Bladder cancer is a serious condition that often begins with subtle signs that can be mistaken for other urinary tract issues. Detecting the disease at an early stage plays a crucial role in improving treatment outcomes and survival rates. Unfortunately, many people overlook the early symptoms of bladder cancer, delaying diagnosis and allowing the disease to progress.
Understanding the warning signs, risk factors, and available treatments can help individuals take proactive steps toward their health. This article provides a comprehensive overview of bladder cancer, focusing on the early symptoms of bladder cancer, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and the latest research developments.
Definition and Overview
Bladder cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the tissues of the bladder, the organ responsible for storing urine. Most cases begin in the urothelial cells that line the inside of the bladder. It is one of the most common cancers worldwide, especially in older adults.
Types of Bladder Cancer
There are several types of bladder cancer, with the most common being:
- Urothelial carcinoma (transitional cell carcinoma): The most frequent type, accounting for about 90% of cases.
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Linked to chronic irritation or infection of the bladder.
- Adenocarcinoma: A rare form that begins in the bladder’s glandular cells.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of bladder cancer is not always clear, but certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing it:
- Smoking, which exposes the bladder to harmful chemicals.
- Prolonged exposure to industrial chemicals.
- Chronic bladder inflammation or infections.
- Family history of bladder cancer.
- Previous cancer treatments involving radiation or chemotherapy.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
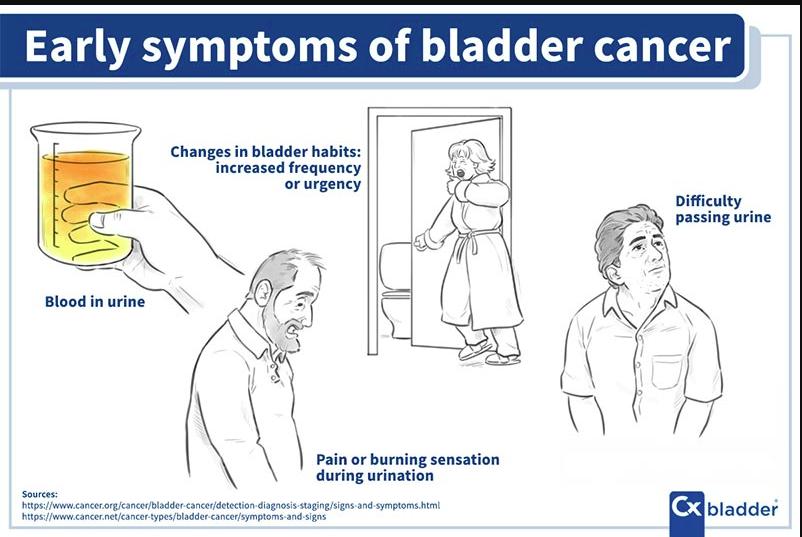
Recognizing the early symptoms of bladder cancer can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment. Common early warning signs include:
- Blood in urine (hematuria): The most noticeable symptom, which may cause urine to appear pink, red, or cola-colored.
- Frequent urination: A sudden increase in the need to urinate.
- Pain or burning sensation during urination.
- Urgency to urinate even when the bladder is not full.
These early symptoms of bladder cancer may resemble urinary tract infections or kidney problems, making it essential to seek medical evaluation if they persist.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing bladder cancer typically involves several tests, such as:
- Urinalysis and urine cytology to detect abnormal cells.
- Cystoscopy, where a small camera is used to examine the bladder.
- Biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
- Imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs to determine the extent of the disease.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. Common approaches include:
- Surgery: To remove cancerous tissue or, in severe cases, the entire bladder.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs used to kill cancer cells before or after surgery.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all cases can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes may lower the risk of bladder cancer:
- Quit smoking to reduce harmful chemical exposure.
- Drink plenty of water to flush toxins from the bladder.
- Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which contain cancer-fighting antioxidants.
- Minimize exposure to workplace chemicals by using proper protective equipment.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for bladder cancer largely depends on how early it is detected. When identified in its early stages, the survival rates are significantly higher. The five-year survival rate for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer is around 70–90%, but this drops for more advanced stages.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent advancements in bladder cancer research focus on precision medicine, targeted therapies, and advanced diagnostic techniques. Liquid biopsies, genetic profiling, and new immunotherapy drugs are offering more personalized treatment options and better outcomes.
Coping and Support for Patients
A bladder cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but support is available. Patients are encouraged to join support groups, seek counseling, and maintain open communication with healthcare providers. Family and friends also play an important role in providing emotional strength and encouragement.
Conclusion
Bladder cancer is a condition where early detection makes a significant difference in treatment success. By recognizing the early symptoms of bladder cancer—such as blood in the urine, frequent urination, and painful urination—individuals can seek medical help promptly. Awareness, preventive measures, and advancements in treatment continue to improve survival rates and quality of life for patients.
FAQ
1. What are the early symptoms of bladder cancer?
The most common early symptoms include blood in the urine, frequent urination, urgency, and pain during urination.
2. Can bladder cancer be cured if detected early?
Yes, early-stage bladder cancer is often highly treatable with surgery and other therapies.
3. Who is most at risk of bladder cancer?
Smokers, older adults, and individuals with prolonged exposure to industrial chemicals are at higher risk.
4. Is bladder cancer hereditary?
While family history can increase the risk, most cases are linked to lifestyle and environmental factors.
5. How can I reduce my risk of bladder cancer?
Avoid smoking, stay hydrated, eat a healthy diet, and minimize exposure to harmful chemicals.