are benefiting from access to cutting-edge treatments and contributing to the advancement of brain metastasis treatment for individuals with lung cancer. As the field continues to evolve, individuals with lung cancer and brain metastasis can have hope for improved outcomes and a brighter future.
Coping with the Prognosis
Being diagnosed with lung cancer that has spread to the brain can be overwhelming for patients and their families. Coping with the prognosis requires emotional support and access to resources that provide guidance and comfort. Support groups are an excellent source of support that can help patients connect with others who are going through similar experiences and provide them with a sense of community.
It is important to communicate openly with healthcare professionals regarding the diagnosis, prognosis, and available treatment options. They can offer guidance and provide information on support groups and other resources that can be helpful during this time.
Additionally, engaging in self-care practices such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management can help patients cope with the diagnosis and the treatment process. Speaking with a mental health professional can be an excellent way to manage anxiety and depression that can arise from living with cancer.
Coping with lung cancer that has spread to the brain is a difficult journey, but with the right support, resources, and self-care practices, patients can maintain their hope, resilience, and quality of life.
Survivor Stories and Inspirational Accounts
Reading about others who have faced a lung cancer diagnosis with brain metastasis can be a source of hope and encouragement during a difficult time. So, we’ve compiled a few inspirational accounts from individuals who have fought against this disease and come out victorious.
Case 1: Bill T.
| Age | 52 |
|---|---|
| Cancer Diagnosis | Lung Cancer with Brain Metastasis |
| Treatment Received | Radiation and Immunotherapy |
| Survival Time | 5 years and counting |
After being diagnosed with lung cancer that had spread to his brain, Bill was given a grim prognosis of only a few months to live. But he never lost hope and pursued a combination of radiation and immunotherapy treatments. Today, five years later, Bill is still thriving and credits his faith and positivity for his success.
Case 2: Mary S.
| Age | 68 |
|---|---|
| Cancer Diagnosis | Lung Cancer with Brain Metastasis |
| Treatment Received | Surgery and Chemotherapy |
| Survival Time | 2 years and counting |
Mary was diagnosed with lung cancer that had spread to her brain, which left her feeling scared and hopeless. Despite the odds, she opted for surgery to remove the metastasis and underwent chemotherapy to target the cancer cells. Today, two years later, Mary is still fighting and proud of how far she’s come.
Case 3: Mike R.
| Age | 58 |
|---|---|
| Cancer Diagnosis | Lung Cancer with Brain Metastasis |
| Treatment Received | Stereotactic Radiosurgery |
| Survival Time | 1 year and counting |
When Mike learned that his lung cancer had spread to his brain, he turned to a type of radiation therapy known as stereotactic radiosurgery. This precise form of treatment delivered targeted radiation to the metastasis, sparing healthy brain tissue. Today, one year later, Mike feels grateful for each day and encourages others to never lose hope.
These inspiring survival stories showcase that life with lung cancer and brain metastasis is not just about surviving-it’s about thriving. By pursuing personalized treatment approaches and maintaining a positive outlook, individuals can overcome their diagnosis and continue living life to the fullest.
Conclusion
Lung cancer spread to the brain can have a significant impact on an individual’s life expectancy and quality of life. Early detection and personalized treatment are critical in improving outcomes for those diagnosed with brain metastasis from lung cancer. With the advancement of research, treatment options continue to improve, providing hope for individuals and their families.
It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to explore all available treatment options and develop a comprehensive plan tailored to individual needs. Palliative care and supportive measures can also play a vital role in enhancing quality of life and managing symptoms.
While a diagnosis of lung cancer spread to the brain may be challenging, there is always hope. Survivors’ stories and inspirational accounts serve as a reminder to never lose hope and continue to fight against this disease.
Overall, understanding the various treatment options and taking an active role in healthcare decision-making can significantly improve an individual’s outcome. Ongoing research and advancements will continue to expand treatment options, improving the prognosis and life expectancy for individuals with lung cancer that has spread to the brain.
FAQ
What is brain metastasis from lung cancer?
Brain metastasis occurs when cancer cells from the lungs spread to the brain through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. It is considered a secondary tumor and can affect a person’s prognosis and life expectancy.
What are the symptoms of brain metastasis from lung cancer?
The symptoms of brain metastasis can vary but may include headaches, seizures, changes in vision or speech, cognitive impairments, and physical symptoms such as weakness or loss of coordination.
How is brain metastasis from lung cancer diagnosed?
Diagnostic tests such as MRI, CT scans, and PET scans are commonly used to detect brain metastasis. These imaging techniques can help determine the location, number, and size of tumors in the brain.
What factors can affect life expectancy when lung cancer spreads to the brain?
Several factors can influence life expectancy, including the stage of cancer, overall health, and available treatment options. The response to treatment and individual variations can also impact prognosis.
What are the treatment options for brain metastasis from lung cancer?
Treatment options may include surgical interventions to remove tumors, radiation therapy to target cancer cells, targeted therapy or immunotherapy to address specific genetic mutations, and systemic chemotherapy to attack cancer cells throughout the body.
How does radiation therapy help treat brain metastasis from lung cancer?
Radiation therapy, such as stereotactic radiosurgery or whole-brain radiation therapy, is commonly used to target and destroy cancer cells in the brain. It can help relieve symptoms, reduce tumor size, and improve overall prognosis.
What are targeted therapy and immunotherapy in the treatment of brain metastasis?
Targeted therapy involves using drugs that specifically target genetic mutations or proteins in cancer cells, while immunotherapy activates the body’s immune system to attack cancer cells. Both treatment approaches offer personalized treatment options and can have positive effects on survival rates.
Can chemotherapy be used to treat brain metastasis from lung cancer?
Yes, chemotherapy drugs can be used as a systemic treatment option for brain metastasis in individuals with lung cancer. It aims to kill cancer cells throughout the body, including tumors in the brain.
What is the role of palliative care in brain metastasis treatment?
Palliative care focuses on improving the quality of life for individuals with brain metastasis. It includes pain management, psychological support, and symptom control to relieve physical and emotional distress.
Are there any advancements or ongoing research in brain metastasis treatment?
Yes, there is ongoing research and advancements in the field of brain metastasis treatment for lung cancer. Clinical trials offer potential benefits for individuals seeking innovative treatment options beyond standard therapies.
How can individuals cope with the prognosis of lung cancer that has spread to the brain?
Coping with the prognosis involves emotional support, open communication with healthcare professionals, and seeking support from support groups or counseling services. It’s important to find a support system that helps manage the emotional and practical challenges.
Are there any survivor stories or inspirational accounts of lung cancer with brain metastasis?
Yes, there are many survivor stories and inspirational accounts of individuals who have fought against lung cancer with brain metastasis. These stories offer hope, encouragement, and the understanding that there can be life beyond a diagnosis.