Stagescancer.net – Welcome to our comprehensive guide on schnauzer cancer. As a devoted pet owner, it’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of this disease and take proactive steps to prevent it. In this article, we will explore the various types of cancer that can affect schnauzers, common symptoms to watch for, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and the prognosis for schnauzers with cancer.
Additionally, we will provide valuable tips on prevention strategies, nutritional considerations, the role of genetics, and emotional support for both you and your furry friend. Let’s dive in and equip ourselves with the knowledge and resources needed to protect our beloved schnauzers from cancer.
Understanding Schnauzer Cancer
When it comes to schnauzers, cancer is unfortunately a common concern. Understanding the different types of cancer that commonly affect schnauzers is crucial for early detection and improved treatment outcomes. In this section, we will explore the various types of cancer that can impact these beloved dogs, as well as the causes and risk factors associated with schnauzer cancer.
Types of Cancer in Schnauzers
Schnauzers can be susceptible to a variety of cancer types, including but not limited to:
| Cancer Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Mammary Cancer | Affects the mammary glands and is more common in female schnauzers. |
| Gastrointestinal Cancer | Affects the digestive system, including the stomach, intestines, and colon. |
| Lymphoma | A cancer of the lymphatic system, which plays a vital role in the body’s immune response. |
| Prostate Cancer | Primarily affects male schnauzers and can lead to urinary and reproductive system problems. |
| Osteosarcoma | A bone cancer that predominantly affects the limbs of larger schnauzers. |
These are just a few examples of the types of cancer that can impact schnauzers. Each type of cancer presents unique challenges and requires specific treatment approaches.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of schnauzer cancer can vary and are often multifactorial. While some factors, such as age and genetics, cannot be controlled, there are several known risk factors that pet owners should be aware of. These risk factors include:
- Exposure to environmental toxins
- Obesity
- Advanced age
- Previous history of cancer
- Weak immune system
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with schnauzer cancer can help pet owners take proactive steps to reduce the risk and detect cancer in its early stages.
Common Signs of Schnauzer Cancer
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of schnauzer cancer is crucial for early detection and treatment. Paying close attention to your schnauzer’s health and behavior can help you identify any potential issues. Here are some common symptoms that may indicate the presence of cancer in schnauzers:
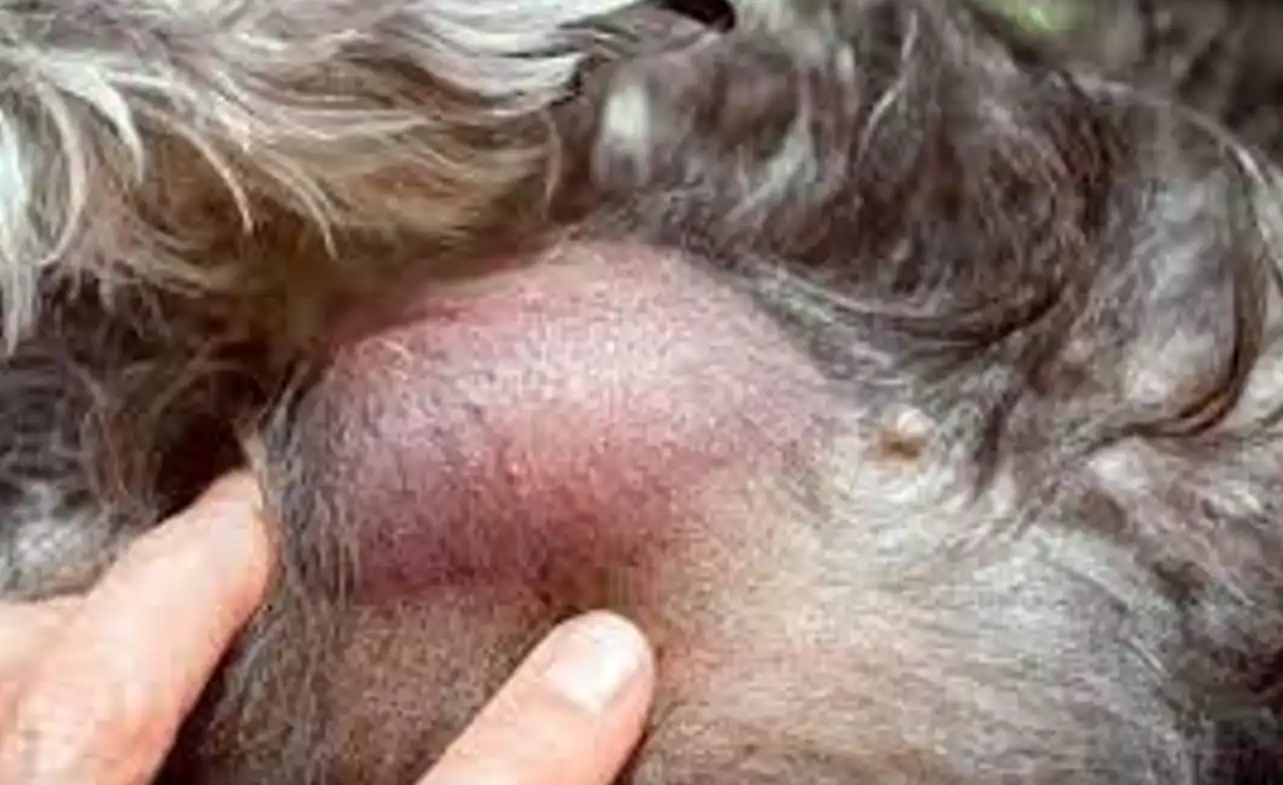
- Lumps or bumps: Feeling any unusual growths or masses on your schnauzer’s body, especially if they are firm or growing rapidly, maybe a sign of cancer.
