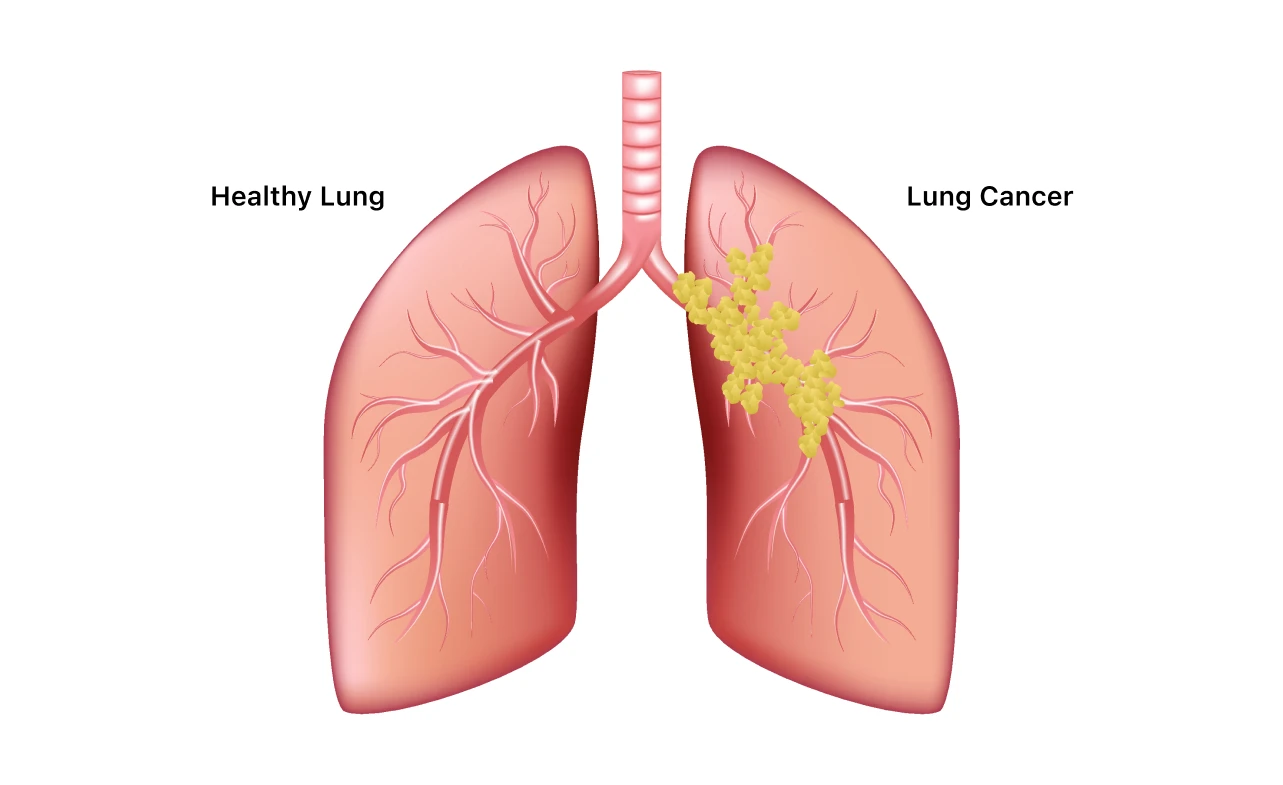
Stage 2 Lung Cancer Treatment – Getting a stage 2 lung cancer diagnosis can feel scary. But knowing about the disease and treatment choices is important. Treatment for stage 2 lung cancer usually includes surgery, chemotherapy, or both. The right treatment depends on the person’s situation, and starting treatment early is crucial.
Dealing with stage 2 lung cancer needs a detailed plan. This plan considers the disease’s specifics and the patient’s health. By looking at all treatment options, people can work with their doctors to create a plan that fits them. A team approach, using different treatments, often leads to the best outcomes.
Understanding Stage 2 Lung Cancer Treatment
Lung cancer symptoms can vary. It’s key to know about stage 2 lung cancer to plan treatment. At this stage, cancer is mainly in the lungs but might have spread to nearby lymph nodes. Early treatment is vital to stop the cancer from getting worse.
In oncology, lung cancer stages are based on tumor size and spread. Accurate staging is crucial for the right treatment. Knowing lung cancer symptoms and stages helps patients and their healthcare team create a tailored treatment plan.
