Cervical cancer is one of the most concerning health challenges for women worldwide, especially when it progresses to advanced stages. Among these, stage 4 cervical cancer represents the most serious form, often associated with significant complications and a more complex treatment journey. Understanding the cervical cancer stage 4 prognosis is essential for patients, families, and healthcare providers to make informed decisions.
This article explores the definition, types, causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, preventive strategies, prognosis, and ongoing research about stage 4 cervical cancer. By examining these aspects in detail, readers will gain valuable insights into how to cope with this condition and what the future holds in terms of medical innovations and patient support.
Definition and Overview
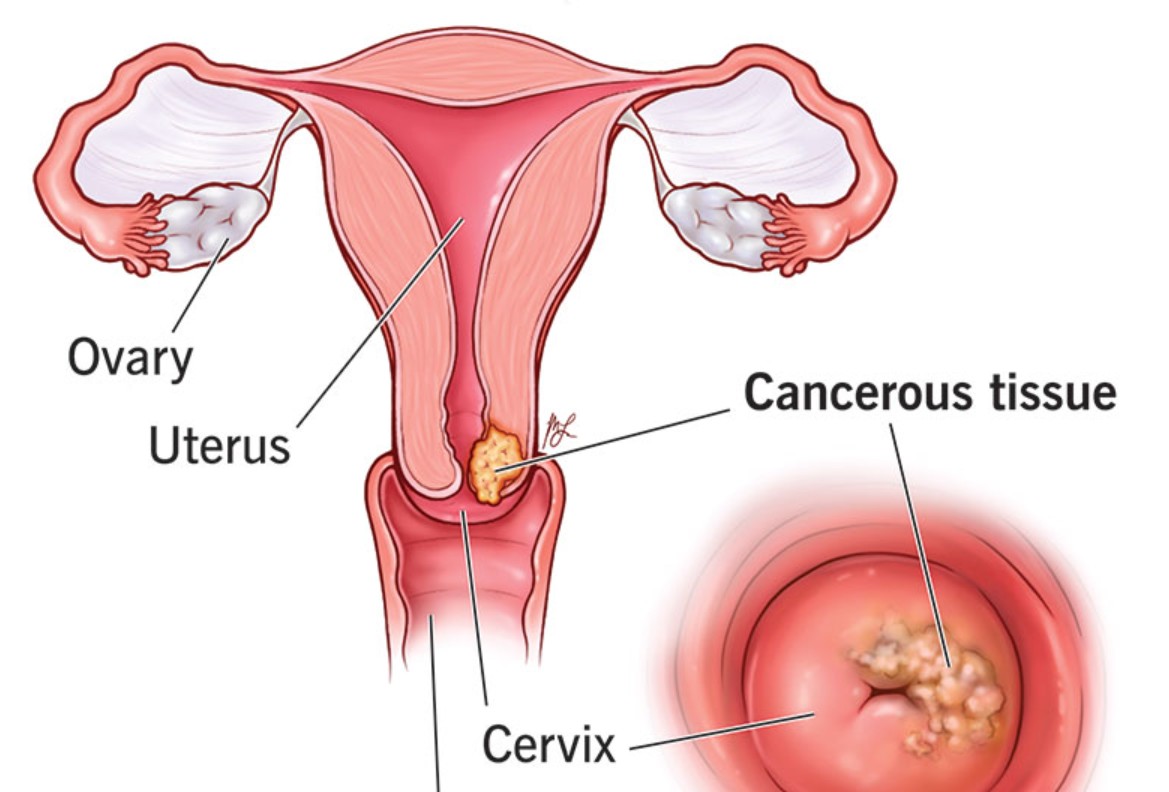
Cervical cancer begins in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. When diagnosed at stage 4, the cancer has spread beyond the pelvis or to distant organs such as the bladder, rectum, lungs, or liver. This makes the condition more difficult to treat compared to earlier stages.
The cervical cancer stage 4 prognosis depends on many factors, including the extent of the spread, the patient’s overall health, and how well the cancer responds to treatment. While the outlook may appear daunting, modern medicine continues to advance, offering new therapies and hope for improved survival.
Types
Stage 4 cervical cancer can be divided into two subcategories:
- Stage IVA: Cancer has spread to nearby organs such as the bladder or rectum.