- Unexplained weight loss: If your schnauzer is losing weight without changes in diet or exercise, it could be a cause for concern.
- Loss of appetite: A sudden decrease in your schnauzer’s appetite or a reluctance to eat can be an indication of an underlying health issue, including cancer.
- Lethargy: If your schnauzer is unusually tired, lacks energy, or seems uninterested in activities, it may be a sign of cancer.
- Difficulty breathing: Rapid or labored breathing, coughing, or wheezing can indicate respiratory issues, which may be related to cancer.
- Changes in bathroom habits: Increased frequency of urination, difficulty urinating, blood in the urine or stool, or prolonged constipation can all be signs of cancer in schnauzers.
- Persistent lameness: If your schnauzer is limping or showing signs of pain or discomfort when walking or running, it may be due to bone cancer.
If you notice any of these symptoms or any other concerning changes in your schnauzer’s health, it is important to consult your veterinarian. Only a veterinary professional can accurately diagnose schnauzer cancer and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Diagnosing Schnauzer Cancer
The diagnosis of schnauzer cancer involves a comprehensive evaluation to determine if a schnauzer has cancer. Early detection is crucial, as it can greatly improve treatment success and the overall prognosis for the dog. Veterinarians may use a variety of tests and procedures to diagnose schnauzer cancer, depending on the suspected type and location of the cancer.
Some common diagnostic tools and techniques used in schnauzer cancer diagnosis include:
- Physical Examination: During a physical examination, the veterinarian will carefully examine the schnauzer for any lumps, tumors, or abnormal growths. They will also assess the dog’s overall health and look for any other signs of illness that may indicate cancer.
- Biopsy: A biopsy involves the removal of a small sample of tissue from the suspected tumor or growth. This sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where a veterinary pathologist examines it under a microscope to determine if cancer cells are present.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasound, and CT scans, may be used to provide detailed images of the internal organs and tissues. These images can help identify the location, size, and extent of the cancerous growth.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can provide valuable information about the schnauzer’s overall health and may also indicate the presence of certain cancers. Elevated levels of certain substances in the bloodstream may suggest the presence of cancer or other underlying conditions.
Once a diagnosis of Schnauzer cancer is confirmed, further tests may be performed to determine the stage of the cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. This information is critical for developing an appropriate treatment plan and assessing the prognosis for the schnauzer.
