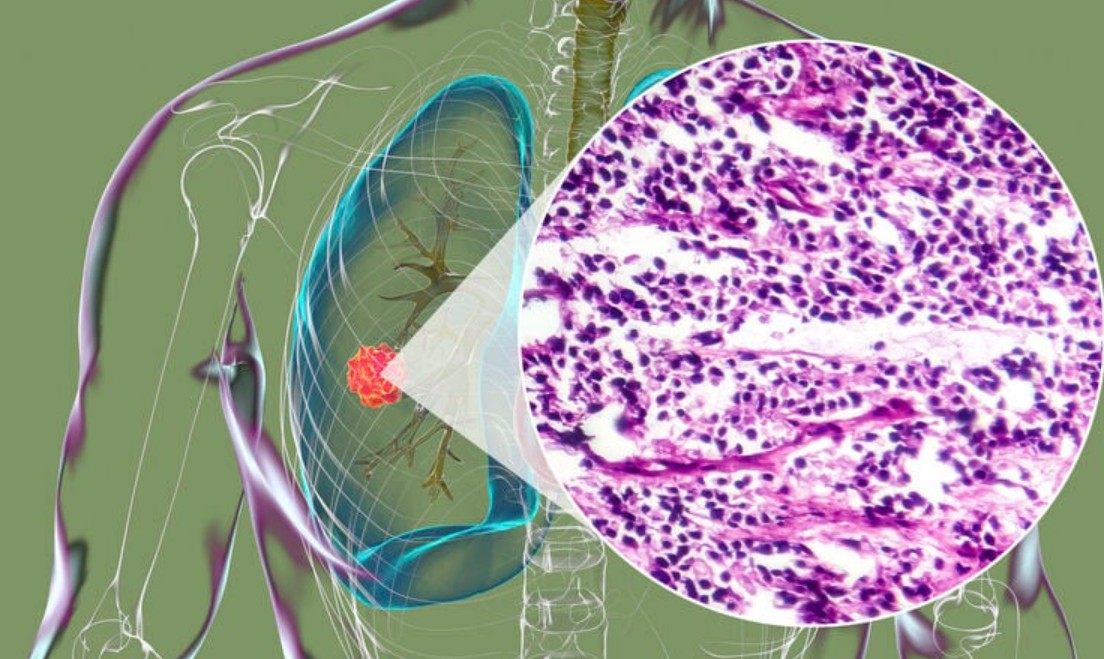
Lung cancer remains one of the most common and deadly forms of cancer worldwide. Among the many genetic alterations driving its growth, the KRAS mutation has become an important focus in both research and treatment. Understanding how this mutation impacts lung cancer development helps patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about therapy.
In recent years, advancements in targeted therapies have opened new opportunities for patients with KRAS mutation lung cancer. These treatments aim to specifically attack cancer cells driven by KRAS alterations, offering hope for improved outcomes. This article will explore the definition, diagnosis, treatment options, and future innovations surrounding KRAS mutation lung cancer treatment.
Definition and Overview
The KRAS gene (Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) plays a key role in regulating cell growth and division. When mutated, KRAS can cause cells to grow uncontrollably, leading to cancer. KRAS mutations are found in approximately 25–30% of non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC), making them one of the most frequent genetic changes in lung tumors.
KRAS mutation lung cancer is often associated with resistance to certain therapies, including older forms of targeted drugs. However, with the emergence of KRAS G12C inhibitors and ongoing research, patients now have more effective and personalized treatment choices.
Types
KRAS mutations can occur in different subtypes of lung cancer, primarily non-small cell lung cancer. The most notable subtypes include:
- Adenocarcinoma: The most common type linked with KRAS mutations.
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Less frequently associated but still possible.
- Small cell lung cancer: Rarely related to KRAS mutations but important to differentiate for treatment.
Among KRAS mutations, the KRAS G12C variant is the most targeted with modern therapies.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing KRAS mutation lung cancer:
- Smoking: The strongest risk factor, with higher mutation prevalence among current or former smokers.
- Environmental exposures: Such as asbestos, radon, or air pollution.
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of lung cancer may play a role.
- Age and gender: KRAS mutations are more frequently observed in older individuals and women with adenocarcinoma.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
KRAS mutation lung cancer shares many symptoms with other forms of lung cancer. Early detection can be difficult, but common warning signs include:
- Persistent cough or coughing up blood
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or tightness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Recurrent respiratory infections
Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of KRAS mutation lung cancer requires a combination of imaging and molecular testing. Key steps include:
- Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, and PET scans to identify lung masses.
- Biopsy: Obtaining tissue samples for histological examination.
- Genomic testing: Detecting KRAS mutations, especially G12C, using next-generation sequencing (NGS).
- Staging: Determining the cancer stage to guide treatment planning.
Treatment Options
Treatment for KRAS mutation lung cancer has evolved significantly in recent years. Available options include:
- Targeted therapy
- KRAS G12C inhibitors (such as sotorasib and adagrasib) specifically block the mutated protein’s activity.
- These therapies have shown promising results in improving progression-free survival.
- Immunotherapy
- Drugs like checkpoint inhibitors (pembrolizumab, nivolumab) can boost the immune system to attack cancer cells.
- Often used in combination with chemotherapy or targeted drugs.
- Chemotherapy
- Platinum-based chemotherapy remains a standard option, particularly when targeted therapies are not suitable.
- Radiation therapy
- Applied in localized tumors or as palliative care to relieve symptoms.
- Surgery
- Possible for early-stage lung cancer without extensive spread.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all cases are preventable, lifestyle changes can lower the risk and support better outcomes:
- Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.
- Adopt a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly to boost lung function and overall health.
- Limit exposure to carcinogens such as asbestos, radon, and industrial pollutants.
- Regular screenings for high-risk individuals can lead to earlier detection.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Historically, patients with KRAS mutation lung cancer had limited treatment options and poorer outcomes. However, with new targeted therapies, survival rates are improving. The prognosis depends on factors such as cancer stage, type of mutation, overall health, and response to treatment.
KRAS G12C inhibitors have demonstrated encouraging results, with many patients experiencing reduced tumor growth and prolonged survival. Clinical outcomes continue to improve as more therapies are tested and approved.
Latest Research and Innovations
Research in KRAS mutation lung cancer treatment is rapidly advancing. Some notable areas include:
- Combination therapies: Pairing KRAS inhibitors with immunotherapy or chemotherapy for enhanced effectiveness.
- Next-generation KRAS inhibitors: Developing drugs targeting additional KRAS mutations beyond G12C.
- Liquid biopsies: Using blood tests to detect KRAS mutations earlier and monitor treatment response.
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatment strategies based on individual tumor genetics.
Coping and Support for Patients
A diagnosis of KRAS mutation lung cancer can be overwhelming. Patients benefit greatly from support networks and coping strategies:
- Emotional support: Counseling, support groups, and mental health services.
- Nutritional guidance: Dietitians can help patients maintain strength during treatment.
- Physical activity: Gentle exercise can improve energy and reduce treatment side effects.
- Palliative care: Symptom management and quality-of-life improvements at all stages of cancer.
Conclusion
KRAS mutation lung cancer treatment has transformed in the past decade, moving from limited options to highly targeted therapies that directly address the underlying mutation. With the approval of KRAS inhibitors and advances in immunotherapy, patients now have a better chance of controlling the disease and extending survival.
As research continues, the future looks promising for individuals with KRAS mutation lung cancer. By combining early diagnosis, innovative therapies, lifestyle improvements, and strong support systems, patients can approach treatment with greater hope and resilience.