Prostate cancer remains one of the most common cancers affecting men worldwide, and finding the most effective treatment is a priority for patients, families, and healthcare professionals. Advances in medicine have led to innovative therapies designed to improve survival rates, minimize side effects, and enhance quality of life. Many people search for solutions under the promise of a new prostate cancer treatment 100 effective, hoping for an option that guarantees complete recovery.
While no single therapy can yet claim absolute effectiveness for all patients, modern approaches are increasingly personalized and significantly more successful than older treatments. By understanding the latest research, medical innovations, and holistic care strategies, patients can make informed decisions that bring them closer to the best possible outcomes.
Definition and Overview
Prostate cancer is a disease that develops in the prostate gland, a small organ located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The condition occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably within the prostate. It ranges from slow-growing cancers that require minimal intervention to aggressive forms that spread rapidly and demand urgent treatment.
The idea of a new prostate cancer treatment 100 effective reflects the ongoing effort to achieve therapies that completely eliminate the disease without recurrence. Although such a universal cure is not yet available, several advanced treatment modalities are showing remarkable promise.
Types
Prostate cancer can be classified into different types, primarily based on how aggressive the disease is:
- Adenocarcinoma: The most common type, accounting for the majority of cases.
- Small cell carcinoma: A rare and aggressive form.
- Neuroendocrine tumors: Less common but often advanced at diagnosis.
- Transitional cell carcinoma: Typically begins in the bladder and spreads to the prostate.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of prostate cancer is not fully understood, but several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing the disease:
- Age: Risk increases significantly after age 50.
- Genetics and family history: Men with close relatives diagnosed with prostate cancer face a higher risk.
- Ethnicity: African American men are more likely to develop aggressive prostate cancer.
- Lifestyle factors: Diets high in red meat, obesity, and sedentary habits may contribute.
- Hormonal imbalance: Elevated testosterone levels can play a role in tumor growth.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Early stages of prostate cancer often show no symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, men may experience:
- Difficulty urinating or weak urine flow
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Blood in urine or semen
- Erectile dysfunction
- Pain in the lower back, hips, or thighs (in advanced cases)
Recognizing these early warning signs and seeking timely medical attention can significantly improve treatment success.
Diagnosis
Doctors use several tools to diagnose prostate cancer, including:
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: Measures levels of PSA in the blood.
- Digital rectal examination (DRE): Allows physicians to feel for abnormalities.
- Biopsy: Confirms cancer by examining tissue samples.
- Imaging tests: MRI, CT scans, or bone scans help assess cancer spread.
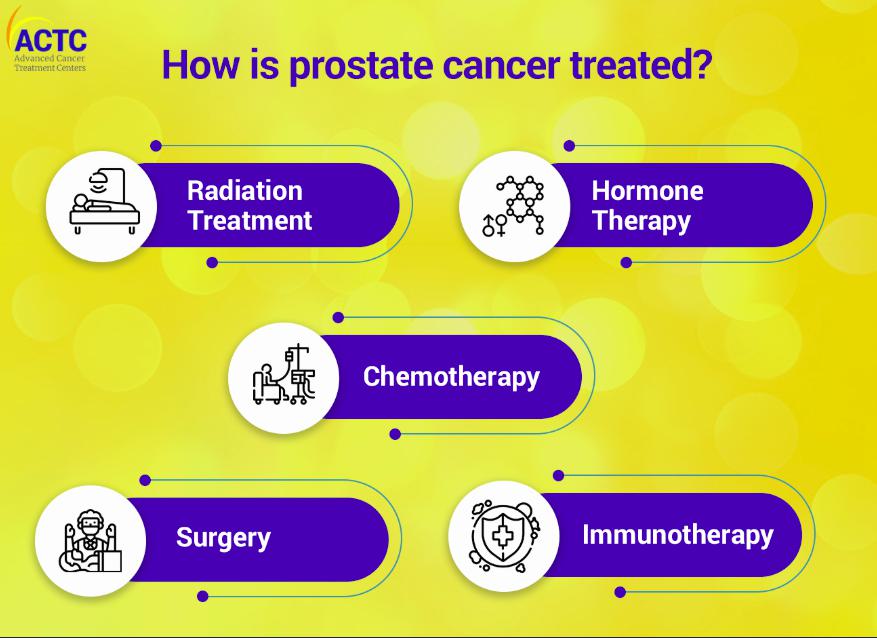
Treatment Options
Current treatments are increasingly effective, with ongoing research moving closer to a new prostate cancer treatment 100 effective. Common options include:
- Surgery (Prostatectomy): Removal of the prostate gland.
- Radiation therapy: External beam or brachytherapy to kill cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy: Reduces testosterone to slow cancer growth.
- Chemotherapy: For advanced or resistant cases.
- Immunotherapy: Stimulates the immune system to attack cancer.
- Targeted therapy: Focuses on specific genetic mutations driving cancer.
- Focal therapies: Newer methods like HIFU (high-intensity focused ultrasound) and cryotherapy that target tumors with minimal side effects.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all cases are preventable, men can lower their risk by adopting healthier lifestyles:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- Limit red meat and processed foods.
- Stay physically active and maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake.
- Get regular medical check-ups and screenings after age 50 (or earlier with family history).
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Prostate cancer is highly treatable when detected early. The five-year survival rate for localized and regional stages is nearly 100%. However, once the cancer spreads to distant organs, the survival rate decreases. Advances in treatment continue to improve long-term outcomes, bringing the medical field closer to achieving a new prostate cancer treatment 100 effective.
Latest Research and Innovations
Cutting-edge research is exploring advanced therapies, including:
- Genomic testing to personalize treatment plans.
- CAR-T cell therapy for targeting prostate cancer cells.
- Nanotechnology-based drug delivery for precision targeting.
- Combination therapies that integrate radiation, immunotherapy, and hormone treatment.
These innovations are promising steps toward the ultimate goal of achieving a fully effective cure.
Coping and Support for Patients
A prostate cancer diagnosis can be emotionally overwhelming. Patients and families benefit from:
- Support groups and counseling
- Mindfulness practices and stress management techniques
- Open communication with healthcare providers
- Practical support for managing side effects and lifestyle changes
Conclusion
While no universal new prostate cancer treatment 100 effective exists today, medical progress is moving closer to this vision. Early detection, advanced therapies, and supportive care significantly improve survival and quality of life. Staying informed, adopting healthy habits, and working closely with medical professionals are the best strategies for navigating a prostate cancer journey with confidence and hope.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is there a prostate cancer treatment that is 100% effective?
Currently, no treatment guarantees complete effectiveness for every patient, but many therapies are highly successful when the disease is detected early.
2. What is the newest treatment available for prostate cancer?
Recent advancements include focal therapies like HIFU, immunotherapy, and targeted treatments based on genetic profiling.
3. Can lifestyle changes reduce prostate cancer risk?
Yes, adopting a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking can lower the risk.
4. What is the survival rate for prostate cancer?
When caught early, the five-year survival rate is nearly 100%. Outcomes decline with advanced-stage diagnoses.
5. How often should men get screened for prostate cancer?
Most guidelines recommend screening starting at age 50, or earlier for men with higher risk factors.