Stagescancer.net – When it comes to liver cancer, early detection plays a vital role in determining life expectancy, especially in stage 1 liver cancer. This is when cancerous cells are present in a small part of the liver, and there is a high chance of successful treatment. The prognosis for stage 1 liver cancer patients varies based on various factors, such as tumor size, location, and the overall health of the patient. In this section, we will explore these factors and the overall prognosis for patients diagnosed with stage 1 liver cancer, providing valuable insights into the treatment journey ahead.
Understanding Stage 1 Liver Cancer
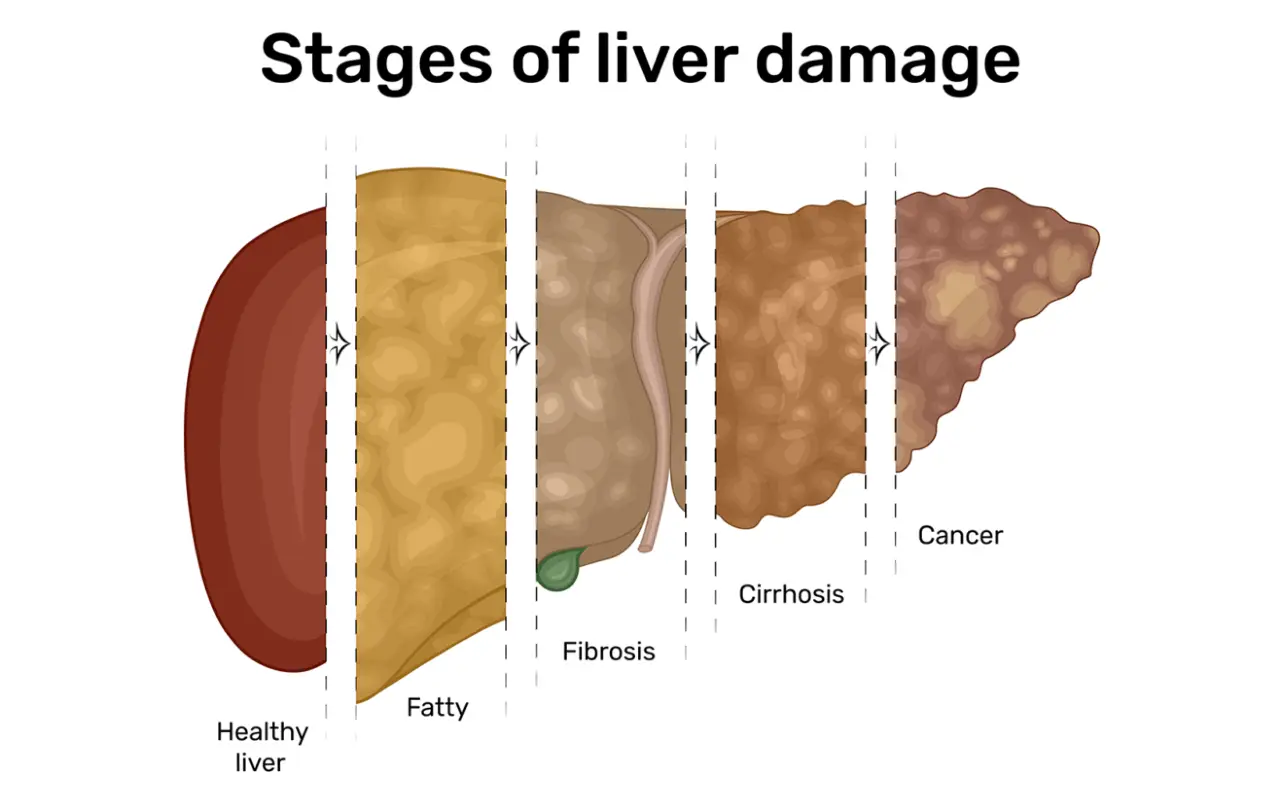
Stage 1 liver cancer, also known as early-stage liver cancer, refers to the first stage of liver cancer. At this stage, the cancer is limited to the liver and has not spread to nearby blood vessels or lymph nodes.
Some common symptoms of stage 1 liver cancer include:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Unintentional weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
It is important to note that some patients with stage 1 liver cancer may not experience any symptoms, which is why regular medical check-ups and screening tests are crucial in detecting liver cancer in its early stages.
Diagnosis of stage 1 liver cancer typically involves imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, or PET scan. A liver biopsy may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Understanding the characteristics of stage 1 liver cancer is vital in determining appropriate treatment plans and predicting life expectancy for patients. In the next section, we will take a closer look at the staging and prognostic factors for liver cancer.