Table:
| Diagnostic Procedure | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Physical Examination | To assess the schnauzer’s overall health, look for signs of cancer, and identify any abnormal growths |
| Biopsy | To obtain a tissue sample for microscopic examination to confirm the presence of cancer cells |
| Imaging Tests | To visualize and evaluate the location, size, and extent of cancerous growths within the body |
| Blood Tests | To assess the schnauzer’s overall health, identify any abnormalities, and detect potential markers of cancer |
Treatment Options for Schnauzer Cancer
When it comes to treating schnauzer cancer, there are several options available to pet owners. The choice of treatment will depend on various factors, including the type and stage of cancer, as well as the overall health of the schnauzer. The main treatment modalities for schnauzer cancer include:
Surgery
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for localized tumors and can involve the removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue. This can help to eliminate the cancerous cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or prevent them from dividing. It is commonly used in cases where the cancer has spread or in conjunction with surgery to target any remaining cancer cells.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy involves using high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells. It can be used as a primary treatment for localized tumors or in combination with surgery or chemotherapy.
Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies are a newer form of treatment that specifically targets cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells. These therapies can be tailored to the specific molecular characteristics of the tumor, increasing their effectiveness.
The goals of treatment for schnauzer cancer are to eliminate or control the cancer, relieve symptoms, and improve the quality of life for the dog. It’s important to note that treatment options for schnauzer cancer can have potential side effects, and the veterinarian will carefully consider the risks and benefits of each treatment plan. Close monitoring and follow-up care are crucial to ensure the best possible outcome for the schnauzer.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Understanding the prognosis and survival rates for schnauzer cancer is essential for pet owners who are navigating this difficult journey. While each case is unique, several factors can influence the overall outlook for schnauzers with cancer.
Prognosis:
The prognosis for schnauzer cancer depends on various elements, including the type and stage of cancer, as well as the overall health and age of the dog. It is important to remember that a prognosis is an estimation and not a definitive outcome. Consulting with a veterinarian will provide a clearer understanding of your schnauzer’s specific prognosis.
Survival Rates:
The survival rates for schnauzer cancer can vary widely depending on the type of cancer, the stage at diagnosis, and the treatment received. It is crucial to prioritize early detection and prompt treatment to improve your schnauzer’s chances of survival.
Types of Schnauzer Cancer and Survival Rates
Here is a breakdown of some common types of schnauzer cancer and their associated survival rates:
| Type of Cancer | Survival Rate |
|---|---|
| Skin Cancer | 80-95% |
| Lymphoma | 70-85% |
| Osteosarcoma | 10-30% |
| Bladder Cancer | 45-65% |
Please note that these survival rates are general estimates and can vary from case to case. They serve as a reference point to understand the potential outcomes for schnauzers with specific types of cancer.
Preventing Schnauzer Cancer
Schnauzer cancer is a serious health concern for pet owners. Fortunately, there are several strategies you can implement to help prevent this devastating disease in your furry companion. By focusing on lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise, you can reduce the risk of schnauzer cancer and promote overall well-being for your beloved pet.
Dietary Considerations
A balanced and nutritious diet plays a crucial role in preventing schnauzer cancer. Choose high-quality commercial pet foods that are specifically formulated for schnauzers, taking into account their unique nutritional needs. Incorporate cancer-fighting foods into their meals, such as:
- Broccoli: Rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals that help combat cancer.
- Blueberries: Packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that may reduce the risk of cancer.
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, which exhibits anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties.
Exercise and Weight Management
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of cancer in schnauzers. Engage your furry friend in daily activities that promote physical fitness, such as brisk walks or play sessions. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise every day to keep your schnauzer active and fit. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through proper diet and exercise can help prevent obesity-related cancers.
Veterinary Check-ups and Screenings
Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial in preventing and detecting schnauzer cancer at an early stage. Schedule routine appointments with your veterinarian to monitor your schnauzer’s health and discuss cancer prevention strategies. Your vet may recommend specific screenings, such as blood tests or imaging, to identify any potential signs of cancer before they become advanced.
Minimizing Environmental Risks
Reducing your schnauzer’s exposure to environmental risks can help prevent cancer. Avoid exposing your pet to harmful substances such as tobacco smoke, pesticides, and toxic chemicals. When walking your schnauzer, be cautious of potential exposure to environmental hazards, such as polluted areas or excessive sun exposure. Taking these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer in your beloved schnauzer.
| Prevention Strategies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Feeding a balanced diet | Provides essential nutrients and boosts the immune system |
| Regular exercise | Helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces the risk of obesity-related cancers |
| Scheduling veterinary check-ups | Ensures early detection and intervention |
| Minimizing environmental risks | Reduces exposure to potential carcinogens |
By incorporating these preventive measures into your schnauzer’s lifestyle, you can make a significant impact on reducing their risk of developing cancer. Remember, prevention is always better than cure.