- Stage IVB: Cancer has spread to distant organs like the lungs, liver, or bones.
Understanding these subtypes helps determine the most appropriate treatment strategy and gives a clearer picture of the patient’s prognosis.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of cervical cancer is persistent infection with high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). However, not all HPV infections lead to cancer. Other contributing factors include:
- Early onset of sexual activity and multiple sexual partners
- Smoking, which increases the risk of cervical cancer
- Weakened immune system due to conditions like HIV
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives
- Family history of cervical cancer
These factors collectively influence the likelihood of developing cervical cancer and may also impact the stage at which the disease is diagnosed.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
In earlier stages, cervical cancer may not cause obvious symptoms. By the time it reaches stage 4, signs are usually more pronounced, including:
- Unusual vaginal bleeding or discharge
- Pelvic or back pain
- Pain during urination or bowel movements
- Swelling in the legs due to lymphatic obstruction
- Fatigue and unexplained weight loss
Recognizing these symptoms is critical, as timely medical attention can lead to earlier diagnosis and more effective interventions.
Diagnosis
To confirm stage 4 cervical cancer, doctors use a combination of diagnostic tests, including:
- Pelvic examination to check for abnormalities
- Pap smear and HPV testing to detect abnormal cells
- Biopsy to confirm cancer presence
- Imaging tests such as CT, MRI, or PET scans to determine the extent of spread
- Cystoscopy or proctoscopy if the cancer is suspected to involve the bladder or rectum
Accurate staging is essential for tailoring treatment and predicting the cervical cancer stage 4 prognosis.
Treatment Options
While treatment becomes more challenging at stage 4, various strategies are available to manage the disease and improve quality of life. Options include:
- Radiation therapy and chemotherapy: Often used in combination to shrink tumors and control cancer spread.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs that attack specific cancer cell mechanisms, such as bevacizumab.
- Immunotherapy: Helps the immune system recognize and fight cancer cells more effectively.
- Palliative care: Focuses on relieving symptoms, reducing pain, and enhancing the patient’s quality of life.
Treatment choice depends on whether the cancer is localized to nearby organs or has spread to distant sites.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While stage 4 cervical cancer cannot be reversed through lifestyle alone, preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer in the first place:
- HPV vaccination for adolescents and young adults
- Routine Pap smears and HPV testing for early detection
- Safe sexual practices to lower HPV exposure
- Quitting smoking to improve overall cervical health
- Healthy diet and exercise to support immune function
Even after diagnosis, adopting a balanced lifestyle can support treatment effectiveness and overall well-being.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The cervical cancer stage 4 prognosis is generally less favorable compared to earlier stages. According to medical statistics, the five-year survival rate for stage IVA ranges from 15% to 20%, while for stage IVB, it drops to around 5% to 10%.
However, survival rates are averages and do not determine individual outcomes. Factors such as the patient’s age, health condition, access to advanced treatment, and response to therapy all play crucial roles in shaping prognosis.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent advancements in medical research offer hope for improving the outlook of stage 4 cervical cancer patients. Innovations include:
- Immunotherapy breakthroughs, such as checkpoint inhibitors, showing promising results in clinical trials
- Personalized medicine, tailoring treatment based on genetic profiles
- Combination therapies, using multiple treatment approaches for better outcomes
- Minimally invasive surgical techniques to reduce recovery time and complications
These developments continue to enhance treatment effectiveness and may improve the cervical cancer stage 4 prognosis in the near future.
Coping and Support for Patients
A diagnosis of stage 4 cervical cancer can be overwhelming, both emotionally and physically. Patients benefit greatly from comprehensive support systems that include:
- Counseling and mental health support to manage anxiety and depression
- Support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges
- Nutritional guidance and physical therapy to maintain strength and resilience
- Palliative care services to improve comfort and quality of life
Family involvement and open communication with healthcare providers also play a crucial role in coping with this stage of the disease.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer stage 4 prognosis may present significant challenges, but it is not without hope. Advances in treatment options, preventive strategies, and supportive care continue to evolve, offering patients better management and improved quality of life.
While survival rates may be lower at this stage, each patient’s journey is unique, shaped by individual health factors and treatment responses. Staying informed, accessing comprehensive care, and embracing supportive resources can make a profound difference in navigating stage 4 cervical cancer with resilience and strength.