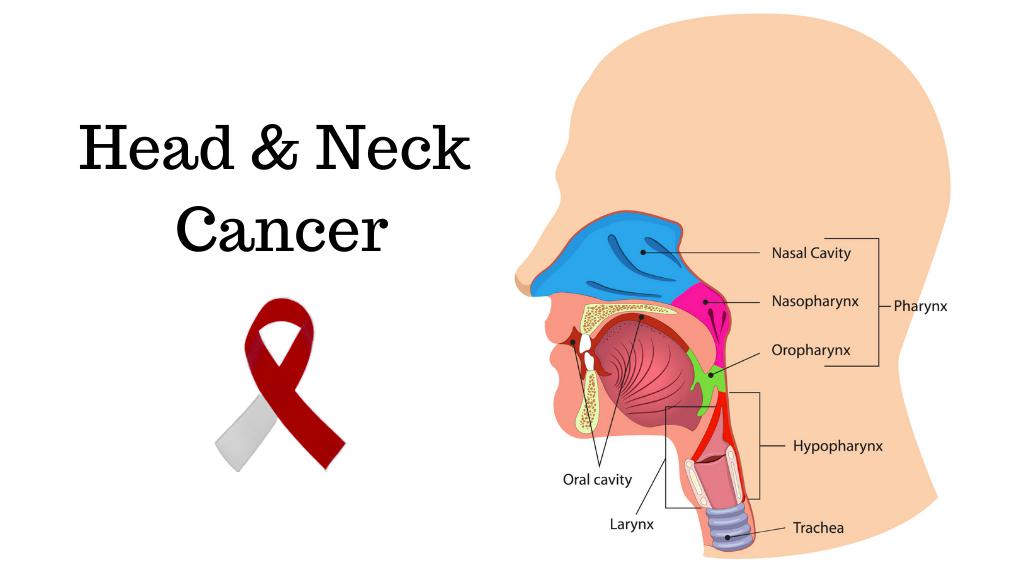
Head and neck cancers are a group of cancers that begin in the mouth, throat, voice box, sinuses, and other related areas. They account for a significant percentage of cancer diagnoses worldwide and are often linked to lifestyle factors such as tobacco and alcohol use. Because early detection plays a crucial role in treatment success, understanding head and neck cancer symptoms is vital.
Unfortunately, many early signs can be mistaken for common health problems like infections, allergies, or dental issues. This often leads to delays in seeking medical attention. By learning more about head and neck cancer symptoms, causes, and treatment options, you can be better prepared to recognize potential warning signs and take timely action.
Definition and Overview
Head and neck cancer refers to malignant growths that develop in or around the throat, larynx, nose, sinuses, and mouth. These cancers often arise from the squamous cells that line the moist surfaces in these regions. They can grow locally and, if left untreated, spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs.
Types
Head and neck cancers are classified based on their origin:
- Oral cancer: Affects the lips, tongue, gums, and inner lining of the cheeks.
- Oropharyngeal cancer: Involves the tonsils, soft palate, and back of the tongue.
- Laryngeal cancer: Develops in the voice box.
- Hypopharyngeal cancer: Found in the lower part of the throat.
- Nasopharyngeal cancer: Starts behind the nose and above the back of the throat.
- Paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer: Affects the air-filled spaces around the nose.
- Salivary gland cancer: Occurs in the glands that produce saliva.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing head and neck cancer:
- Tobacco use (cigarettes, cigars, smokeless tobacco)
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Poor oral hygiene
- Exposure to harmful chemicals or asbestos
- Family history of cancer
- Chronic acid reflux (GERD)
- Weakened immune system
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Recognizing head and neck cancer symptoms early can save lives. Common warning signs include:
- Persistent sore throat
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Unexplained lumps in the neck or mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or chewing
- Ear pain or ringing
- Nosebleeds or nasal congestion
- Non-healing mouth ulcers
- Unexplained weight loss
- Swelling in the jaw or face
- Numbness in parts of the face
If these symptoms last more than two weeks, medical evaluation is essential.
Diagnosis
Doctors use a combination of methods to diagnose head and neck cancer:
- Physical examination of the mouth, throat, and neck
- Imaging tests such as MRI, CT scans, and PET scans
- Endoscopy for detailed throat examination
- Biopsy to confirm cancer presence
- HPV testing for certain throat cancers
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on cancer type, location, and stage. Common approaches include:
- Surgery to remove tumors
- Radiation therapy to target cancer cells
- Chemotherapy for advanced or spread cases
- Targeted therapy that attacks specific cancer cell mechanisms
- Immunotherapy to boost the body’s defense system
- Rehabilitation for speech, swallowing, and physical recovery
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all cases can be prevented, healthy choices reduce risks:
- Quit smoking and avoid all tobacco products
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Maintain good oral hygiene
- Get HPV vaccination
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Protect yourself from occupational exposure to harmful chemicals
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Prognosis varies depending on cancer stage, type, and patient health. Early-stage head and neck cancers have higher survival rates, often exceeding 70%. However, advanced stages are more difficult to treat. Regular screening and prompt treatment improve chances of recovery.
Latest Research and Innovations
Ongoing research focuses on:
- HPV-related cancer therapies
- Minimally invasive surgical techniques
- Personalized medicine with genetic profiling
- Advanced radiation methods that reduce side effects
- New immunotherapies and targeted drugs
These innovations are improving treatment outcomes and reducing complications.
Coping and Support for Patients
Dealing with head and neck cancer symptoms and treatment can be overwhelming. Support systems are crucial:
- Counseling and mental health support
- Speech and swallowing therapy
- Nutrition guidance
- Cancer support groups
- Family and caregiver involvement
Conclusion
Head and neck cancer symptoms can be subtle, but early recognition and timely treatment make a huge difference. Understanding risk factors, seeking medical advice when symptoms persist, and adopting preventive measures are essential for better outcomes. Advances in treatment continue to improve survival rates, giving patients more hope and support than ever before.
FAQ
What are the first signs of head and neck cancer?
Common early signs include persistent sore throat, hoarseness, unexplained lumps, and difficulty swallowing.
Is head and neck cancer curable?
Yes, especially when diagnosed early. Surgery, radiation, and targeted therapies can be highly effective.
Who is at the highest risk for head and neck cancer?
Smokers, heavy alcohol users, and individuals with HPV infection face the highest risk.
Can head and neck cancer come back after treatment?
Yes, recurrence is possible, which is why regular follow-up care is important.
How can I reduce my risk of developing head and neck cancer?
Avoid tobacco and alcohol, maintain oral hygiene, get vaccinated against HPV, and practice healthy lifestyle habits.