Staging and Prognostic Factors
Staging of liver cancer is a critical process that involves examining the size and number of tumors, as well as their location in the liver and whether or not they have metastasized to surrounding tissues or organs. This helps determine the extent and severity of cancer and the most appropriate treatment plan for the patient.
Prognostic factors are additional characteristics that provide insight into the likelihood of a positive outcome. Factors such as underlying liver disease, age, and overall health can influence the prognosis, as can the specific features of the cancer cells themselves, including grade, stage, and molecular markers.
| Prognostic Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Tumor size | Larger tumors often indicate a more advanced stage and a lower chance of survival. |
| Lymph node involvement | Spread of cancer cells to lymph nodes can increase the risk of recurrence and lower life expectancy. |
| Cirrhosis | Prior liver damage from cirrhosis or other conditions can make treatment and recovery more difficult and can impact the overall prognosis. |
| Viral hepatitis | Viral hepatitis, particularly hepatitis B or hepatitis C, is a significant risk factor for liver cancer and can require additional treatment considerations. |
| Blood alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels | Elevated AFP levels in the blood can indicate the presence of liver cancer and may be used as a prognostic factor. |
Understanding the staging and prognostic factors for liver cancer is essential for patients and their caregivers, as it allows them to make informed decisions about treatment options and plans for the future.
Survival Rates for Stage 1 Liver Cancer
Survival rates for stage 1 liver cancer are encouraging, with a five-year survival rate of approximately 50% for patients who undergo treatment. However, it is important to note that individual outcomes depend on several factors, including the extent of cancer spread and the effectiveness of treatment. According to recent studies, early detection and treatment can significantly improve survival rates.
| Cancer Stage | Five-Year Survival Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Stage 1 | 50% |
| Stage 2 | 37% |
| Stage 3 | 16% |
| Stage 4 | 5% |
As seen in the table above, the five-year survival rate for stage 1 liver cancer is substantially higher than for later stages. It is essential to note that these rates serve as general benchmarks rather than precise indicators of individual outcomes. Treatments available for stage 1 liver cancer such as surgery, radiation therapy, and targeted drug therapies can play a significant role in improving patients’ survival rates and overall prognosis. Patients and their healthcare providers must collaborate to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to their individual needs.
Impact of Treatment on Life Expectancy
The treatment options for stage 1 liver cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, and targeted drug therapies. These interventions can have a significant impact on life expectancy, depending on various factors.
Surgical Interventions
Resection involves removing the section of the liver containing the tumor, while liver transplantation involves replacing the patient’s liver with a donor’s liver. These surgical interventions have been shown to improve overall survival rates for stage 1 liver cancer patients. According to a study published in the Journal of Hepatology, resection had a 5-year survival rate of 63.5%, and liver transplantation had a rate of 73.3%. However, the suitability of these surgical interventions may depend on the patient’s overall health and the characteristics of the tumor.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target cancer cells and can be administered externally or internally. Although it is effective in treating liver cancer, it can also cause side effects such as fatigue and nausea. According to a retrospective study published in the Annals of Oncology, radiation therapy significantly improved survival rates for stage 1 liver cancer patients, with a 3-year survival rate of 62.9% compared to 29.3% for patients who did not receive radiation therapy. However, further research is needed to determine the optimal dosage and duration of radiation therapy in this early-stage cancer.
Targeted Drug Therapies
Targeted drug therapies involve medications that specifically target cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissue. These drug therapies are effective in prolonging the progression-free survival (PFS) of liver cancer patients. According to a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the median PFS for sorafenib, a commonly used targeted drug therapy for advanced liver cancer, was 5.5 months, compared to 2.8 months for the placebo group, indicating the potential of these drug therapies for improving life expectancy in stage 1 liver cancer patients.
In conclusion, the impact of treatment on life expectancy for stage 1 liver cancer patients varies depending on the individual’s overall health, tumor characteristics, and the effectiveness of the chosen intervention. Surgery, radiation therapy, and targeted drug therapies have all demonstrated potential for improving survival rates in these patients, highlighting the importance of considering all treatment options for an individualized approach.
Surgical Treatment for Stage 1 Liver Cancer
Surgical treatment options are available for stage 1 liver cancer patients. Two main procedures are generally offered: resection and liver transplantation.