Nutritional Considerations for Schnauzers
Nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and well-being of schnauzers, and it can also contribute to the prevention of cancer. Providing a balanced diet that is rich in cancer-fighting foods can help support your schnauzer’s immune system and reduce the risk of developing cancer.
Choosing a Balanced Diet
When it comes to selecting a diet for your schnauzer, it’s important to prioritize high-quality ingredients that meet their nutritional needs. Look for dog food formulas that contain a balance of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Avoid foods that are high in artificial preservatives, colors, and flavors.
Consult with your veterinarian to determine the right portion sizes and feeding frequency based on your schnauzer’s age, weight, and activity level. Remember to provide fresh water at all times to keep your schnauzer hydrated.
Cancer-Fighting Foods for Schnauzers
Incorporating cancer-fighting foods into your schnauzer’s meals can provide additional protection against the disease. These foods are rich in antioxidants, phytochemicals, and other beneficial compounds that help boost the immune system and fight off cancer cells.
Here are some cancer-fighting foods that you can consider adding to your schnauzer’s diet:
- Fish: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fish like salmon and sardines have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the risk of cancer.
- Leafy greens: Vegetables such as spinach, kale, and broccoli are packed with nutrients and antioxidants that support overall health and can help prevent cancer.
- Berries: Blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries contain powerful antioxidants that can help protect against cancer and other diseases.
- Turmeric: This spice contains a compound called curcumin, which has been shown to have anti-cancer properties.
- Tomatoes: Tomatoes are rich in lycopene, a potent antioxidant that has been linked to a reduced risk of cancer.
Remember to introduce new foods gradually to avoid gastrointestinal upset, and monitor your schnauzer’s response to any dietary changes. If you have any concerns about your schnauzer’s nutrition, consult with your veterinarian for personalized advice.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for maintaining the health and well-being of your schnauzer. These check-ups play a crucial role in the early detection and prevention of schnauzer cancer, ensuring that any potential issues are identified and addressed promptly.
During these check-ups, your veterinarian will perform a thorough examination of your schnauzer, monitoring for any signs or symptoms of cancer. They may also recommend specific screening tests to assess your schnauzer’s risk and detect cancer at its earliest stages.
Schnauzer cancer screenings can include:
- Blood tests to evaluate organ function and detect any abnormalities
- Imaging tests such as X-rays or ultrasounds to examine internal structures
- Tissue biopsies to analyze suspicious growths or masses
It is crucial to follow your veterinarian’s recommendations regarding the frequency of check-ups and screenings for your schnauzer. By staying proactive and attentive to your schnauzer’s health, you can increase the chances of detecting cancer early, when treatment options are often more effective.
Remember, early detection saves lives. Regular veterinary check-ups are not only an opportunity to catch potential health concerns early on but also to establish a strong relationship with your veterinarian, who can provide guidance and support throughout your schnauzer’s life.
Environmental Factors and Schnauzer Cancer
In addition to genetic factors, environmental risks can also play a role in the development of cancer in schnauzers. Pet owners need to be aware of potential toxins and hazards that their schnauzers may encounter, to minimize their exposure and reduce the risk of cancer.
Potential Environmental Toxins and Hazards
Several environmental factors have been linked to an increased risk of cancer in dogs, including schnauzers. These factors can include:
- Pesticides and herbicides
- Air pollution
- Contaminated water sources
- Household chemicals and cleaning products
- Secondhand smoke
- Excessive sun exposure
- Hazardous materials in the workplace
Exposure to these toxins and hazards can potentially lead to the development of cancer in schnauzers. Pet owners need to take steps to minimize their schnauzer’s exposure to these environmental risks.
