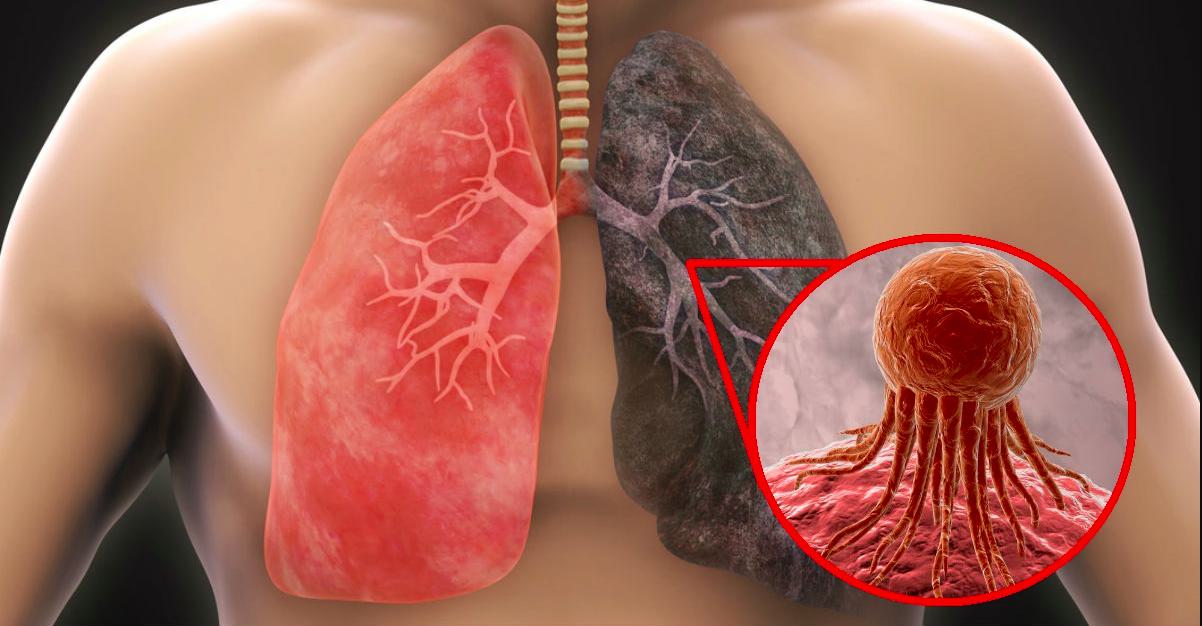
Lung cancer is one of the most common and deadly forms of cancer worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. Understanding the early warning signs and risk factors is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. For many individuals, recognizing the sintomas de cancer de pulmon can make a life-saving difference.
This article provides a detailed overview of lung cancer, including its types, causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and coping strategies. By the end, you will have a clearer understanding of how to recognize sintomas de cancer de pulmon and the importance of timely medical intervention.
Definition and Overview
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the lungs. These cells can form tumors, interfere with normal lung function, and potentially spread to other parts of the body. Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally, but early detection significantly improves survival rates.
Types
There are two main types of lung cancer:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): The most common type, accounting for around 85% of cases. Subtypes include adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): Less common but more aggressive, often spreading quickly to other organs.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of lung cancer:
- Smoking: The leading cause, responsible for the majority of cases.
- Secondhand smoke exposure
- Exposure to harmful substances: Such as asbestos, radon, and air pollution.
- Family history of lung cancer
- Chronic lung diseases: Like COPD and pulmonary fibrosis.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Recognizing the sintomas de cancer de pulmon early can help in seeking timely medical care. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough that does not go away
- Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Hoarseness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue or weakness
- Frequent respiratory infections like bronchitis or pneumonia
In some cases, symptoms may not appear until the cancer is advanced, which is why regular check-ups are important for those at high risk.
Diagnosis
Doctors use several methods to diagnose lung cancer:
- Imaging tests: Chest X-rays, CT scans, or PET scans to detect abnormal growths.
- Sputum cytology: Analyzing mucus coughed up from the lungs.
- Biopsy: Removing a tissue sample for microscopic examination.
- Blood tests: To evaluate overall health and detect cancer markers.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. Options include:
- Surgery: Removing the tumor or part of the lung.
- Radiation therapy: Targeting cancer cells with high-energy rays.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Attacking specific mutations in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all cases of lung cancer can be prevented, lifestyle changes can reduce risks:
- Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke
- Test your home for radon exposure
- Reduce exposure to carcinogens at work
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Exercise regularly to strengthen lung health
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for lung cancer varies depending on the stage at diagnosis and overall health. Early-stage lung cancer has a much higher survival rate compared to advanced stages. On average, the five-year survival rate is around 25%, but early detection can improve outcomes significantly.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent advances in lung cancer treatment focus on personalized medicine, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy. Researchers are also exploring early detection methods, such as liquid biopsies, to identify cancer through blood tests before symptoms appear.
Coping and Support for Patients
A lung cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, both physically and emotionally. Patients benefit from:
- Support groups and counseling
- Nutritional guidance
- Stress management techniques
- Family and caregiver support
- Access to palliative care for symptom management
Conclusion
Understanding the sintomas de cancer de pulmon is key to early detection and effective treatment. By recognizing warning signs, adopting preventive habits, and seeking timely medical care, individuals can improve their chances of survival and maintain a better quality of life. Awareness, research, and support remain vital in the fight against lung cancer.
FAQ
1. What are the most common sintomas de cancer de pulmon?
Persistent cough, coughing up blood, chest pain, and shortness of breath are among the most common symptoms.
2. Can lung cancer be cured?
Yes, if detected early, lung cancer can often be treated successfully with surgery or a combination of therapies.
3. Who is most at risk of developing lung cancer?
Smokers, individuals exposed to secondhand smoke, and people with occupational exposure to harmful substances are at higher risk.
4. How can I lower my risk of lung cancer?
Quitting smoking, avoiding carcinogen exposure, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and regular health screenings can help lower risk.
5. When should I see a doctor about sintomas de cancer de pulmon?
If you experience persistent cough, coughing up blood, chest pain, or unexplained weight loss, consult a healthcare professional immediately.