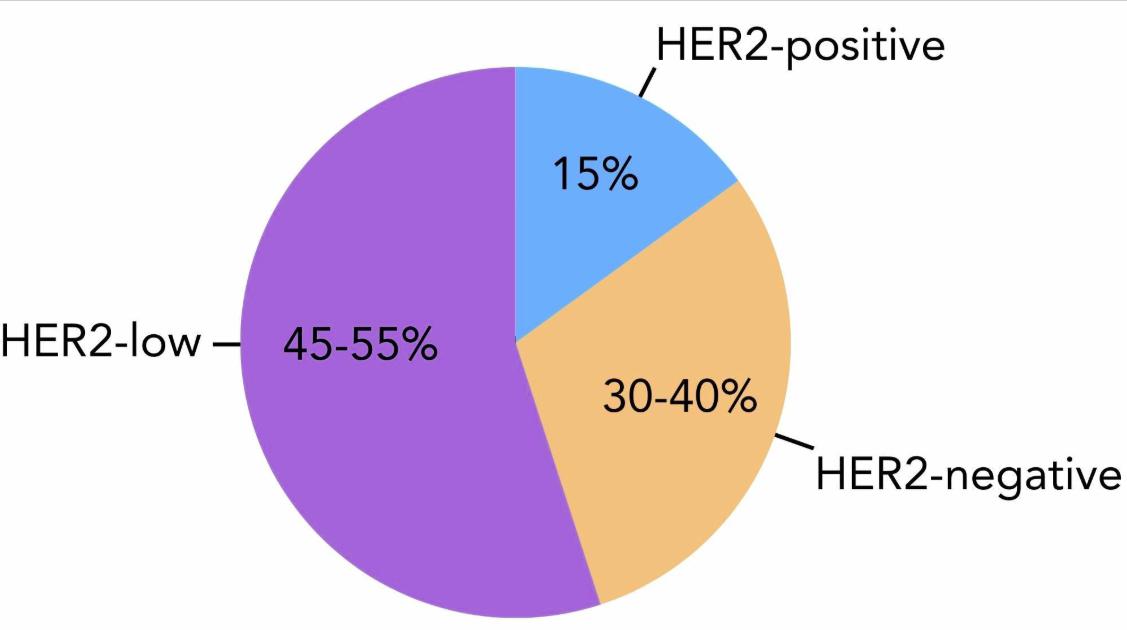
Breast cancer remains one of the most common cancers worldwide, affecting millions of women and some men every year. Among the various subtypes, HER2-positive breast cancer is known for being particularly aggressive. However, advances in targeted therapies and medical research have significantly improved treatment outcomes, survival rates, and overall HER2 breast cancer life expectancy.
For patients and families, understanding this condition goes beyond medical terms—it is about knowing the risk factors, early warning signs, and the latest treatment strategies that can extend and improve life. This article provides a detailed overview of HER2-positive breast cancer, its prognosis, and what current research means for those diagnosed.
Definition and Overview
HER2-positive breast cancer is a type of breast cancer in which cancer cells have higher-than-normal levels of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) protein. This protein promotes the growth of cancer cells, making the disease more aggressive than HER2-negative breast cancer. The presence of HER2 is determined through specialized diagnostic tests, guiding treatment decisions and impacting HER2 breast cancer life expectancy.
Types
HER2-positive breast cancer can appear in different forms:
- HER2-positive and hormone receptor (HR)-positive: Responds to both targeted therapy and hormone therapy.
- HER2-positive and HR-negative: Relies heavily on HER2-targeted treatments.
- Metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer: Cancer has spread beyond the breast to other parts of the body.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of HER2 gene amplification is not fully understood, several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing this subtype:
- Family history of breast cancer
- Genetic mutations such as BRCA1/BRCA2
- Exposure to radiation
- Hormonal factors and lifestyle influences such as obesity, alcohol use, and lack of exercise
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
HER2-positive breast cancer shares similar symptoms with other breast cancers, including:
- A lump or thickening in the breast or underarm
- Changes in breast size, shape, or appearance
- Nipple discharge or inversion
- Redness or swelling of breast tissue
Recognizing these early warning signs and seeking medical attention promptly can positively affect HER2 breast cancer life expectancy.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves several steps, including:
- Mammogram and ultrasound for imaging
- Biopsy to analyze tissue samples
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) tests to confirm HER2 status
Treatment Options
The advancement of targeted therapies has transformed treatment outcomes for HER2-positive breast cancer. Options include:
- Targeted therapies: Trastuzumab, pertuzumab, and other HER2 inhibitors
- Chemotherapy: Often combined with HER2-targeted treatments
- Hormone therapy: For HR-positive HER2 breast cancer
- Surgery: Lumpectomy or mastectomy depending on stage
- Radiation therapy: Reduces recurrence risk
These treatments, when personalized, have significantly improved HER2 breast cancer life expectancy compared to past decades.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While HER2-positive breast cancer cannot always be prevented, lifestyle choices can lower overall breast cancer risk:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular physical activity
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Avoiding smoking
- Regular screening for early detection
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis of HER2-positive breast cancer has improved dramatically. In the past, this subtype was associated with poor survival, but with targeted therapies, many patients now live long and fulfilling lives. According to recent studies, the HER2 breast cancer life expectancy has increased significantly, with five-year survival rates reaching 90% or more in early-stage cases. Metastatic cases, while more challenging, also see better outcomes thanks to newer treatment strategies.
Latest Research and Innovations
Research continues to bring hope for patients, focusing on:
- Next-generation HER2-targeted therapies
- Combination treatments with immunotherapy
- Liquid biopsies for better monitoring and precision care
- Personalized medicine based on genetic profiling
These innovations are expected to further extend HER2 breast cancer life expectancy in the coming years.
Coping and Support for Patients
A breast cancer diagnosis brings emotional, physical, and financial challenges. Patients benefit greatly from:
- Support groups and counseling
- Nutrition and wellness programs
- Open communication with healthcare providers
- Family and community support networks
Coping strategies play an essential role in overall quality of life, alongside medical treatment.
Conclusion
HER2-positive breast cancer, once considered a highly aggressive disease with poor prognosis, now has a much-improved outlook. Thanks to advancements in targeted therapies and ongoing research, HER2 breast cancer life expectancy continues to rise, offering patients real hope for longer survival and better quality of life. Staying informed, seeking early diagnosis, and embracing both medical and emotional support are key steps in navigating this journey.
FAQ
What is HER2-positive breast cancer?
It is a breast cancer subtype characterized by high levels of the HER2 protein, which promotes cancer cell growth.
Is HER2 breast cancer more aggressive?
Yes, it tends to grow and spread faster than HER2-negative breast cancer, but modern treatments have greatly improved outcomes.
What is the average HER2 breast cancer life expectancy?
With early detection and targeted therapies, many patients achieve high survival rates, often exceeding 90% at five years.
Can HER2 breast cancer be cured?
Early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer can often be treated successfully, and some patients achieve long-term remission.
What lifestyle changes can help after diagnosis?
Maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, reducing alcohol intake, and joining support groups can improve well-being and outcomes.