Minimizing Exposure to Environmental Risks
While it may not be possible to eliminate exposure to all environmental risks, there are steps that pet owners can take to minimize their schnauzer’s exposure. These include:
- Avoiding the use of pesticides and herbicides in areas where schnauzers spend time
- Ensuring that the household environment is well-ventilated to reduce indoor air pollution
- Providing clean and filtered water sources for schnauzers
- Using pet-friendly and environmentally-friendly cleaning products in the home
- Keeping schnauzers away from areas where smoking occurs
- Limiting sun exposure and providing shade for schnauzers during outdoor activities
- Ensuring that workplaces where schnauzers may spend time are free from hazardous materials
By being mindful of these environmental risks and taking appropriate precautions, pet owners can help reduce the likelihood of their schnauzer developing cancer.
| Environmental Risk | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|
| Pesticides and herbicides | Avoid using these chemicals in areas where schnauzers spend time. Opt for natural alternatives. |
| Air pollution | Ensure good ventilation in the household and limit exposure to polluted areas. |
| Contaminated water sources | Provide clean and filtered water for schnauzers. |
| Household chemicals and cleaning products | Use pet-friendly and environmentally-friendly alternatives. |
| Secondhand smoke | Avoid exposing schnauzers to areas where smoking occurs. |
| Excessive sun exposure | Limit sun exposure and provide shade during outdoor activities. |
| Hazardous materials in the workplace | Ensure that workplaces where schnauzers spend time are free from hazardous materials. |
Genetics and Schnauzer Cancer
When it comes to schnauzer cancer, genetic factors play an important role in determining an individual dog’s risk of developing the disease. Certain genetic predispositions and markers may increase the chances of a schnauzer developing cancer. Understanding these genetic factors can help pet owners and veterinarians take proactive measures to protect their beloved schnauzers.
Genetic predispositions refer to inherited traits that can make a schnauzer more susceptible to cancer. These predispositions can be passed down from parent dogs to their offspring. By identifying these predispositions, breeders and pet owners can make informed decisions about breeding and preventive care.
Genetic markers, on the other hand, are specific variations in DNA sequences that have been associated with an increased risk of certain types of cancer in schnauzers. Scientists have been studying these markers to develop genetic testing methods that can help identify at-risk individuals early on.
Genetic testing for schnauzer cancer can provide valuable insights into an individual dog’s genetic makeup and potential risk for developing cancer. This information can guide veterinarians in implementing preventive measures and developing personalized treatment plans.
Genetic Testing and Counseling
Genetic testing for schnauzer cancer involves collecting a sample of the dog’s DNA, typically through a simple cheek swab or blood test. This sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where genetic markers associated with cancer risk are identified.
Once the results are obtained, veterinarians and pet owners can work together to understand the implications of genetic testing and make informed decisions about the dog’s care. Genetic counseling may also be available to provide guidance and support in managing the dog’s health based on the results.
Benefits of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing for schnauzer cancer offers several benefits, including:
- Early detection: Identifying genetic markers associated with cancer risk allows for early detection and intervention, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
- Preventive measures: Knowing a schnauzer’s genetic predispositions can help pet owners implement preventive measures, such as lifestyle changes or specific screenings, to minimize the risk of cancer development.
- Informed breeding decisions: Breeders can use genetic testing to make informed decisions about breeding pairs, reducing the likelihood of passing on cancer-related genetic variations to future generations.
While genetic testing can provide valuable insights, it is important to remember that it is just one tool in managing Schnauzer cancer risk. Regular veterinary check-ups, preventive care, and a healthy lifestyle are also essential components of maintaining a schnauzer’s overall well-being.
Emotional Support for Schnauzer Cancer Patients
Dealing with a diagnosis of schnauzer cancer can be emotionally overwhelming for pet owners. It is important to remember that you are not alone in this journey. Finding emotional support can make a significant difference in your ability to cope with the challenges that come with caring for a schnauzer with cancer. Here are some tips to help you navigate this difficult period:
1. Acknowledge Your Emotions:
Allow yourself to feel a range of emotions, including fear, sadness, and anger. It is normal to experience these emotions when faced with a cancer diagnosis. Acknowledging your feelings can help you process them and move forward healthily.
2. Seek Professional Help:
Consider reaching out to a therapist or counselor who specializes in pet loss and grief. They can provide a safe space for you to express your emotions and offer valuable guidance in coping with the challenges of schnauzer cancer.
3. Join Support Groups:
Connect with other pet owners who are going through similar experiences. Online support groups or local meetups can provide a sense of community and an opportunity to share your feelings, gain insights from others, and receive practical advice.