Characteristics of Stage 2 Lung Cancer
Some common traits of stage 2 lung cancer include:
- Tumors that are larger than 4 cm but smaller than 7 cm
- Cancer that has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- No distant metastasis
Importance of Early Treatment
Early treatment is key for lung cancer patients. Seeing a doctor at the first sign of symptoms can lead to better outcomes. In oncology, early action is often the best way to stop cancer from getting worse.
Surgical Options for Stage 2 Lung Cancer
Cancer surgery is a common treatment for stage 2 lung cancer. Surgical oncology is key in treating lung cancer. The decision to have surgery depends on the tumor’s size and location.
There are several surgical procedures for stage 2 lung cancer. These include lobectomy and pneumonectomy. Here are the benefits and risks of these procedures:
- Lobectomy: removal of the affected lobe of the lung
- Pneumonectomy: removal of the entire lung
- Segmentectomy: removal of a smaller section of the lung
Talking to a healthcare professional is important for lung cancer treatment. They can help decide the best treatment. Experts in surgical oncology guide patients in making informed choices.
<table>
Chemotherapy as Primary Treatment Strategy
Chemotherapy is a common way to treat cancer. It targets and destroys cancer cells. In stage 2 lung cancer, it’s used to control cancer growth and spread.
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. This can shrink tumors and ease symptoms. It’s a key part of lung cancer treatment.
Knowing about chemotherapy in lung cancer treatment is important. Side effects can be big, but they can be managed. Working with a healthcare team helps create a treatment plan that suits you.
Common Chemotherapy Drugs
- Cisplatin
- Carboplatin
- Docetaxel
- Gemcitabine
Treatment cycles and length vary based on the chemotherapy plan and patient needs. Chemotherapy is given in cycles. Each cycle has treatment and rest periods. This helps the body recover and reduces long-term damage risk.
Managing Side Effects
Chemotherapy side effects can be tough, but they can be managed. Patients can work with their healthcare team to lessen side effects. This includes medicines for nausea and vomiting, and other support to handle chemotherapy’s physical and emotional effects.
Radiation Therapy Approaches
Radiation therapy is a common treatment for stage 2 lung cancer. It uses high-energy particles or waves to kill cancer cells. This method can be used alone or with other treatments like surgery or chemotherapy.
There are different types of radiation therapy. These include external beam radiation therapy, internal radiation therapy, and stereotactic body radiation therapy. Each type has its own benefits and limitations. The choice depends on the patient’s needs and the cancer’s characteristics.
Some benefits of radiation therapy for lung cancer include:
- It’s non-invasive, which reduces the risk of complications and side effects.
- It can treat tumors that are hard to reach with surgery.
- It can be combined with other treatments, like chemotherapy, to work better.
Radiation therapy can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for stage 2 lung cancer patients. A personalized treatment plan, developed with a healthcare team, ensures the most effective therapy for each patient.
| Type of Radiation Therapy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| External Beam Radiation Therapy | Uses a machine outside the body to deliver radiation | Non-invasive, can be used to treat large tumors |
| Internal Radiation Therapy | Uses a small implant to deliver radiation directly to the tumor | Can be used to treat small tumors, reduces side effects |
| Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy | Uses a specialized machine to deliver high doses of radiation to small tumors | Can be used to treat small tumors, reduces side effects and treatment time |
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy Options
For stage 2 lung cancer patients, targeted therapy and immunotherapy are promising. These treatments focus on specific targets or immune mechanisms to fight cancer. Targeted therapy uses drugs that target genes or proteins in cancer cells.
Immunotherapy uses the immune system to attack cancer cells. It includes checkpoint inhibitors and vaccine-based therapies. These options offer targeted and effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Molecular Testing
Molecular testing is key for targeted therapy and immunotherapy. It analyzes tumor samples for genetic mutations or biomarkers. This helps doctors choose the best treatment for each patient.
Available Targeted Drugs
Many targeted drugs are available for stage 2 lung cancer. These include drugs for EGFR, ALK, and ROS1 genes. They have shown great results in clinical trials and can be used with other treatments.
Immunotherapy protocols like pembrolizumab and nivolumab also show promise. They help the immune system fight lung cancer.
Immunotherapy Protocols
Immunotherapy for stage 2 lung cancer combines treatments. It includes checkpoint inhibitors, vaccine-based therapies, and cytokine-based therapies. These aim to boost the immune system to fight cancer cells.
