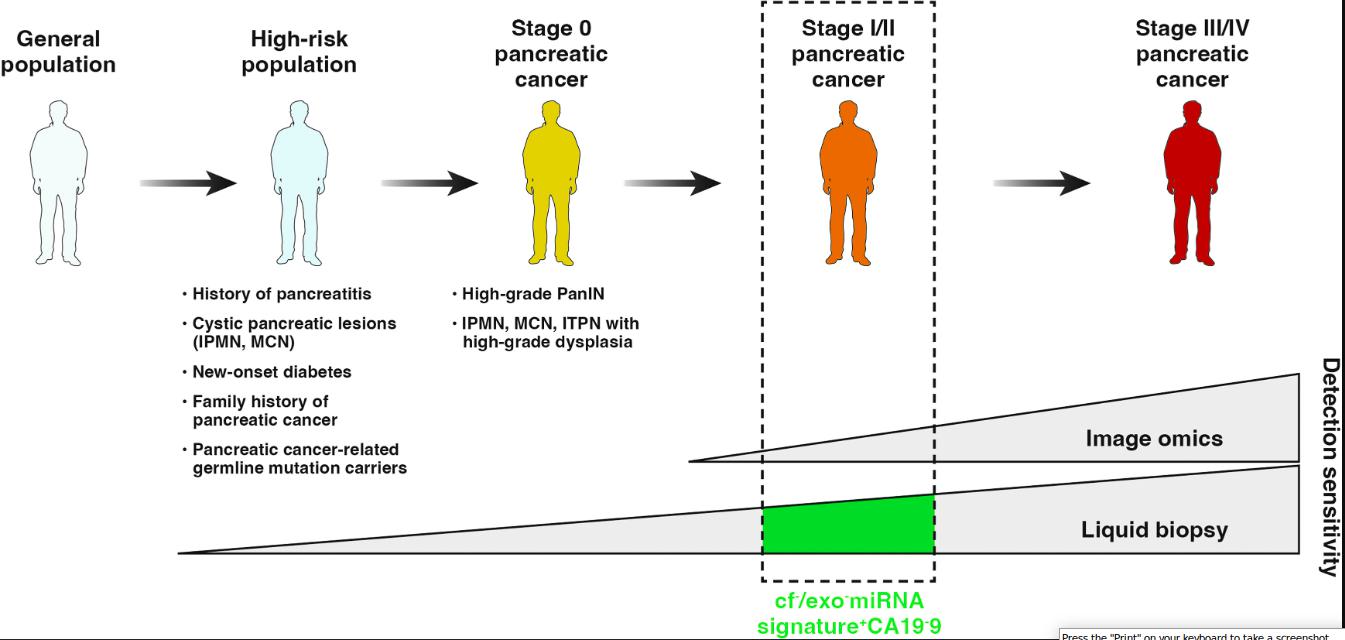
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most challenging cancers to diagnose and treat due to its subtle symptoms and rapid progression. Many cases are discovered at advanced stages, which is why early detection of pancreatic cancer is critical for improving survival rates. Detecting the disease at an earlier stage provides more treatment options and significantly increases the chances of successful outcomes.
Raising awareness about the importance of early detection can save lives. By understanding the signs, risk factors, and modern diagnostic methods, individuals can take proactive steps toward protecting their health. This article explores everything you need to know about pancreatic cancer, with a focus on identifying it as early as possible.
Definition and Overview
Pancreatic cancer begins in the tissues of the pancreas, a gland located behind the stomach that plays a vital role in digestion and blood sugar regulation. It is often called a “silent killer” because it typically does not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. Without early detection of pancreatic cancer, the disease often spreads before being diagnosed, making treatment more difficult.
Types
There are two main types of pancreatic cancer:
- Exocrine tumors – The most common type, usually adenocarcinomas, starting in the ducts of the pancreas.
- Endocrine tumors – Rare cancers, also known as pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), which develop in hormone-producing cells.
Understanding these types helps guide diagnosis and treatment options.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact causes remain unclear, several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing pancreatic cancer, including:
- Family history of pancreatic cancer
- Genetic mutations (such as BRCA1 and BRCA2)
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Smoking and heavy alcohol use
- Obesity and diabetes
- Older age (most common after 60)
Recognizing these risk factors is an important step toward early detection of pancreatic cancer.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Symptoms of pancreatic cancer often go unnoticed until the disease progresses. However, some early warning signs may include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent abdominal or back pain
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Loss of appetite
- New-onset diabetes
- Digestive issues such as nausea or bloating
Being aware of these potential warning signs can encourage individuals to seek medical advice sooner.
Diagnosis
The early detection of pancreatic cancer relies on a combination of medical imaging, blood tests, and genetic screening. Common diagnostic tools include:
- CT scans and MRI scans for detailed imaging
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) for closer examination of the pancreas
- Biopsy to confirm cancer cells
- CA 19-9 blood test, a tumor marker sometimes elevated in pancreatic cancer
Those at high risk may also undergo regular screenings to increase the chances of detecting the disease early.
Treatment Options
Treatment for pancreatic cancer depends on the stage and type of the disease. Options may include:
- Surgery (such as the Whipple procedure) for eligible early-stage cases
- Chemotherapy to target cancer cells
- Radiation therapy to shrink tumors and relieve symptoms
- Targeted therapy and immunotherapy for specific genetic mutations
When detected early, patients often have more treatment choices and improved survival chances.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all cases are preventable, certain lifestyle changes may lower risk:
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Regular physical activity
- Managing diabetes and chronic pancreatitis effectively
Preventive measures, combined with awareness, support early detection of pancreatic cancer.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for pancreatic cancer is often poor when diagnosed late. However, early detection of pancreatic cancer significantly improves survival rates. According to research, patients diagnosed at stage 1 have a much higher five-year survival rate compared to those diagnosed at advanced stages.
Latest Research and Innovations
Medical research is advancing rapidly to improve early detection of pancreatic cancer. Innovations include:
- Liquid biopsy tests for detecting cancer DNA in blood
- Artificial intelligence in imaging scans to spot abnormalities sooner
- Genetic testing for individuals with a family history
- Development of more effective targeted therapies
These advancements hold promise for earlier diagnoses and more successful treatments.
Coping and Support for Patients
A pancreatic cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but support is available. Patients are encouraged to:
- Seek counseling and mental health support
- Join support groups for shared experiences
- Rely on family and friends for assistance
- Explore palliative care options for managing symptoms and improving quality of life
Emotional and social support play a crucial role in coping with the challenges of the disease.
Conclusion
The early detection of pancreatic cancer is vital to improving survival rates and expanding treatment options. By understanding the risk factors, recognizing early symptoms, and seeking timely medical advice, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health. With ongoing research and medical advancements, the future holds greater hope for earlier diagnoses and better patient outcomes.
FAQ
1. Why is early detection of pancreatic cancer so important?
Because pancreatic cancer progresses quickly, detecting it early provides more treatment options and significantly increases survival chances.
2. Who is at higher risk of pancreatic cancer?
People with a family history, genetic mutations, chronic pancreatitis, diabetes, smoking habits, or obesity are at higher risk.
3. What tests help in early detection?
CT scans, MRI, endoscopic ultrasound, CA 19-9 blood tests, and genetic screening are commonly used.
4. Can lifestyle changes prevent pancreatic cancer?
While not all cases are preventable, healthy lifestyle choices—like quitting smoking, eating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly—can reduce risk.
5. What is the survival rate if pancreatic cancer is detected early?
Patients diagnosed at stage 1 may have significantly higher five-year survival rates compared to late-stage diagnoses.