Resection
Resection involves removing the entire tumor together with a part of the liver. The extent of the liver to be removed depends on the size and location of the tumor, and a margin of healthy liver tissue is often removed along with the tumor to prevent recurrence. This surgery is generally preferred when the tumor is small and can be removed, leaving enough healthy liver tissue for the liver to function properly.
According to research, liver resection for stage 1 liver cancer has a 5-year survival rate of around 50-60%.
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation involves the removal of the entire liver and replacement with a healthy liver from a donor. This surgery is reserved for only a small number of patients, such as those with cirrhosis as a primary underlying issue.
Prognosis after liver transplantation for stage 1 liver cancer is generally favorable, with a 5-year survival rate of around 70-75%.
| Surgical Treatment for Stage 1 Liver Cancer: Comparing Resection and Liver Transplantation | |
|---|---|
| Procedure | 5-year survival rate |
| Resection | 50-60% |
| Liver Transplantation | 70-75% |
While both resection and liver transplantation can be effective in treating stage 1 liver cancer, the decision on which surgery to choose depends on several factors such as tumor location, size, and overall health of the patient
It is important to discuss surgical treatment options with a hepatobiliary surgeon or a transplant specialist to determine the best approach for individual cases.
Radiation Therapy for Stage 1 Liver Cancer
Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles to destroy cancer cells and can be a potentially effective treatment for stage 1 liver cancer. It is sometimes used as an alternative treatment for patients who cannot undergo surgery due to their overall health or the size or location of their tumors.
Types of Radiation Therapy
Two types of radiation therapy are commonly used for treating liver cancer: external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) and brachytherapy.
| External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) | Brachytherapy |
|---|---|
| Uses a machine that aims radiation beams from outside the body at the liver cancer. | Involves the insertion of tiny radioactive beads directly into the liver. |
| Usually given over several weeks with visits every weekday. | Typically a one-time procedure. |
| May cause side effects such as fatigue, skin changes, and gastrointestinal symptoms. | May cause diarrhea, nausea, or pain in the liver area but with a lower risk of damaging surrounding healthy tissue. |
Side Effects of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy can cause side effects that vary depending on the type of therapy and the individual. Common side effects include fatigue, skin irritation, and gastrointestinal problems. In rare cases, radiation therapy can damage the liver, leading to complications such as liver failure.
It is important to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider and report any symptoms to them promptly to ensure proper management of complications.
Impact on Life Expectancy
The effect of radiation therapy on life expectancy for stage 1 liver cancer patients is not fully understood. While some studies have shown positive outcomes, others have shown no significant improvement. However, radiation therapy may be useful in controlling symptoms and providing palliative care for those with advanced-stage cancer.
Overall, radiation therapy is a potential treatment option that may be effective for stage 1 liver cancer. However, it is important to discuss the benefits, risks, and potential outcomes of radiation therapy with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for individual patients.
Targeted Drug Therapies for Stage 1 Liver Cancer
Targeted drug therapies for stage 1 liver cancer are medications that use a unique approach to cancer treatment. They work by targeting specific genes and proteins that play a role in the growth and spread of cancer cells. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which can damage normal cells, targeted therapies aim to destroy cancer cells while minimizing side effects.
One example of a targeted therapy for stage 1 liver cancer is sorafenib (Nexavar). This medication works by inhibiting the protein that stimulates cancer cell growth and blood vessel formation. Clinical trials have shown that sorafenib can improve overall survival rates for patients with liver cancer.
Another targeted therapy for stage 1 liver cancer is lenvatinib (Lenvima), which also targets the protein that promotes cancer cell growth. In clinical trials, lenvatinib demonstrated significant improvements in progression-free survival and response rates in patients with advanced liver cancer.
While targeted drug therapies for stage 1 liver cancer have shown promising results in clinical trials, they are not suitable for all patients. Factors such as the patient’s overall health, genetic makeup, and other medical conditions may influence the effectiveness and suitability of targeted therapy treatments.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Less damage to normal cells | Not suitable for all patients |
| Potentially fewer side effects | May require ongoing treatment |
| Improved overall survival rates | May be expensive |
Targeted drug therapies for stage 1 liver cancer may be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy, to improve outcomes and life expectancy. Patients should consult with their healthcare team to determine the best treatment options for their individual needs.
Multidisciplinary Approaches to Treatment
When it comes to stage 1 liver cancer treatment, a multidisciplinary approach is crucial to ensure the best possible outcomes. This approach involves a team of medical specialists who collaborate to develop a personalized treatment plan based on the patient’s unique needs and circumstances.