4. Practice Self-Care:
Take care of your own physical and emotional well-being. Make time for activities that bring you joy and help you relax. Engaging in self-care can reduce stress, improve your overall well-being, and give you the strength to support your schnauzer through their cancer journey.
5. Communicate with Your Veterinary Team:
Your veterinary team is not only there to provide medical care for your schnauzer but also to offer support and guidance to you as the owner. Be open and honest with them about your emotions and concerns. They can provide valuable resources and suggestions to help you cope.
6. Educate Yourself:
Gaining knowledge about schnauzer cancer can help you better understand your pet’s diagnosis and treatment options. It can also empower you to play an active role in their care. However, remember to rely on reputable sources for information and consult with your veterinary team for personalized advice.
7. Lean on Loved Ones:
Reach out to friends and family members who can provide a listening ear and emotional support. Sharing your feelings with trusted loved ones can make a significant difference in your ability to cope with the challenges of schnauzer cancer.
8. Celebrate the Good Days:
While dealing with schnauzer cancer can be challenging, it is important to cherish the happy moments with your pet. Celebrate the good days and create positive memories together. These moments of joy can uplift your spirits and remind you of the love and special bond you share with your schnauzer.
Remember, coping with schnauzer cancer is not a journey you have to face alone. Reach out for support, take care of yourself, and lean on the resources available to you. With emotional support, you can navigate this difficult time and provide the love and care your schnauzer needs.
| Emotional Support Resources | Contact Information |
|---|---|
| Pet Loss and Grief Counseling | Website: www.petlosscounseling.com Phone: 1-800-XXX-XXXX |
| Cancer Support Groups for Pet Owners | Website: www.petsupportgroups.com Email: info@petsupportgroups.com |
| Veterinary Team | Contact your veterinarian or oncologist for support and resources. |
Living with a Schnauzer Cancer Survivor
Life after schnauzer cancer treatment can bring about a range of emotions and adjustments as you and your furry companion navigate the journey of recovery. While the completion of treatment is a major milestone, it is important to remember that the impact of cancer can extend beyond the treatment phase.
Emotional Adjustment: As a pet owner, you may experience a mix of relief, joy, and anxiety once your schnauzer has completed cancer treatment. It is normal to have concerns about possible recurrence or lingering side effects. Providing emotional support for both yourself and your schnauzer is essential during this time.
Long-Term Care Considerations: Depending on the type of cancer and the treatment received, your schnauzer may require ongoing care to support their overall well-being. Regular check-ups, monitoring for any signs of cancer recurrence, and making necessary adjustments to their lifestyle and diet are important in promoting their long-term health.
Physical Rehabilitation: Some schnauzers may require physical rehabilitation following cancer treatment, especially if surgery or other invasive procedures are involved. Working with your veterinarian to develop an appropriate rehabilitation plan can help your schnauzer regain strength, mobility, and comfort.
Supportive Environment: Creating a supportive environment for your schnauzer is crucial in their post-treatment phase. Providing a comfortable and stress-free living space, engaging in gentle exercise, and offering mental stimulation can aid in their recovery and overall well-being.
Monitoring and Communication: Regular communication with your veterinarian ensures your schnauzer’s continued health. Be vigilant in observing any changes in their behavior, appetite, or energy levels, and report these to your veterinarian promptly. They can offer guidance and address any concerns that may arise.
With proper care, attention, and support, living with a schnauzer cancer survivor can be a rewarding experience. Cherish the moments you share with your beloved companion and continue to provide them with the love they deserve.
Conclusion
In conclusion, schnauzer cancer is a serious health concern that requires attention and proactive care from pet owners. Through this article, we have explored the signs, prevention strategies, diagnosis, treatment options, and prognosis of schnauzer cancer. Early detection is crucial in ensuring successful outcomes and routine veterinary check-ups play an essential role in identifying potential issues. Maintaining a balanced diet, incorporating cancer-fighting foods, and minimizing environmental risks can significantly reduce the chances of schnauzers developing cancer.
Pet owners need to be vigilant and aware of the common signs of schnauzer cancer, such as unexplained weight loss, lethargy, and changes in appetite. Seeking prompt veterinary care is vital if any concerning symptoms arise. While the journey may be emotionally challenging, there is support available from veterinary professionals and support groups to help navigate through the process.
