Breast cancer remains one of the most common cancers among women worldwide, making early detection a critical component of reducing mortality rates. Screening programs, guided by standardized codes and diagnostic systems, play an essential role in identifying breast cancer in its earliest stages. One such coding system is the ICD 10, which provides globally recognized codes for diseases, conditions, and medical procedures.
Understanding the ICD 10 breast cancer screening code is crucial for healthcare providers, insurance companies, and patients alike. Not only does it facilitate proper medical documentation, but it also ensures accurate billing, reporting, and continuity of care. This article explores the significance of ICD 10 codes in breast cancer screening, along with essential insights into causes, symptoms, treatments, and supportive care.
Definition and Overview
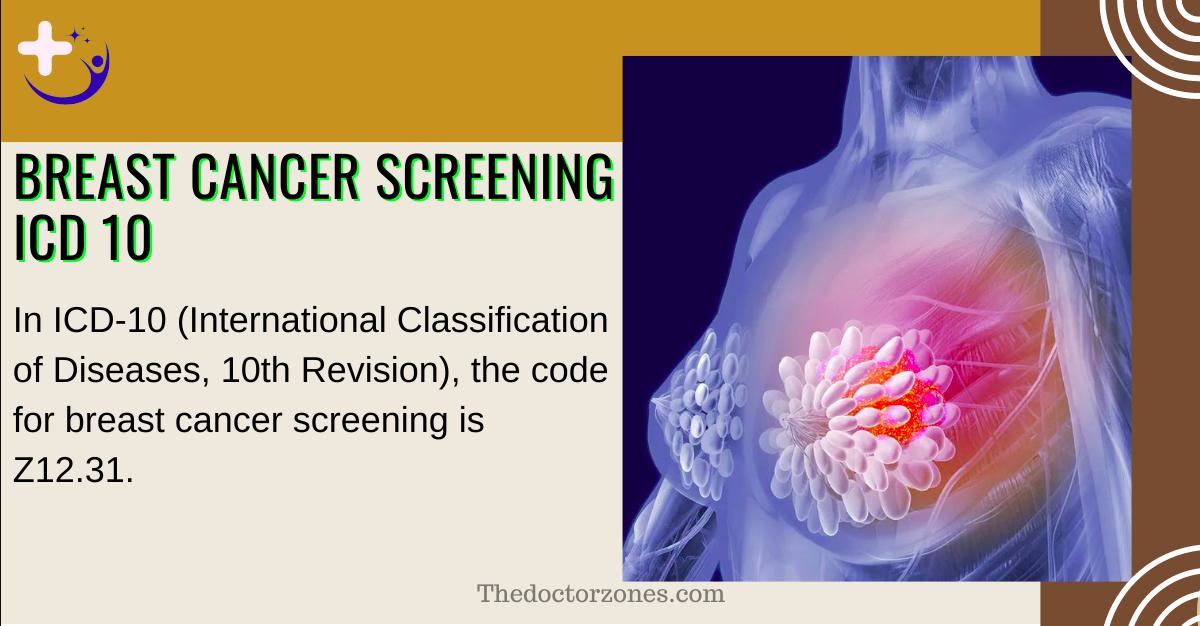
The ICD 10 breast cancer screening code refers to a specific classification within the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision. For breast cancer screening, the ICD 10 code most commonly used is Z12.31 – Encounter for screening mammogram for malignant neoplasm of breast. This code helps track and standardize medical records across different healthcare systems globally.
ICD 10 codes provide clarity for clinicians and insurers, ensuring that breast cancer screenings such as mammograms are properly recorded. This system also supports research, enabling data collection for public health initiatives and cancer prevention strategies.
Types
Breast cancer screening methods include:
- Mammography: The most widely used and recommended screening tool for detecting early breast abnormalities.
- Breast MRI: Used for high-risk patients, especially those with genetic predispositions.
- Ultrasound: Often used as a supplementary test for women with dense breast tissue.
- Clinical Breast Exam (CBE): A physical exam performed by a healthcare provider.
Each screening type may be associated with specific ICD 10 documentation codes, depending on the procedure and clinical context.
Causes and Risk Factors
While ICD 10 codes are primarily administrative, understanding breast cancer causes and risks highlights why screening is vital. Key risk factors include:
- Family history of breast cancer
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic mutations
- Prolonged exposure to estrogen (early menstruation, late menopause)
- Lifestyle factors such as obesity, smoking, and alcohol use
- Previous history of radiation exposure
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Early detection through ICD 10 breast cancer screening often identifies cancer before symptoms develop. However, warning signs may include:
- Lumps or thickening in the breast or underarm
- Changes in breast shape or size
- Nipple discharge or inversion
- Skin dimpling or redness on the breast
Diagnosis
A positive screening result typically leads to diagnostic follow-ups, including:
- Diagnostic mammogram
- Biopsy (fine needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, or surgical biopsy)
- MRI and ultrasound for further imaging clarification
Correct ICD 10 coding ensures these procedures are properly documented for continuity of care.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on cancer stage and patient factors. Common approaches include:
- Surgery (lumpectomy, mastectomy)
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Hormone therapy for hormone receptor-positive cancers
- Targeted therapy (HER2 inhibitors, immunotherapy)
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
Prevention focuses on lifestyle and proactive screenings. Recommendations include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Exercising regularly
- Avoiding smoking
- Undergoing routine mammograms as recommended by healthcare providers
Prognosis and Survival Rates
When detected early through proper screening and documented under ICD 10 breast cancer screening, prognosis improves significantly. The 5-year survival rate for localized breast cancer exceeds 90%. Advanced-stage detection, however, reduces survival outcomes, emphasizing the importance of timely screening.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent innovations include:
- 3D mammography (tomosynthesis) for clearer imaging
- Liquid biopsies for detecting circulating tumor DNA
- AI-assisted mammogram analysis to improve accuracy
- Personalized treatment plans based on genetic profiling
Coping and Support for Patients
A breast cancer diagnosis can be emotionally overwhelming. Patients benefit from:
- Support groups and counseling
- Patient navigation services
- Educational resources to understand ICD 10 codes and treatment processes
- Family and community involvement in care
Conclusion
The ICD 10 breast cancer screening code, particularly Z12.31, is an essential element in modern healthcare documentation. It ensures consistent reporting, accurate billing, and better coordination of care. More importantly, it supports the broader mission of early detection and improved patient outcomes. By understanding the role of ICD 10 codes in breast cancer screening, patients and healthcare providers can work together more effectively toward prevention, timely diagnosis, and successful treatment.
FAQ
What is the ICD 10 code for breast cancer screening?
The most common code is Z12.31 – Encounter for screening mammogram for malignant neoplasm of breast.
Is breast cancer screening covered by insurance if coded under ICD 10?
Yes, most insurance providers recognize ICD 10 codes for breast cancer screening, which helps ensure coverage.
At what age should women start breast cancer screening?
Guidelines vary, but most recommend starting mammograms between ages 40 and 50, with continued screenings every 1–2 years.
Does ICD 10 coding affect patient care?
Yes, accurate ICD 10 coding ensures proper documentation, billing, and continuity of care across healthcare providers.
Can men undergo breast cancer screening with ICD 10 codes?
Yes, although less common, men at risk can also be screened, and ICD 10 codes apply to both genders.