By exploring these options, patients can work with doctors to create a personalized treatment plan. This plan addresses their unique needs and circumstances.
Integrative Treatment Approaches
When treating stage 2 lung cancer, integrative medicine is key. It mixes traditional treatments with natural therapies like acupuncture and meditation. This creates a complete plan for treating cancer.
Benefits of cancer integrative treatment include fewer symptoms and better mood. Patients can also feel more in control of their health. Here are some integrative treatments:
- Nutrition counseling to promote healthy eating and manage treatment side effects
- Acupuncture to reduce pain and improve sleep quality
- Meditation and mindfulness practices to reduce stress and anxiety
- Yoga and other exercise programs to improve physical function and overall health
Exploring integrative medicine helps patients with stage 2 lung cancer. They can make a treatment plan that fits their needs. Always talk to a healthcare provider about these options.
| Treatment Approach | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrition Counseling | Improved nutrition, reduced side effects | None |
| Acupuncture | Pain reduction, improved sleep | Minor bleeding, bruising |
| Meditation and Mindfulness | Reduced stress, improved mood | None |
Managing Treatment Side Effects
When fighting stage 2 lung cancer, patients face many side effects. Cancer side effects can be physical, like tiredness, nausea, and pain. They can also be emotional, such as feeling anxious or depressed. It’s key to find ways to handle these side effects, both physical and emotional.
To manage side effects well, a full approach is needed. This includes medical help, emotional support, and practical tips. Patients should talk to their healthcare team to figure out how to lessen side effects. They might use medicine, change their lifestyle, or try things like meditation and acupuncture.
Physical Side Effects
- Fatigue and weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain and discomfort
Emotional Impact
Cancer treatment can really affect a person’s mood. Many feel anxious, depressed, or stressed. Cancer coping strategies can help manage these feelings. This might include talking to a counselor, joining a support group, or doing yoga and meditation.
Coping Strategies
It’s vital to find good ways to cope with cancer side effects. Working with your healthcare team is a big help. They can guide you on how to deal with both physical and emotional challenges. This way, you can better handle your cancer side effects and feel better overall.
Recovery and Rehabilitation Process
After beating stage 2 lung cancer, patients start their recovery journey. This is a crucial time for getting back to normal. The right care is key to help patients regain their strength and function.
The road to recovery is tough, but with the right help, patients can make it through. Here are some important parts of the recovery and rehabilitation process:
- Follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to monitor progress and address any concerns
- Physical therapy to improve mobility and strength
- Emotional support to cope with the emotional impact of cancer treatment
- Nutritional counseling to promote healthy eating habits
Recovering from cancer needs a full approach. It’s about the patient’s physical, emotional, and social health. With the right care and support, patients can smoothly move into life after treatment.
Support Systems and Resources
Having a strong support network is key for patients with stage 2 lung cancer. This network can include doctors, support groups, and family care resources. These cancer support and resources can greatly help a patient’s treatment journey.
Medical Support Team
A medical support team is vital for patients. They include doctors, nurses, and other healthcare experts in lung cancer treatment. This team offers essential cancer support and resources.
Support Groups
Cancer support groups give patients and their families a sense of community. They offer a place to share experiences, get emotional support, and learn about cancer resources and support.
Family Care Resources
Family care resources are crucial for stage 2 lung cancer patients. They include home care services, counseling, and financial help. These resources help patients manage their treatment and recovery.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| American Cancer Society | Provides cancer support, resources, and information on lung cancer treatment |
| National Cancer Institute | Offers cancer resources, including information on clinical trials and treatment options |
| Lung Cancer Alliance | Provides cancer support, resources, and advocacy for lung cancer patients and their families |
Taking the Next Steps in Your Treatment Journey
Dealing with stage 2 lung cancer treatment can be tough. But, you can play a big role in your care. Talk to your healthcare team about the options in this guide. They will help you find the best plan for you.
Every person’s fight against cancer is different. Your doctor will work with you to make a plan that fits your needs. This way, you can get the right treatment.
It’s key to stay informed and speak up for your health. Learn about new lung cancer treatments. Don’t be afraid to ask questions or get a second opinion if needed. With the right care, many people with stage 2 lung cancer can live better lives.
You’re not fighting this alone. Reach out to your loved ones and cancer support groups for help. They can offer emotional and practical support. Together, you can face this tough time and focus on your health.
Read more: