When lung cancer spreads to the brain, it becomes a serious and complex health condition that requires immediate medical attention. This condition, also known as brain metastases from lung cancer, can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life and treatment options. Understanding the signs, risks, and management strategies is crucial for patients, caregivers, and families facing this diagnosis.
With advancements in medical research, there are now more effective treatments available for patients with lung cancer spread to the brain. From targeted therapies to advanced radiation techniques, hope is growing for longer survival and better symptom control. This article will explore the key aspects of this condition, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and the latest treatment approaches.
Definition and Overview
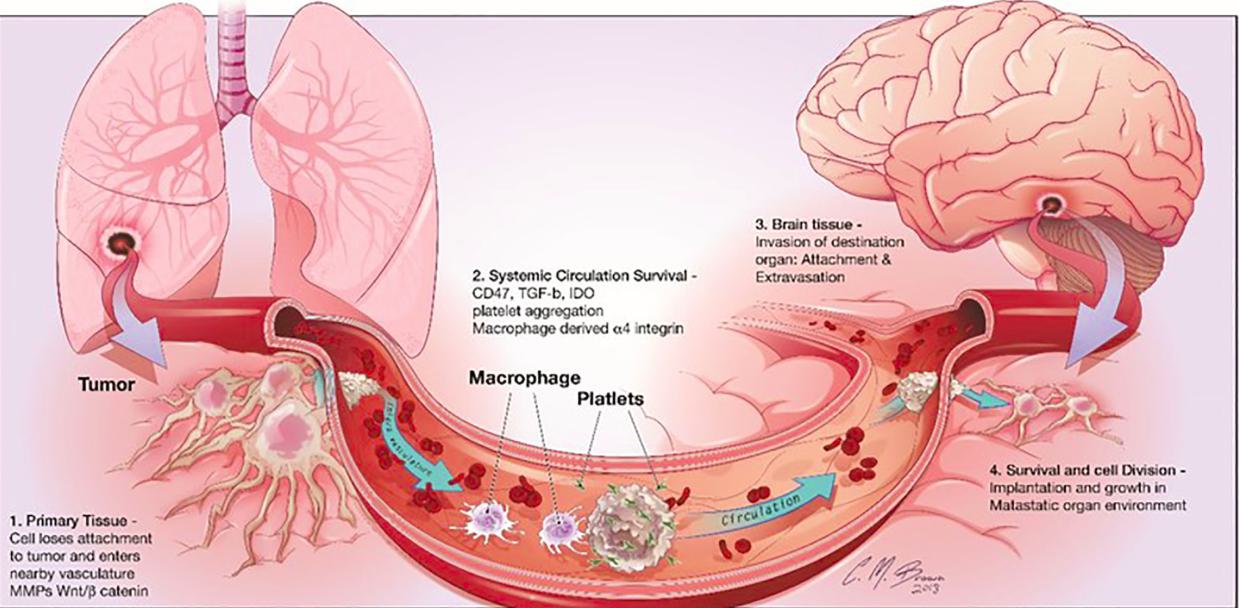
Lung cancer spread to the brain occurs when cancerous cells from the lungs travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system and form tumors in the brain. This stage of cancer is often considered advanced, also known as stage IV or metastatic lung cancer. Brain metastases are among the most common complications in lung cancer patients, especially in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Types
There are two main types of lung cancer that often spread to the brain:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): The most common form of lung cancer. Brain metastases are more frequently seen in adenocarcinoma, a subtype of NSCLC.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): A more aggressive form that tends to spread quickly, including to the brain, even in the early stages.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of lung cancer spreading to the brain:
- Advanced stage lung cancer
- Small cell lung cancer type
- Genetic mutations in cancer cells
- Smoking history and long-term tobacco exposure
- Weak immune system or underlying chronic illnesses
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Brain metastases from lung cancer can cause a variety of neurological symptoms, depending on the location and size of the tumors. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent headaches
- Seizures
- Vision or speech problems
- Weakness or numbness in one part of the body
- Memory loss, confusion, or mood changes
- Difficulty with balance or coordination
Recognizing these early warning signs can help patients seek timely medical care.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing lung cancer spread to the brain involves multiple steps, including:
- Neurological examination to assess reflexes, coordination, and brain function
- Imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to detect brain tumors
- Biopsy in rare cases to confirm metastatic cancer cells
- PET scans to evaluate the spread of cancer throughout the body
Treatment Options
Treatment for lung cancer spread to the brain depends on the number of tumors, overall health, and type of lung cancer. Options include:
- Radiation therapy: Whole-brain radiation or stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for targeted treatment
- Surgery: Removal of accessible brain tumors to relieve symptoms
- Targeted therapy: Medications that attack specific genetic mutations in cancer cells
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells
- Chemotherapy: Used less frequently for brain metastases but may help in certain cases
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While it is not always possible to prevent lung cancer spread to the brain, certain lifestyle changes can lower overall cancer risks:
- Quit smoking and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in antioxidants
- Exercise regularly to support immune health
- Attend regular screenings and follow-up appointments
- Manage chronic illnesses effectively
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for patients with lung cancer spread to the brain varies. Factors such as overall health, number of brain tumors, and response to treatment play a role. On average, survival rates may range from several months to a few years, but advances in therapy are improving outcomes and extending life expectancy for many patients.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent innovations in cancer research provide new hope for patients with lung cancer brain metastases. These include:
- Next-generation targeted therapies addressing genetic mutations such as EGFR and ALK
- Combination treatments using immunotherapy with radiation or targeted drugs
- Improved stereotactic radiosurgery techniques for precise treatment
- Ongoing clinical trials testing novel therapies for better survival and quality of life
Coping and Support for Patients
A diagnosis of lung cancer spread to the brain can be emotionally overwhelming. Patients and families benefit from supportive care, counseling, and connecting with cancer support groups. Palliative care services can also help manage symptoms, improve comfort, and enhance quality of life throughout treatment.
Conclusion
Lung cancer spread to the brain is a challenging condition, but with modern medical advances, patients have more options than ever before. Early detection, personalized treatment, and supportive care can make a significant difference in outcomes. Staying informed and proactive in managing health can empower patients and their loved ones to face this journey with hope.
FAQ
What does it mean when lung cancer spreads to the brain?
It means that cancer cells from the lungs have traveled to the brain, forming metastatic tumors. This indicates advanced-stage cancer.
What are the first signs of lung cancer spread to the brain?
Common early signs include headaches, seizures, vision problems, weakness, or confusion.
Can lung cancer spread to the brain be treated?
Yes, treatments such as radiation therapy, surgery, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy can manage symptoms and improve survival.
How long can you live with lung cancer spread to the brain?
Survival varies by patient, but advancements in treatment are helping many live longer than before.
Is lung cancer spread to the brain preventable?
While not always preventable, reducing risk factors like smoking and maintaining a healthy lifestyle may help lower the chances.