The team typically includes hepatologists, surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and interventional radiologists. They work together to determine the most appropriate treatment options for the patient, considering factors such as tumor size, location, and overall health status.
For example, a patient with stage 1 liver cancer may undergo surgery to remove the tumor or receive targeted drug therapy to shrink the tumor before surgery. Radiation therapy may also be an option, either on its own or in combination with other treatments.
Each specialist brings their expertise and knowledge to the table, ensuring that the patient receives the most effective and comprehensive care possible. The team also considers the patient’s preferences and goals when developing the treatment plan, ensuring that it aligns with their overall quality of life and long-term prognosis.
A multidisciplinary approach also supports ongoing monitoring and follow-up care, which is essential for ensuring that the patient remains in remission and that any potential recurrence is caught and treated as early as possible.
Follow-up Care and Surveillance
After treatment for stage 1 liver cancer, follow-up care, and surveillance are essential to ensure early detection of any potential recurrence. Regular medical check-ups, imaging scans, and blood tests are necessary to monitor the patient’s health and detect any signs of cancer.
The frequency of follow-up visits may vary based on the patient’s individual case and treatment plan. However, it is common for patients to have follow-up check-ups every three to six months during the first two years after treatment.
During these visits, doctors will perform a physical examination and recommend follow-up imaging tests, such as ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs, to monitor the liver and abdominal area for any signs of cancer.
Blood tests may also be conducted to check for specific tumor markers that can indicate cancer recurrence. These include alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin (DCP) tests.
Regular follow-up care and surveillance are critical to identifying any potential recurrence early and ensuring timely treatment. Patients are encouraged to maintain a healthy lifestyle, attend all follow-up appointments, and discuss any concerning symptoms with their healthcare provider.
Lifestyle Factors and Life Expectancy
The influence of lifestyle factors on the life expectancy of stage 1 liver cancer patients cannot be overstated. Proper nutrition can improve the effectiveness of treatment, alleviate symptoms, and boost overall health and well-being.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that help support the immune system when battling cancer. Consuming moderate amounts of lean protein and low-fat dairy products can also be beneficial in maintaining muscle mass and bone health.
Equally important is regular physical activity, which can help boost energy, minimize the side effects of treatment, and decrease stress levels. Whether it is walking, practicing yoga, or engaging in resistance training, exercise can aid in maintaining body weight and improving overall quality of life.
Conversely, excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can severely impact a patient’s prognosis. Alcohol is known to increase the risk of liver cancer, and continued consumption can worsen the condition and slow down recovery. Similarly, smoking can also inhibit healing and increase the likelihood of recurrence.
While lifestyle factors alone cannot cure liver cancer, they are important adjunctive therapies that can help in the management of the disease. Incorporating healthy habits into one’s everyday routine can increase the chances of survival and long-term success in fighting liver cancer.
Research Advances and Future Outlook
Research advances in the field of stage 1 liver cancer are ongoing, with many promising developments in the pipeline. In recent years, precision medicine has emerged as a viable approach to treat cancer, including stage 1 liver cancer. Targeted therapies that focus on specific genetic mutations are being developed to improve treatment efficacy and minimize side effects.
Clinical trials are also underway to explore new treatments for stage 1 liver cancer, including immunotherapy, which aims to boost the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells. Another avenue of research has been exploring the use of nanoparticles to deliver drugs directly to the tumor site, which could improve drug uptake and reduce toxicity.
Futuristic technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are also being investigated to improve cancer diagnoses and personalized treatment planning. AI can analyze vast amounts of data, including patient histories, genetic profiles, and treatment outcomes, to identify patterns and predict the most effective treatments for individual patients.
Potential Future Therapies for Stage 1 Liver Cancer
| Therapy Type | Description | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Targeted Therapy | Focuses on specific mutations in cancer cells with minimal impact on normal cells | Improved treatment efficacy and reduced toxicity |
| Immunotherapy | Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells | Potentially improved survival rates and reduced side effects |
| Nanoparticle Drug Delivery | Uses tiny particles to deliver drugs directly to the tumor site | Improved drug uptake and reduced toxicity |
| Artificial Intelligence | Uses machine learning algorithms to analyze patient data and predict the most effective treatments | Improved treatment planning and personalized care |
While the future holds much promise for stage 1 liver cancer treatment, continued research is necessary to ensure that emerging therapies are safe and effective for patients. As research advances, patients must receive access to cutting-edge treatments through clinical trials and other avenues, ultimately leading to improved life expectancy and better quality of life.
