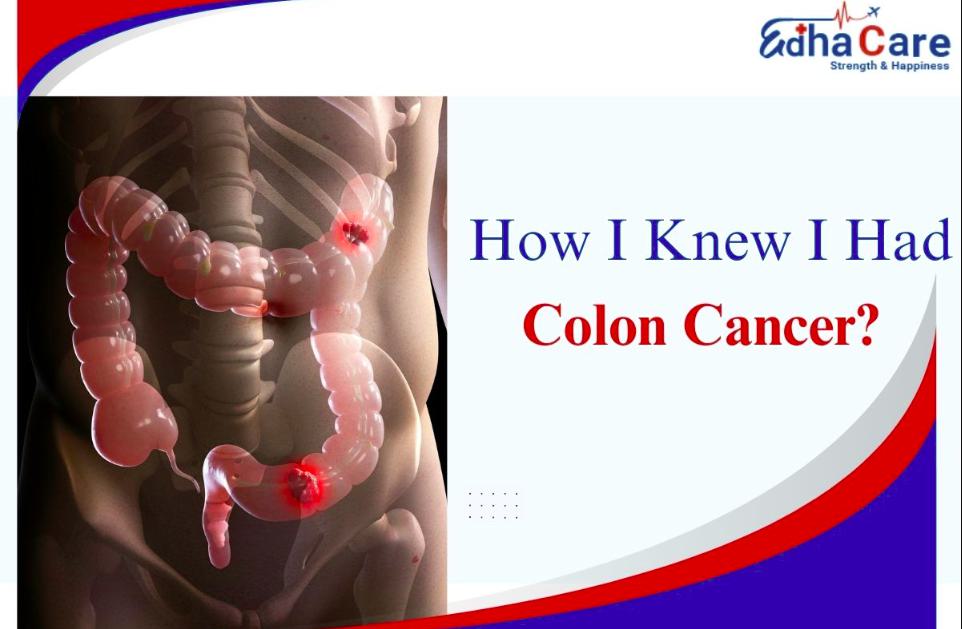
When it comes to serious health conditions, colon cancer is one that often goes unnoticed until symptoms become too significant to ignore. Many people wonder, “how I knew I had colon cancer?” because the disease can progress quietly before showing clear warning signs. Sharing personal experiences and medical insights can help raise awareness and encourage early detection.
This article provides a comprehensive look at colon cancer, from its definition and risk factors to symptoms, treatment, and prevention. Whether you are searching for answers because of personal concerns, supporting a loved one, or simply want to stay informed, understanding the signs and knowledge around colon cancer is crucial for better health outcomes.
Definition and Overview
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, begins in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum. It usually develops from small growths called polyps, which can become cancerous over time if not detected and removed. This type of cancer is one of the most common worldwide, yet it is also one of the most preventable with proper screening.
Types
Colon cancer can vary depending on the type of cells involved:
- Adenocarcinomas: The most common type, forming in the cells that produce mucus in the colon.
- Carcinoid tumors: Develop from hormone-producing cells.
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs): Rare tumors starting in specialized cells of the colon wall.
- Lymphomas: Begin in the immune cells of the colon.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of colon cancer is not always clear, but several factors increase the risk, including:
- Family history of colorectal cancer or polyps
- Age over 50, although younger cases are rising
- Diet high in red or processed meats
- Sedentary lifestyle and obesity
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Certain medical conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
For many people, recognizing how I knew I had colon cancer starts with paying attention to early warning signs such as:
- Persistent changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or narrowing of stool)
- Blood in stool, which may appear bright red or very dark
- Unexplained abdominal pain or cramping
- Sudden weight loss without trying
- Fatigue and weakness
- A feeling that the bowel does not empty completely
Diagnosis
If symptoms are present, doctors may recommend diagnostic tests such as:
- Colonoscopy: The most effective method to detect and remove polyps.
- Stool tests: To identify hidden blood or abnormal DNA.
- Imaging scans: CT scans or MRIs to determine the spread of cancer.
- Biopsy: Taking a tissue sample for laboratory testing.
Treatment Options
Treatment for colon cancer depends on the stage and overall health of the patient. Common options include:
- Surgery: Removing cancerous sections of the colon.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy: Often used when cancer affects the rectum.
- Targeted therapy and immunotherapy: Advanced options for certain patients.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all cases are preventable, steps to reduce risk include:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Limiting red and processed meats
- Staying physically active
- Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol
- Undergoing regular screenings, especially after age 45 or earlier with a family history
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Prognosis depends on the stage at diagnosis. When colon cancer is found early, survival rates are significantly higher. According to recent statistics, the 5-year survival rate for localized colon cancer can be over 90%. However, the survival rate decreases if the cancer has spread to distant organs, highlighting the importance of early detection.
Latest Research and Innovations
Research in colon cancer treatment is advancing rapidly. Some notable innovations include:
- Liquid biopsies for early detection through blood samples
- Artificial intelligence in colonoscopy to detect polyps more accurately
- Immunotherapy drugs that boost the body’s natural defenses against cancer
- Personalized medicine, tailoring treatment to a patient’s genetic profile
Coping and Support for Patients
A colon cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. Coping strategies may include:
- Joining support groups for emotional strength
- Seeking counseling or therapy to manage stress
- Maintaining open communication with family and healthcare providers
- Following a healthy lifestyle to support treatment and recovery
Conclusion
Understanding how I knew I had colon cancer can help others recognize the warning signs and seek medical advice early. Colon cancer may start quietly, but knowledge, awareness, and proactive health care make a life-saving difference. Prioritizing screenings, healthy habits, and timely treatment can greatly improve outcomes and provide hope for those facing this condition.
FAQ
1. What was the first sign of colon cancer for many patients?
Changes in bowel habits or blood in the stool are often the first noticeable signs.
2. Can young adults get colon cancer?
Yes, although it is more common in older adults, colon cancer cases in people under 50 are increasing.
3. Is colon cancer hereditary?
Family history can increase the risk, especially with inherited syndromes like Lynch syndrome.
4. How is colon cancer treated in its early stages?
Often, surgery alone is enough to remove polyps or localized tumors.
5. How can I reduce my risk of colon cancer?
Adopting a healthy diet, staying active, avoiding smoking, and getting regular screenings are key steps.