Remember, prevention is always better than cure. By implementing preventive measures, regular screenings, and genetic testing for at-risk schnauzers, the likelihood of schnauzer cancer can be minimized. Committing to a comprehensive care plan and ensuring the well-being of our beloved schnauzers is of utmost importance. Stay informed, remain proactive, and cherish the moments spent with your furry companions.
FAQ
What are the signs and symptoms of schnauzer cancer?
Signs of schnauzer cancer may include lumps or bumps, unexplained weight loss, changes in appetite or drinking habits, lethargy, difficulty breathing, and abnormal bleeding or discharge. If you notice any of these symptoms in your schnauzer, it’s important to consult with your veterinarian for a proper diagnosis.
What are the different types of cancer that commonly affect schnauzers?
Schnauzers can be susceptible to various types of cancer, including lymphoma, mast cell tumors, melanoma, and bladder cancer. Each type of cancer may exhibit different symptoms and require specific treatment approaches. Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for effective treatment.
When should I seek veterinary care if I suspect schnauzer cancer?
If you notice any unusual symptoms or changes in behavior in your schnauzer, it’s important to schedule a veterinary appointment. Your veterinarian will be able to assess your schnauzer’s condition and perform any necessary tests or screenings to determine if cancer is present.
How is schnauzer cancer diagnosed?
Schnauzer cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, bloodwork, imaging tests (such as X-rays or ultrasound), and biopsies. These diagnostic tools help determine the presence and extent of cancer in your schnauzer’s body.
What are the treatment options for schnauzer cancer?
Treatment options for schnauzer cancer may vary depending on the type and stage of the cancer. Common treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies. Your veterinarian will recommend the most suitable treatment plan for your schnauzer based on their specific situation.
What is the prognosis for schnauzer cancer?
The prognosis for schnauzer cancer depends on various factors, including the type and stage of cancer, the overall health of the schnauzer, and the response to treatment. Some schnauzers can achieve remission or long-term survival with timely and appropriate treatment, while others may face more challenges. It’s important to discuss the prognosis with your veterinarian.
How can I prevent schnauzer cancer?
While it may not be possible to entirely prevent cancer in schnauzers, there are steps you can take to minimize the risk. Providing a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding exposure to harmful environmental factors can help reduce the chances of developing cancer. Regular veterinary check-ups and screening tests are also important for early detection.
Does nutrition play a role in preventing schnauzer cancer?
Yes, nutrition can play a significant role in preventing cancer in schnauzers. Ensuring your schnauzer has a balanced diet that includes cancer-fighting foods, such as fresh fruits and vegetables, can help boost their immune system and reduce the risk of developing cancer. Consult with your veterinarian for specific dietary recommendations.
How often should I take my schnauzer for veterinary check-ups?
It is recommended to take your schnauzer for regular veterinary check-ups at least once a year. However, for older or high-risk schnauzers, more frequent check-ups may be necessary. Your veterinarian will advise you on the appropriate frequency of check-ups and any additional screenings that may be required.
Are there any environmental factors that contribute to schnauzer cancer?
Yes, certain environmental factors can increase the risk of schnauzer cancer. Exposure to secondhand smoke, pesticides, and other toxins can be harmful. It’s important to minimize your schnauzer’s exposure to these hazards and provide a safe and clean living environment.
Is genetics a factor in Schnauzer cancer?
Yes, genetics can influence a schnauzer’s risk of developing cancer. Some schnauzers may inherit certain genetic markers or have predispositions that make them more susceptible to cancer. Genetic testing can help identify potential risks, allowing for early detection and preventive measures.
How can I cope with the emotional impact of schnauzer cancer?
Dealing with a schnauzer’s cancer diagnosis can be emotionally challenging. Seeking support from veterinary professionals, support groups, and other pet owners who have gone through similar experiences can be helpful. Taking care of yourself, managing stress, and focusing on providing the best care for your schnauzer can aid in coping.
What should I expect after Schnauzer’s cancer treatment?
Life after Schnauzer cancer treatment may involve adjustments and ongoing care. Some schnauzers may require long-term medication or monitoring. It’s important to follow your veterinarian’s guidance, maintain regular check-ups, and provide your schnauzer with a supportive and loving environment.