Support and Resources for Stage 1 Liver Cancer Patients
Receiving a diagnosis of stage 1 liver cancer can be overwhelming and stressful, not only for the patient but also for their loved ones. However, it is important to remember that there are various resources and support networks available to help you navigate this journey.
Organizations such as the American Cancer Society, Liver Cancer Foundation, and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network offer valuable information on coping strategies, treatment options, and financial assistance. These organizations can also connect you to local support groups, where you can meet other patients and share experiences.
In addition to these organizations, healthcare facilities often provide various resources for patients, including dietitians, counselors, and nurse navigators. These professionals can provide emotional support, nutritional guidance, and help with managing treatment-related side effects.
Online resources such as the American Liver Foundation and Liver Cancer Connect offer educational materials, webinars, and discussion forums that allow patients and their families to learn about liver cancer and connect with others in similar situations.
Remember, seeking support is an essential aspect of coping with a diagnosis of stage 1 liver cancer. You are not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to help you every step of the way.
FAQ
What is stage 1 liver cancer?
Stage 1 liver cancer refers to an early stage of liver cancer where the tumor is still confined to the liver and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs.
What are the symptoms of stage 1 liver cancer?
In many cases, stage 1 liver cancer may not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, some individuals may experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or jaundice.
How is stage 1 liver cancer diagnosed?
Stage 1 liver cancer is typically diagnosed through imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, and confirmed with a biopsy. Blood tests may also be conducted to assess liver function and evaluate tumor markers.
What are the prognostic factors for stage 1 liver cancer?
The prognosis for stage 1 liver cancer is influenced by various factors, including the size of the tumor, the presence of vascular invasion, liver function, and the overall health of the patient.
What is the life expectancy for stage 1 liver cancer?
The life expectancy for individuals with stage 1 liver cancer can vary depending on several factors. On average, the 5-year survival rate for stage 1 liver cancer is around 50% to 70%, indicating a favorable prognosis.
What are the treatment options for stage 1 liver cancer?
Treatment options for stage 1 liver cancer may include surgical resection, liver transplantation, radiation therapy, targeted drug therapies, or a combination of these approaches. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the size and location of the tumor, the liver function, and the overall health of the patient.
How does surgical treatment affect life expectancy for stage 1 liver cancer?
Surgical treatments, such as resection or liver transplantation, can have a significant impact on life expectancy for stage 1 liver cancer patients. Successful removal of the tumor or transplantation of a healthy liver can increase the chances of long-term survival.
What is the role of radiation therapy in stage 1 liver cancer?
Radiation therapy may be used in stage 1 liver cancer as a localized treatment to target and destroy cancer cells. It can help reduce the size of the tumor and improve the chances of long-term survival.
Can targeted drug therapies improve life expectancy for stage 1 liver cancer?
Targeted drug therapies, such as sorafenib or lenvatinib, have shown promise in the treatment of stage 1 liver cancer. These medications can help slow down the progression of the disease and improve overall prognosis, potentially extending life expectancy.
What is a multidisciplinary approach to treatment for stage 1 liver cancer?
A multidisciplinary approach involves a team of specialists, including surgeons, oncologists, radiation oncologists, and hepatologists, working together to develop a personalized treatment plan for stage 1 liver cancer patients. This approach takes into account the individual’s specific condition, overall health, and treatment goals to optimize outcomes.
Why is follow-up care important for stage 1 liver cancer patients?
Follow-up care, including regular medical check-ups, imaging scans, and blood tests, is crucial for monitoring the patient’s condition, detecting any signs of recurrence or progression, and ensuring early intervention. It plays a vital role in managing the disease and maximizing life expectancy.
How do lifestyle factors impact the life expectancy of stage 1 liver cancer patients?
Lifestyle factors, such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking, can contribute to improved overall health and potentially enhance life expectancy for stage 1 liver cancer patients.
What are the latest research advances in the treatment of stage 1 liver cancer?
Ongoing research in the field of stage 1 liver cancer focuses on novel therapies, such as immunotherapies and targeted therapies, as well as advancements in surgical techniques and detection methods. These research advances hold promise for improving life expectancy and overall outcomes for patients.
Where can stage 1 liver cancer patients find support and resources?
Stage 1 liver cancer patients and their families can access support networks and resources offered by organizations such as the American Cancer Society, Liver Cancer Connect, and local cancer centers. These resources provide valuable information, emotional support, and assistance throughout the treatment journey.