Kidney cancer is one of the most common types of cancer affecting the urinary system, with cases steadily increasing worldwide. While advances in treatment and early detection have improved survival outcomes, the prognosis can vary significantly depending on multiple factors such as stage, type, overall health, and age. Many patients and families are particularly interested in understanding kidney cancer survival rates by age, as age plays a critical role in treatment response and long-term outlook.
In this article, we will explore kidney cancer from its definition and types to its causes, risk factors, and treatment options. We will also take a closer look at how survival rates differ across age groups, supported by the latest research and innovations. Additionally, we will discuss prevention strategies, coping mechanisms, and patient support resources to provide a comprehensive guide for those seeking information about kidney cancer.
Definition and Overview
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, begins in the kidneys, the bean-shaped organs that filter waste and balance fluids in the body. The most common type is renal cell carcinoma (RCC), which accounts for about 90% of all kidney cancers. While kidney cancer can affect people at any age, it is most frequently diagnosed in adults over 50 years old.
Understanding the basics of kidney cancer is essential because early detection and proper treatment significantly improve outcomes. The disease may remain unnoticed in its early stages but can become more aggressive if not addressed promptly.
Types of Kidney Cancer
The main types of kidney cancer include:
- Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC): The most common form, with several subtypes such as clear cell, papillary, and chromophobe.
- Transitional Cell Carcinoma (TCC): Occurs in the lining of the renal pelvis.
- Wilms Tumor: A rare kidney cancer that typically affects children.
- Renal Sarcoma: Extremely rare and originates in the connective tissues of the kidney.
Causes and Risk Factors
Although the exact cause of kidney cancer remains unclear, several risk factors increase susceptibility:
- Smoking
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- Family history of kidney cancer
- Long-term dialysis
- Exposure to workplace chemicals like cadmium or asbestos
- Genetic conditions such as von Hippel–Lindau disease
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Kidney cancer often goes undetected until it has advanced. However, some common signs include:
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Persistent back or side pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Fever not caused by infection
- Abdominal lump or swelling
Diagnosis
Doctors use a variety of diagnostic tools to confirm kidney cancer:
- Imaging tests: CT scan, MRI, and ultrasound
- Urinalysis and blood tests: To check kidney function and overall health
- Biopsy: Tissue sample to confirm cancer cells
- Physical examination: To identify any unusual swelling or tenderness
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on cancer stage, overall health, and patient age. The main approaches include:
- Surgery: Partial or radical nephrectomy (removal of part or all of the kidney)
- Targeted therapy: Drugs that block cancer growth at a molecular level
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer
- Radiation therapy: Used in certain cases to relieve symptoms
- Active surveillance: For small, slow-growing tumors in older or high-risk patients
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all kidney cancer cases can be prevented, certain lifestyle choices can lower the risk:
- Quit smoking
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Control blood pressure
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Stay physically active
- Limit exposure to harmful chemicals
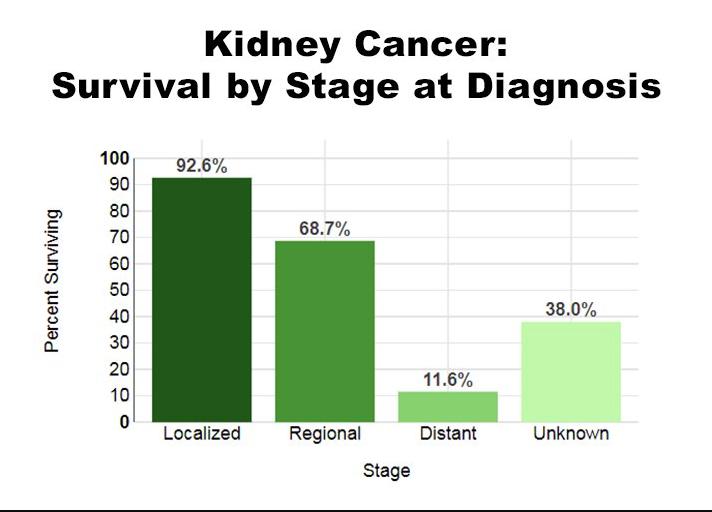
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The outlook for kidney cancer patients has improved due to medical advancements. However, survival rates differ depending on the cancer stage and the patient’s age.
When discussing kidney cancer survival rates by age, studies show that younger patients generally have better outcomes due to stronger immune systems, fewer health complications, and higher treatment tolerance. For example:
- Patients under 50 tend to have higher 5-year survival rates, especially if diagnosed early.
- Patients between 50–70 often face moderate survival outcomes, influenced by co-existing health conditions.
- Patients over 70 may have lower survival rates due to weaker immunity and other chronic illnesses.
According to the American Cancer Society, the overall 5-year relative survival rate for localized kidney cancer is above 90%, but this number decreases for advanced stages and in older age groups.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent breakthroughs in treatment have improved kidney cancer survival rates across all ages. Immunotherapy combinations, such as checkpoint inhibitors, have shown promising results. Precision medicine and genetic testing are also helping doctors tailor treatments based on individual patient profiles. Research continues to focus on reducing side effects and increasing effectiveness for older patients, who are often more vulnerable.
Coping and Support for Patients
A kidney cancer diagnosis can be emotionally and physically challenging. Patients and families can benefit from:
- Support groups and counseling
- Nutrition guidance to maintain strength during treatment
- Stress-reducing practices like yoga and meditation
- Financial and practical assistance programs
- Open communication with healthcare providers for emotional reassurance
Conclusion
Kidney cancer is a serious but increasingly manageable disease. Understanding kidney cancer survival rates by age helps patients and families set realistic expectations and make informed decisions about treatment. With early detection, advanced therapies, and supportive care, many patients can achieve positive outcomes and maintain a good quality of life.
FAQ
1. Does age affect kidney cancer survival rates?
Yes, survival rates generally decrease with age, as younger patients often tolerate treatments better than older adults.
2. What is the average survival rate for kidney cancer?
The overall 5-year survival rate is around 75%, but this varies depending on stage and age.
3. Can lifestyle changes improve survival chances?
Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and controlling blood pressure can positively impact survival.
4. Is kidney cancer curable?
If detected early and treated appropriately, kidney cancer can often be cured, especially in younger patients.
5. What is the best treatment for older kidney cancer patients?
Treatment depends on overall health, but many older patients benefit from targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or minimally invasive surgery.