Colorectal cancer, often referred to as colon cancer, is one of the most common types of cancer affecting both men and women worldwide. Understanding cuales son los sintomas del cancer de colon (what are the symptoms of colon cancer) is essential for early detection and successful treatment. While the disease often develops silently, recognizing its warning signs can make a significant difference in outcomes.
In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about colon cancer—from its definition, causes, and risk factors to its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Whether you are concerned about your health or supporting a loved one, this comprehensive guide will help you stay informed and proactive.
Definition and Overview
Colon cancer begins in the large intestine (colon), the final part of the digestive tract. It usually starts as small, noncancerous clumps of cells called polyps that can gradually turn into cancer over time. Detecting these polyps early through screening tests can help prevent the development of colon cancer.
The condition is often associated with age, lifestyle, and genetic factors. Most cases occur in adults over 50, but recent studies show that it’s increasingly affecting younger populations as well.
Types of Colon Cancer
There are several types of colon cancer, categorized by the cells where the cancer begins:
- Adenocarcinomas – The most common type, making up over 90% of cases, starts in the mucus-producing glands of the colon.
- Carcinoid tumors – These begin in hormone-producing cells of the intestine.
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) – Rare tumors that form in the connective tissue of the colon.
- Lymphomas – Cancers that start in the immune system cells of the colon.
- Sarcomas – Tumors that originate in blood vessels, muscles, or connective tissues within the colon wall.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of colon cancer is not always clear, several risk factors increase a person’s likelihood of developing the disease:
- Age: Risk increases after age 50.
- Family history: A close relative with colon cancer raises the risk.
- Genetic mutations: Conditions like Lynch syndrome or familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP).
- Diet: High consumption of red or processed meats.
- Lifestyle: Sedentary habits, smoking, and excessive alcohol use.
- Obesity: Being overweight can heighten the risk.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases: Such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
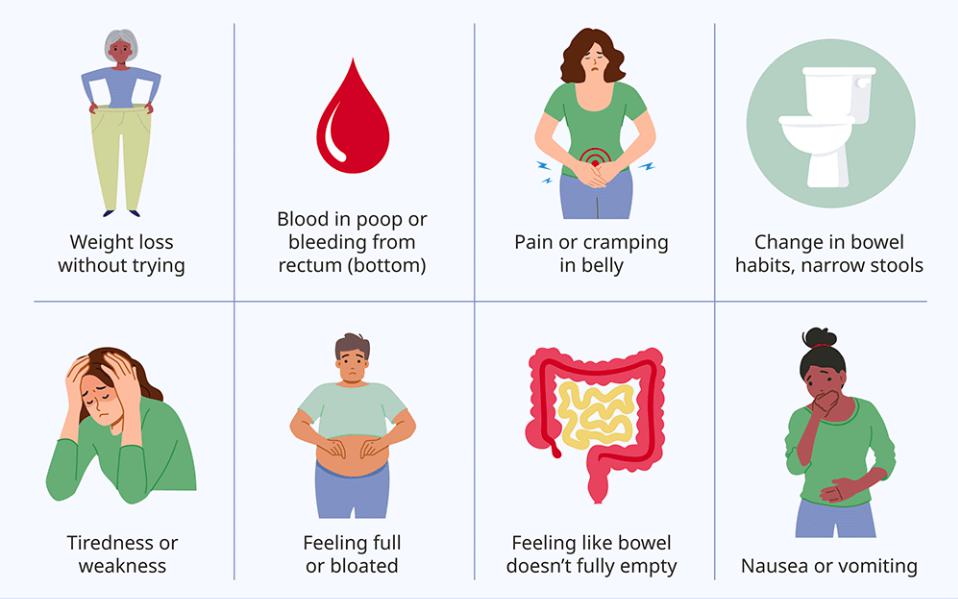
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Recognizing cuales son los sintomas del cancer de colon is critical for early diagnosis. Symptoms may vary depending on the stage and location of the cancer, but common signs include:
- Persistent changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or narrow stools)
- Blood in the stool or rectal bleeding
- Abdominal discomfort, cramps, or bloating
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue or weakness
- A feeling that the bowel doesn’t empty completely
- Iron-deficiency anemia
In the early stages, colon cancer may cause no symptoms, which is why regular screenings such as colonoscopies are vital.
Diagnosis
To confirm a diagnosis, doctors use several tests, including:
- Colonoscopy – The gold standard for detecting polyps or tumors.
- Fecal occult blood test (FOBT) – Checks for hidden blood in the stool.
- CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy) – A non-invasive imaging option.
- Biopsy – Tissue samples examined under a microscope to confirm cancer.
- Blood tests – To evaluate organ function and detect tumor markers like CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen).
Treatment Options
Treatment for colon cancer depends on the stage, overall health, and patient preferences. Common approaches include:
- Surgery – The most common treatment, involving the removal of cancerous sections of the colon.
- Chemotherapy – Drugs used to kill cancer cells or prevent their growth.
- Radiation therapy – Often used for rectal cancer or to shrink tumors before surgery.
- Targeted therapy – Drugs that specifically attack cancer cells with minimal damage to healthy tissue.
- Immunotherapy – Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer more effectively.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
Prevention plays a key role in reducing colon cancer risk. Experts recommend:
- Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Limiting red and processed meats
- Exercising regularly
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol
- Getting regular screenings starting at age 45 or earlier if you have risk factors
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for colon cancer depends heavily on the stage at diagnosis. When detected early (Stage I or II), the five-year survival rate can exceed 90%. However, in advanced stages where cancer has spread to other organs, survival rates drop significantly.
Modern treatment advancements, early detection programs, and genetic testing continue to improve survival outcomes globally.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent medical research focuses on improving early detection and personalized treatment. Innovations include:
- Liquid biopsy – Detecting cancer DNA fragments in blood for early screening.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) – Enhancing colonoscopy accuracy by identifying small or flat polyps.
- New immunotherapies – Tailored to individual genetic profiles for better response rates.
- Microbiome studies – Exploring the link between gut bacteria and colon cancer risk.
Coping and Support for Patients
A colon cancer diagnosis can be emotionally overwhelming. Support systems play a crucial role in recovery and quality of life. Patients are encouraged to seek:
- Emotional support through counseling or support groups
- Nutritional guidance to maintain strength during treatment
- Physical therapy to manage fatigue and restore energy
- Patient advocacy organizations for information and assistance
Maintaining mental well-being and open communication with healthcare providers can make a significant difference in coping with treatment.
Conclusion
Understanding cuales son los sintomas del cancer de colon is vital for early detection and prevention. While colon cancer can be life-threatening, it is often treatable—especially when caught early. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, staying informed, and undergoing regular screenings are the best ways to protect yourself and your loved ones.
FAQ
1. What are the first signs of colon cancer?
Common early signs include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, and unexplained fatigue or weight loss.
2. Can colon cancer be cured?
Yes, especially when detected early. Surgery combined with other treatments often leads to full recovery.
3. At what age should I start screening for colon cancer?
Most guidelines recommend beginning at age 45, but earlier if you have family history or genetic risks.
4. How fast does colon cancer spread?
It varies, but in most cases, colon cancer develops slowly over several years from precancerous polyps.
5. Is colon cancer hereditary?
Yes, certain genetic mutations such as Lynch syndrome increase the risk of developing colon cancer.